CXR in severe pulmonary hypertension
CXR in severe pulmonary hypertension
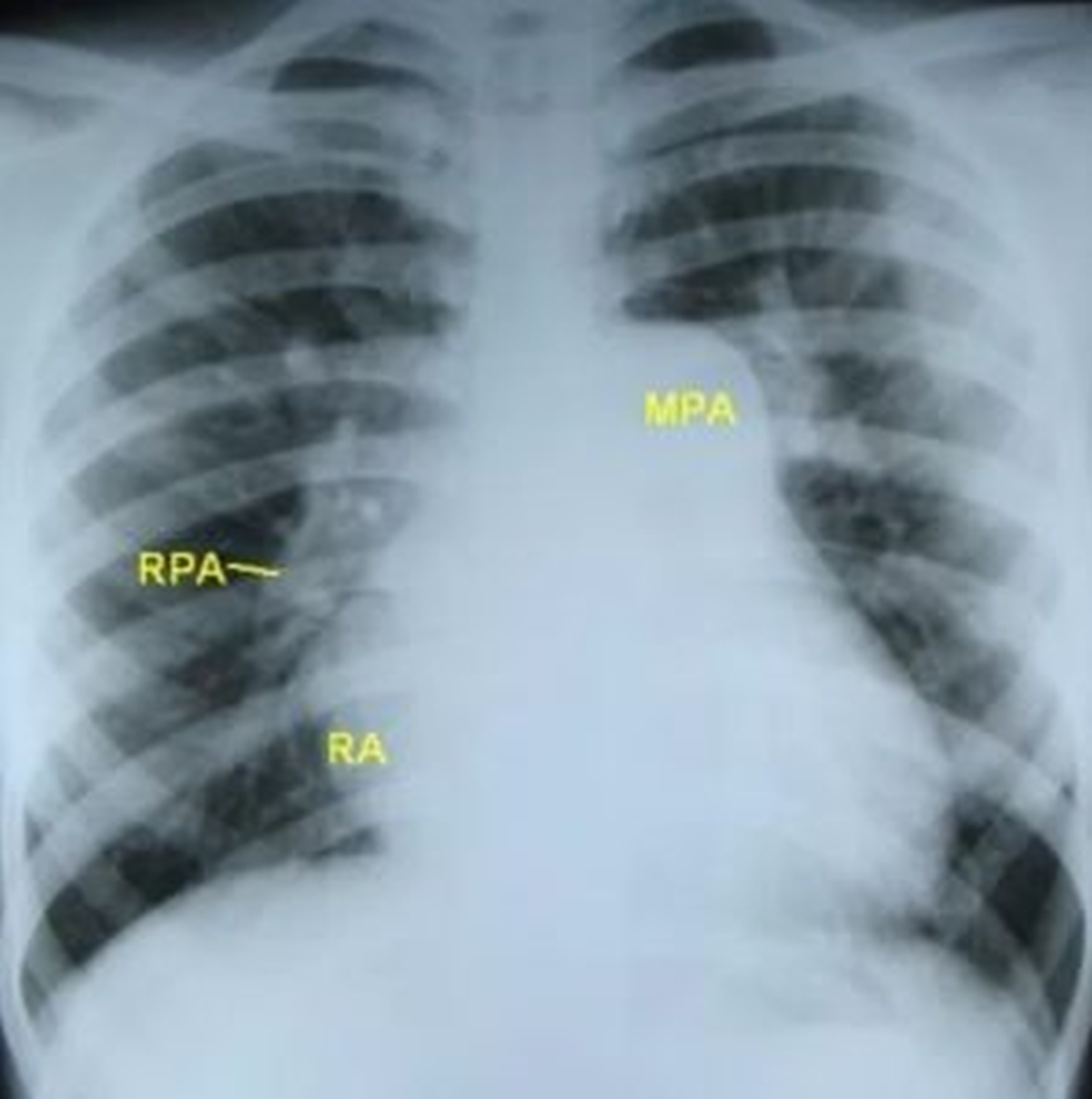
The striking feature in this chest X-ray is the remarkably prominent main pulmonary artery segment (MPA), which appears to be aneurysmally dilated. Right pulmonary artery (RPA) is also enlarged. Enlargement of right pulmonary artery differentiates it from the post stenotic dilatation of main pulmonary artery in pulmonary stenosis. In post stenotic dilatation, even though the left pulmonary artery which is in line with the main pulmonary artery may be dilated, the right pulmonary artery which does not have the effect of the jet and eddy currents, is not dilated. This X-ray also shows a prominent right atrial contour, indicating right atrial dilatation as a consequence of pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular hypertrophy. The end on views of blood vessels seen through the right pulmonary artery shadow are tiny, indicating that the RPA dilatation is unlikely to be due to increased pulmonary blood flow. Large end on vessels are a feature of pulmonary hypertension due to excessive left to right shunt causing increased pulmonary blood flow. In this case, the absence of them would make one think that the severe pulmonary hypertension is probably primary. The right ventricular systolic pressure and hence the pulmonary artery systolic pressure estimated by continuous wave Doppler interrogation of the tricuspid regurgitation jet was over 110 mm Hg.