ETCO2 monitoring in ICU – capnography
ETCO2 monitoring in ICU – capnography
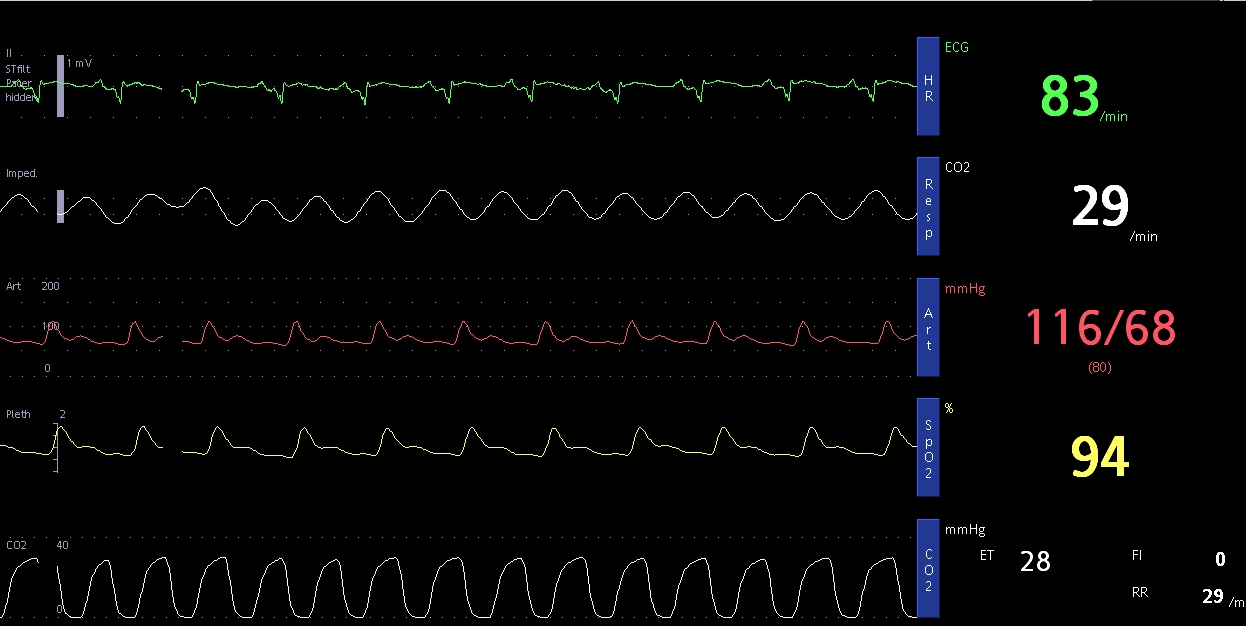
ETCO2 monitoring in ICU – capnography: End tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO2) is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (CO2) in exhaled air at the end of expiration. Normal values are in the range of 35 – 45 mm Hg. Carbon dioxide monitoring is also known as capnography. The graphical representation of CO2 is known as capnogram. In the monitor screenshot shown above, the capnogram is at the bottom. Here the ETCO2 is shown as 28 mm Hg. It is below the lower limit and could be due to hyperventilation in a spontaneously breathing person. Respiratory rate drawn from the capnography is 29/min, which matches with the respiratory rate measured by transthoracic impedance monitoring in the second tracing from the top. Top most tracing is the electrocardiogram, which shows regular sinus rhythm at 83/min. Invasive blood pressure monitoring, usually with a cannula in the radial artery, shows a blood pressure of 116/68 mm Hg. The remaining tracing is of pulse oximetry which shows an oxygen saturation of 94%.
Capnography is useful after endotracheal intubation to confirm the position of the tube in the trachea and is used routinely in most modern centres in the emergency department. ETCO2 monitoring is common place in the operating room and most of the state-of-the-art intensive care units. Capnography provides instantaneous information on ventilation, perfusion and cellular respiration, all of which are important in maintaining ETCO2 values in the normal range. Hence ETCO2 monitoring is also useful in assessing the effectiveness of cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Mainstream and side-stream devices for measurement of ETCO2
Mainstream devices for measurement of ETCO2 are connected at the hub of the endotracheal tube. The sensor is located at the same location. Side-stream devices aspirate a small sample of exhaled air from the endotracheal tube or nasal cannula and the sensor is located in the monitor. Side-stream monitoring can be used for intubated and non-intubated patients [1]. Pekdemir M et al found that ETCO2 values by mainstream and side-stream methods were significantly lower than simultaneously obtained PaCO2 values, in their study of 114 subjects [1].
Reference
- Pekdemir M, Cinar O, Yilmaz S, Yaka E, Yuksel M. Disparity between mainstream and sidestream end-tidal carbon dioxide values and arterial carbon dioxide levels. Respir Care. 2013 Jul;58(7):1152-6.