Angiographic classification of Takayasu arteritis
Angiographic classification of Takayasu arteritis
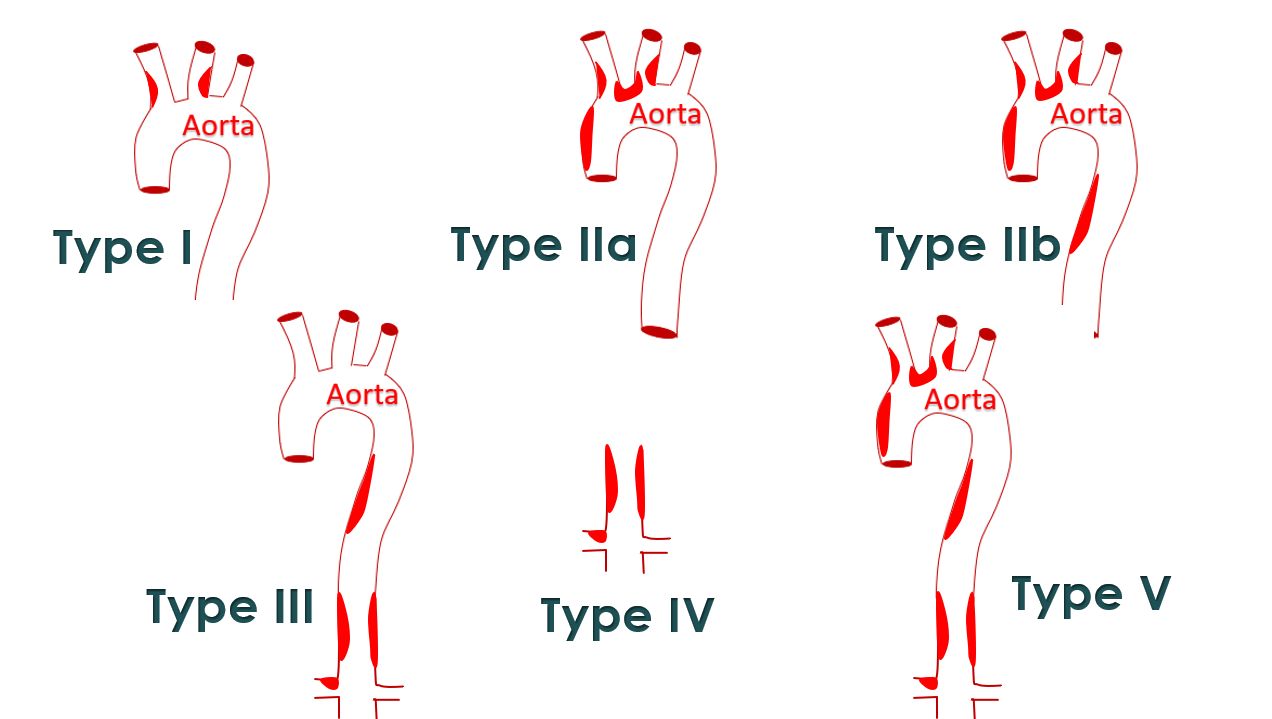
Angiographic classification of Takayasu arteritis was suggested by Moriwaki et al after a review of 102 Indian and 80 Japanese patients with Takayasu arteritis. [1].
