Triphasic left ventricular filling pattern
Triphasic left ventricular filling pattern
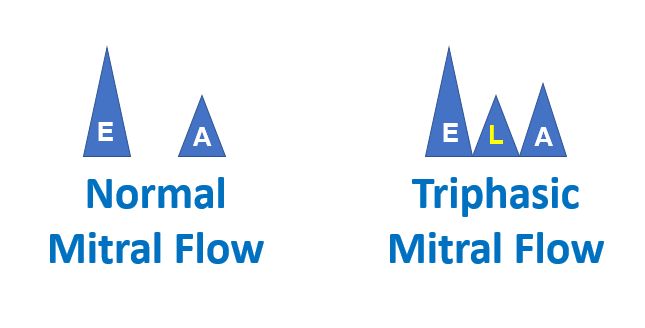
Triphasic left ventricular filling pattern (Representative image)
Normal left ventricular filling pattern is biphasic with an early diastolic E wave which occurs soon after the opening of the mitral valve and a late diastolic A wave during atrial systole. Normally E wave is taller than A wave, but A wave can be taller in situations of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (E/A reversal). A triphasic left ventricular filling pattern with an additional mid diastolic wave, called T wave 1 by some authors and L wave 2 by others, can occur in situations of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction, especially in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. A corresponding L’ wave3,4 or T’ wave1 in tissue Doppler has also been described. Same pattern has been documented in color M-Mode with additional T wave. The name T wave was probably derived as short form for a third wave, though it occurs between the first and second diastolic waves. Third wave has also been documented in pulmonary venous Doppler in which the T wave is between the early diastolic D wave and AR wave of atrial reversal. AR wave is negative while D and T waves of pulmonary venous Doppler are positive waves.1 Triphasic pattern of mitral inflow and mitral annular tissue Doppler has also been reported in a hypertensive emergency.5 L wave has also been reported in M-Mode echocardiogram along with a mitral inflow L wave.6 L wave indicates mid diastolic flow from pulmonary veins into the left atrium and further into the left ventricle.7 In those with left ventricular diastolic dysfunction, an L wave indicates high risk of risk hospitalization for heart failure as it connotes high left ventricular filling pressures.8 It is associated with clinical heart failure in case of left ventricular systolic dysfunction.9
Mechanism of triphasic left ventricular filling pattern
Triphasic left ventricular filling pattern has been considered to be a mixed pattern of restrictive filling and impaired relaxation. The third longitudinal movement of the mitral annulus on tissue Doppler is thought to be due to extra myocardial relaxation with a suction force.1 This suction force due to the delayed relaxation causes the mid diastolic flow which is manifest as the T wave or L wave. There is also a view that the third mid diastolic wave indicates advanced left ventricular diastolic dysfunction as is often present in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.3 This was suggested by an association of L’ with higher E/E’ ratio, larger left atrium and higher proBNP levels.
References
- Araujo AQ, Arteaga E, Salemi VMC, Mady C. Triphasic left ventricular filling in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Heart 2005;91(4):538.
- Coppini R, Ho CY, Ashley E, Day S, Ferrantini C, Girolami F, Tomberli B, Bardi S, Torricelli F, Cecchi F, Mugelli A, Poggesi C, Tardiff J, Olivotto I. Clinical Phenotype and Outcome of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Associated With Thin-Filament Gene Mutations. Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64(24):2589-2600.
- Ha JW, Ahn JA, Moon JY, Suh HS, Kang SM, Rim SJ, Jang Y, Chung N, Shim WH, Cho SY. Triphasic mitral inflow velocity with mid-diastolic flow: the presence of mid-diastolic mitral annular velocity indicates advanced diastolic dysfunction. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2006 Jan;7(1):16-21.
- Debl K, Djavidani B, Buchner S, Poschenrieder F, Feuerbach S, Riegger G, Luchner A. Triphasic mitral inflow pattern and regional triphasic mitral annulus velocity in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008 Apr;21(4):407.e5-6.
- Schiano Lomoriello V, Esposito R, Marzano A, Raia R, Galderisi M. Triphasic diastolic pattern and delayed timing of myocardial relaxation identify dynamic changes of left ventricular filling pressure. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2008 Jun;56(3):371-5.
- Kumar V, Jose J, Jose VJ. L wave in echo Doppler. Indian Heart J. 2014 May-Jun;66(3):392-3.
- Keren G, Meisner JS, Sherez J, Yellin EL, Laniado S. Interrelationship of mid-diastolic mitral valve motion, pulmonary venous flow, and transmitral flow. Circulation. 1986;74:36-44.
- Lam CS, Han L, Ha JW, Oh JK, Ling LH. The mitral L wave: a marker of pseudonormal filling and predictor of heart failure in patients with left ventricular hypertrophy. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005;18:336-341.
- Ha JW, Oh JK, Redfield MM, Ujino K, Seward JB, Tajik AJ. Triphasic mitral inflow velocity with middiastolic filling: clinical implications and associated echocardiographic findings. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2004;17:428-431.

