Small muscular ventricular septal defect – echocardiogram
Small muscular ventricular septal defect – echocardiogram
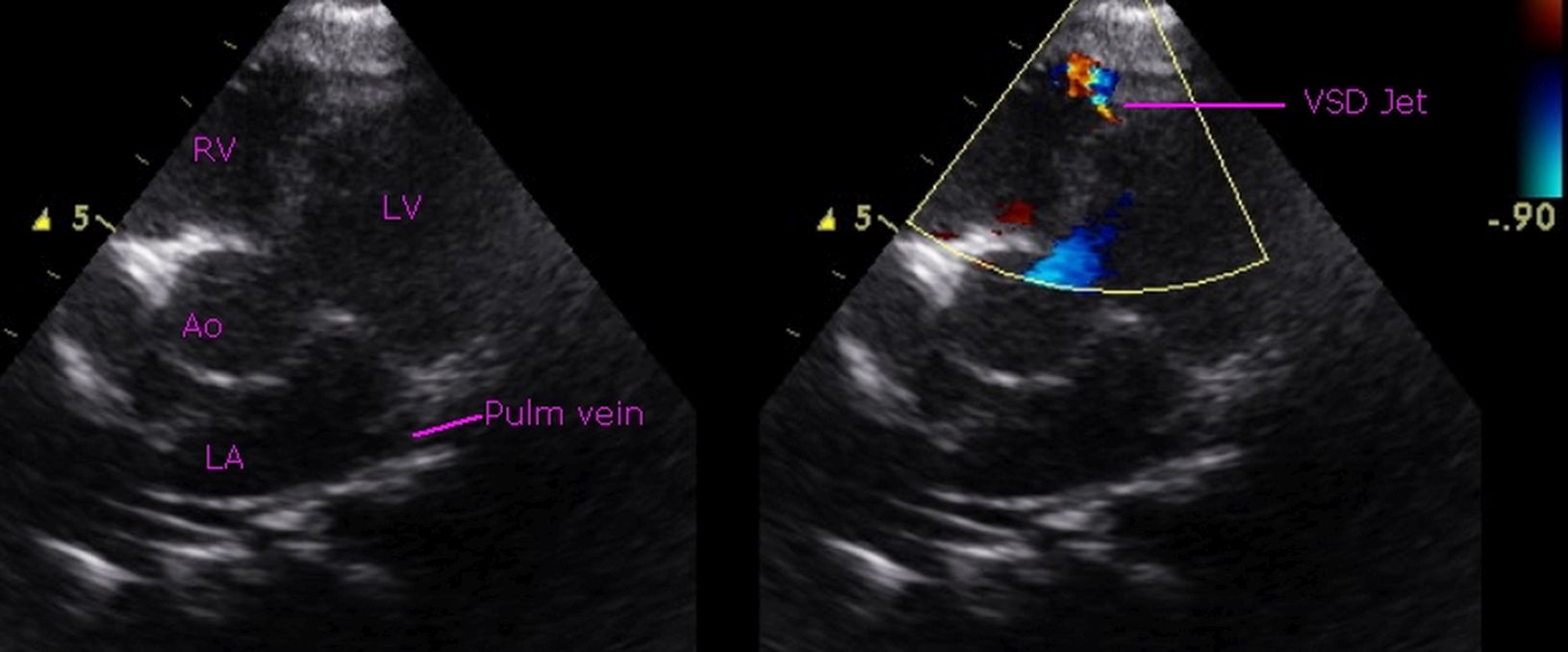 Small muscular ventricular septal defect – echocardiogram: Echocardiogram in apical 5 chamber view shows the mosaic colour jet of a small ventricular septal defect (VSD) near the apex. The cardiac chambers are not dilated. The small defect is difficult to see on two dimensional echocardiography, though it is easily detected clinically with a pan systolic murmur and Doppler echo documents the high velocity jet across the VSD. LV: Left ventricle; RV: right ventricle; Ao: Aorta; LA: Left ventricle; Pulm vein: Pulmonary vein.
Small muscular ventricular septal defect – echocardiogram: Echocardiogram in apical 5 chamber view shows the mosaic colour jet of a small ventricular septal defect (VSD) near the apex. The cardiac chambers are not dilated. The small defect is difficult to see on two dimensional echocardiography, though it is easily detected clinically with a pan systolic murmur and Doppler echo documents the high velocity jet across the VSD. LV: Left ventricle; RV: right ventricle; Ao: Aorta; LA: Left ventricle; Pulm vein: Pulmonary vein.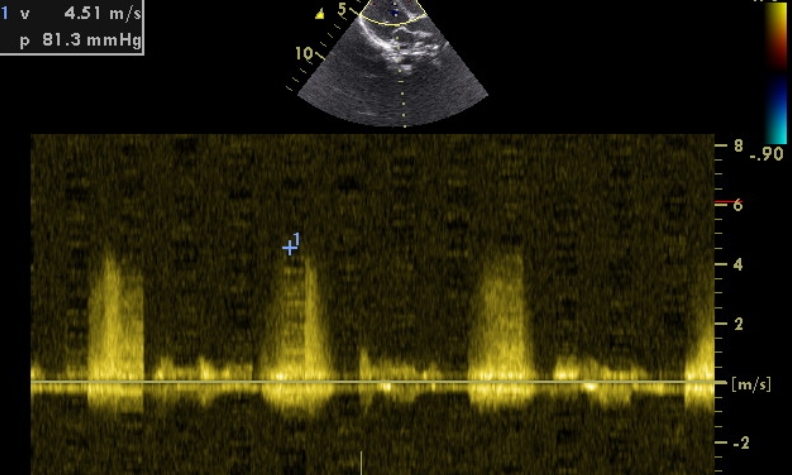
Continuous wave (CW) Doppler interrogation shows the inter-ventricular pressure gradient as 81 mm Hg, which is consistent with a restrictive VSD. Small muscular VSDs like this are likely to close spontaneously on follow up. They will not cause pulmonary hypertension or heart failure and usually have good prognosis unless complicated by infective endocarditis. Natural history studies have shown that small muscular ventricular septal defects have a high likelihood of spontaneous closure. Spontaneous closure occurred in 76% cases by 12 months of age in one study, but apical defects tended to have a higher persistent patency rate than defects in other locations (p<0.05) [1].
Long term course of 600 small and moderate muscular ventricular septal defects diagnosed over a six year period has been reported by Erik L, Shelby Kutty and associates [2]. They found that though pediatric cardiology follow up was recommended, these did not result in any significant active medical or surgical management. Of the 316 follow up visits recommended, only 259 happened, though there were 37 other unplanned follow up visits. Eighty five percent of this cohort had small muscular VSD on initial echocardiogram.
References
- Hiraishi S, Agata Y, Nowatari M, Oguchi K, Misawa H, Hirota H, Fujino N, Horiguchi Y, Yashiro K, Nakae S. Incidence and natural course of trabecular ventricular septal defect: two-dimensional echocardiography and color Doppler flow imaging study. J Pediatr. 1992 Mar;120(3):409-15.
- Frandsen EL, House AV, Xiao Y, Danford DA, Kutty S. Subspecialty surveillance of long-term course of small and moderate muscular ventricular septal defect: heterogenous practices, low yield. BMC Pediatr. 2014 Nov 4;14:282.