Type I: Branches of the aortic arch
Type IIa: Ascending aorta, aortic arch, and branches of the aortic arch
Type IIb: Ascending aorta, aortic arch, and its branches and thoracic descending aorta
Type III: Thoracic descending aorta, abdominal aorta, and/or renal arteries
Type IV: Abdominal aorta and/or renal arteries
Type V: Features of types IIb and IV (diffuse involvement)
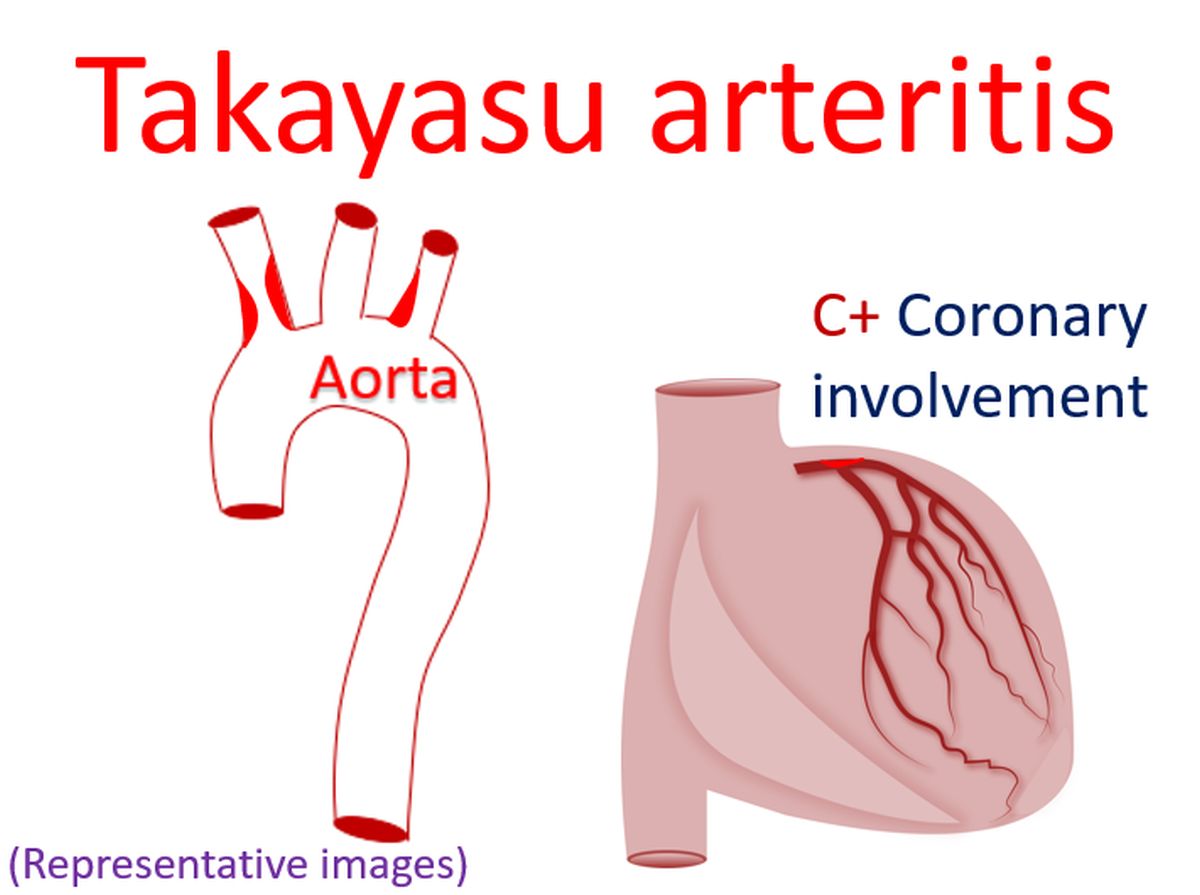
Involvement of coronaries is designated as C+ and that of pulmonary arteries as P+.
In this study, significant difference was found between the two countries in the pattern of involvement and progression of Takayasu arteritis. In Indian patients, vasculitis generally occurred in abdominal aorta involving renal arteries and later spread to thoracic aorta in one or two decades. In Japanese patients, vasculitis generally occurred in ascending aorta, arch or its branches and later extended to thoracic and abdominal aorta. Complicated lesions with prolonged inflammatory activity were noted in Japanese patients while simple lesions were noted in Indian patients.
Reference
- R Moriwaki, M Noda, M Yajima, B K Sharma, F Numano. Clinical manifestations of Takayasu arteritis in India and Japan – new classification of angiographic findings. Angiology. 1997;48:369-79.

