Cornell voltage criteria for LVH
Cornell voltage criteria for LVH
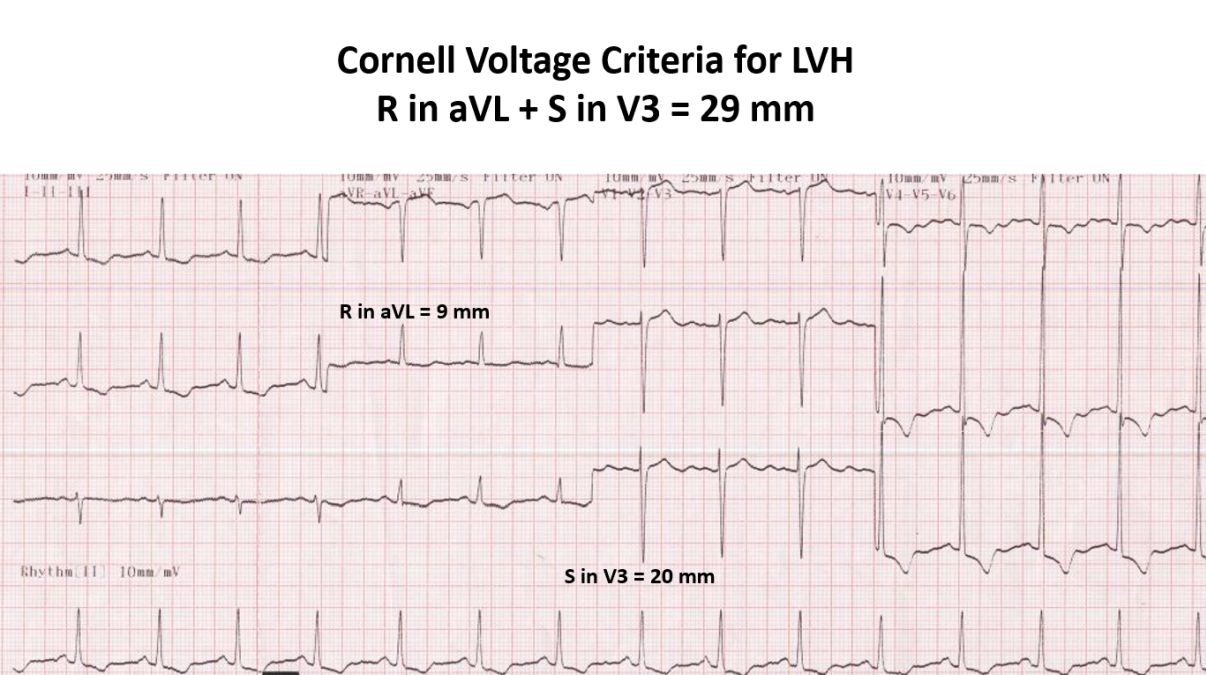
In Cornell voltage criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy, S wave in V3 is added to R wave in aVL. Left ventricular hypertrophy as per Cornell voltage criteria is considered if the sum is 20 mm or more in females and 28 mm or more in males.
Left ventricular mass index (LVMI) can be calculated from Cornell voltage as follows [1]:
- LVMI = 14.5 × Cornell voltage + 78.9 for males
- LVMI = 21.5 × Cornell voltage + 61.5 for females
Cornell product is {(Cornell voltage + 0.6 mV for females) × QRS duration}
LVMI can be calculated from Cornell product as follows:
- LVMI = 0.15 × Cornell product + 68.8.
Rodrigues SL et al, in a study of 682 participants, compared Sokolow-Lyon-Rappaport and Cornell voltage criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy [2]. They found that Cornell voltage criteria had a better correlation with left ventricular mass on echocardiography, compared to Sokolow-Lyon-Rappaport criteria. They also suggested new cut-off values for Cornell voltage criteria as 23 mm in males and 19 mm in females. Their revision had a sensitivity of 22.5% in males and 28% in females. They could obtain a high specificity of 95%.
References
- Ishikawa J, Yamanaka Y, Toba A, Watanabe S, Harada K. Gender-Adjustment and Cutoff Values of Cornell Product in Hypertensive Japanese Patients. Int Heart J. 2017 Dec 12;58(6):933-938.
- Rodrigues SL, D’Angelo L, Pereira AC, Krieger JE, Mill JG. Revision of the Sokolow-Lyon-Rappaport and cornell voltage criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2008 Jan;90(1):46-53.
