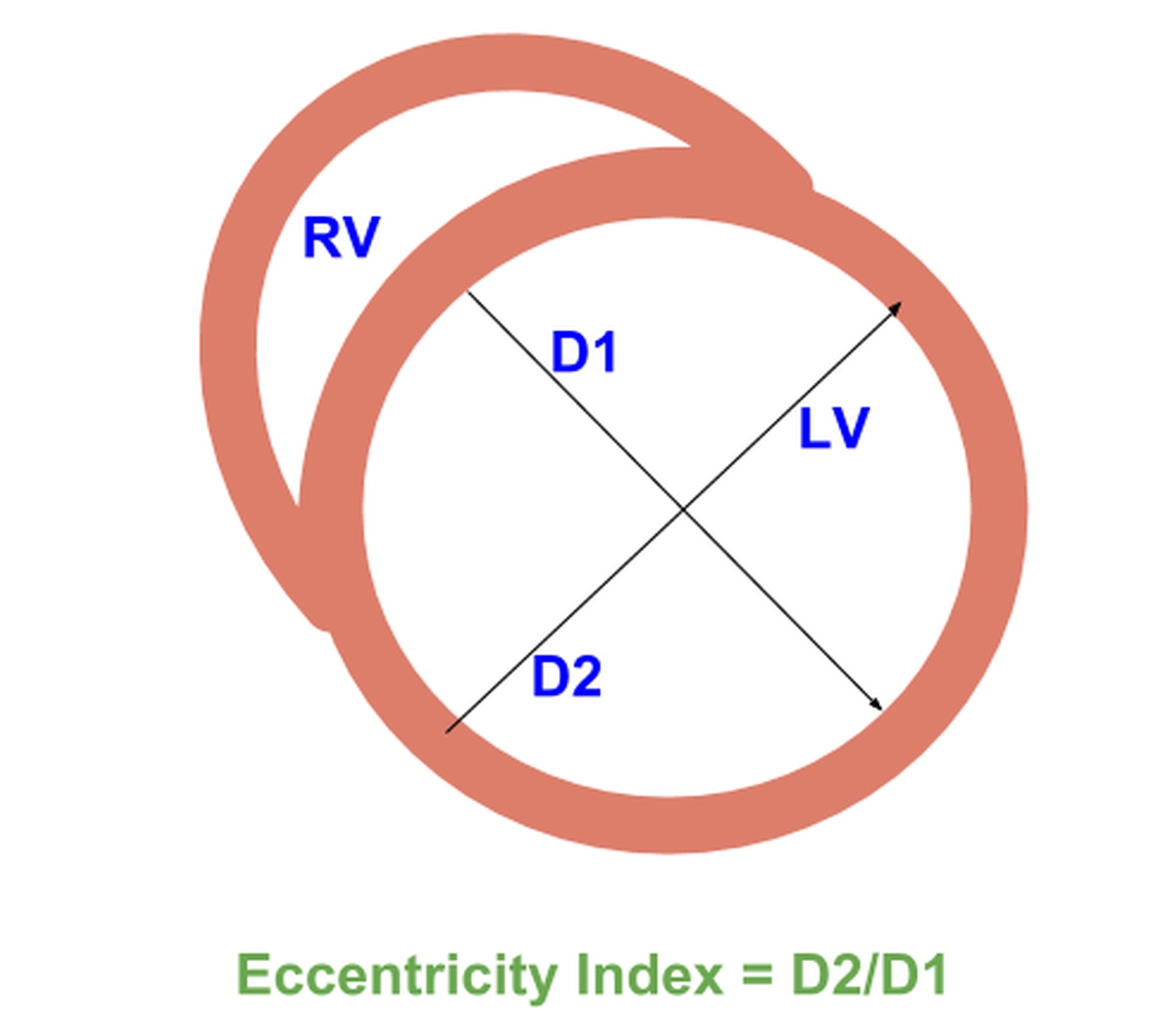
Eccentricity index for right ventricular overload
Eccentricity index for right ventricular overload
(Representative image)
Eccentricity index is an echocardiographic index for separation of right ventricular volume and pressure overload. Abnormal motion of the interventricular septum can occur in both right ventricular volume and pressure overload. Ryan T and associates [1] have described a method to differentiate between the two. Two left ventricular minor axes are measured – one parallel to the interventricular septum and another perpendicular to it. Measurements are made at both end diastole and end systole. In normal subjects, the ratio between the two is equal to 1.0 at both end diastole and end systole. In patients with right ventricular volume overload, the end systolic ratio is approximately 1.0 while that at end diastole is increased. In those with right ventricular pressure overload, the eccentricity index was significantly greater than 1.0 at both end systole and end diastole. Thereby eccentricity index of left ventricular shape reflects the abnormal motion of the interventricular septum depending on the type of right ventricular overload, whether systolic or diastolic.
This eccentricity is reflected in the D shaped left ventricular cavity seen on echocardiography in severe pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular hypertrophy.
Reference
- Ryan T, Petrovic O, Dillon JC, Feigenbaum H, Conley MJ, Armstrong WF. An echocardiographic index for separation of right ventricular volume and pressure overload. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1985; 5:918-927.