Why is 6 Meter Called the Magic Band?
Why is 6 Meter Called the Magic Band?
Six meter band is the lowest among the VHF bands allocated for Ham Radio. According to National Frequency Allocation Plan 2022, the frequencies alloted for amateur service in 6 m band are 50-54 MHz (shared with other services), in India. Even though 6 m band comes in the lower portion of VHF radio spectrum, it occasionally has propagation patterns seen at HF bands. Such propagation patterns are seen when the solar activity increases the ionization in the ionosphere close to sunspot maximum in the solar cycle. Occurence of HF characteristics on VHF band enabling long distance communication is the reason for 6 m being called as the Magic Band!
Another view was shared by my Twitter contact Greg @SP3RNZ “Huh! Long story. In general on HF You can predict when and where You can have propagation to some part of the World. i.e greyline on lowbands, Summer/Winter Longpath to VK/ZL, Voacaps. But not on #SIX. Here You NEVER know what and when some paths will open.. Magic. Pure.”
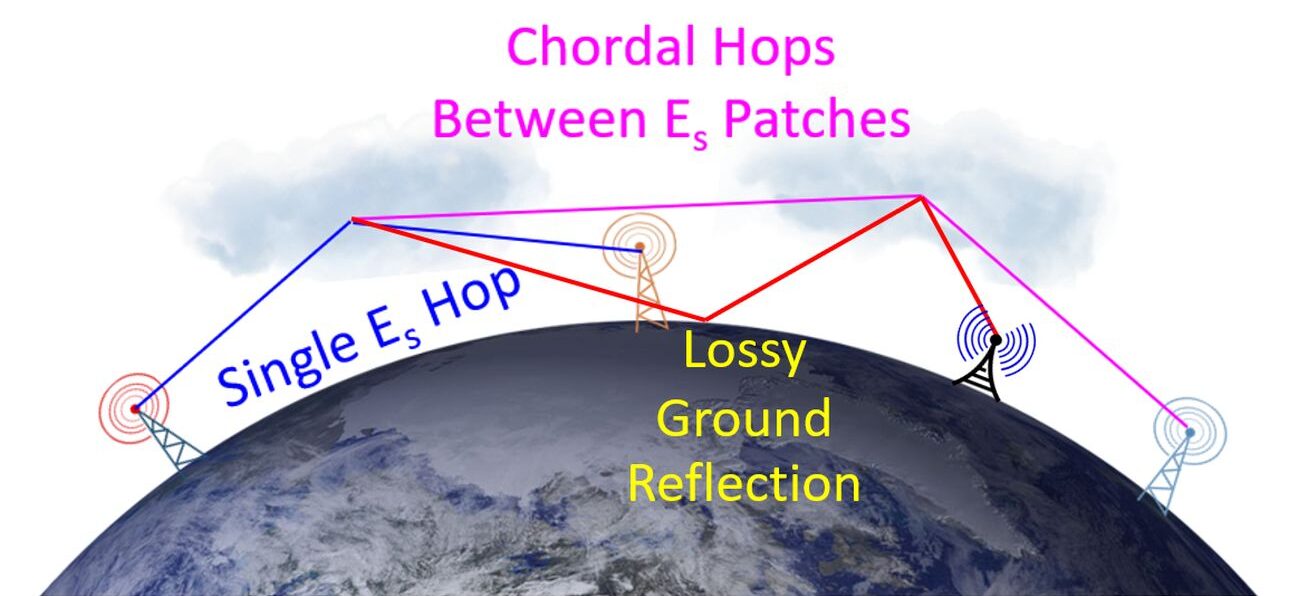
As discussed earlier, sporadic E propagation mostly around the summer solictice allows single Es hop communication up to 2500 km. Multiple hop communications enable inter continental communications up to 10,000 km. Timing of Sporadic E propagation is different in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres according to the difference in timing of summer solictice.
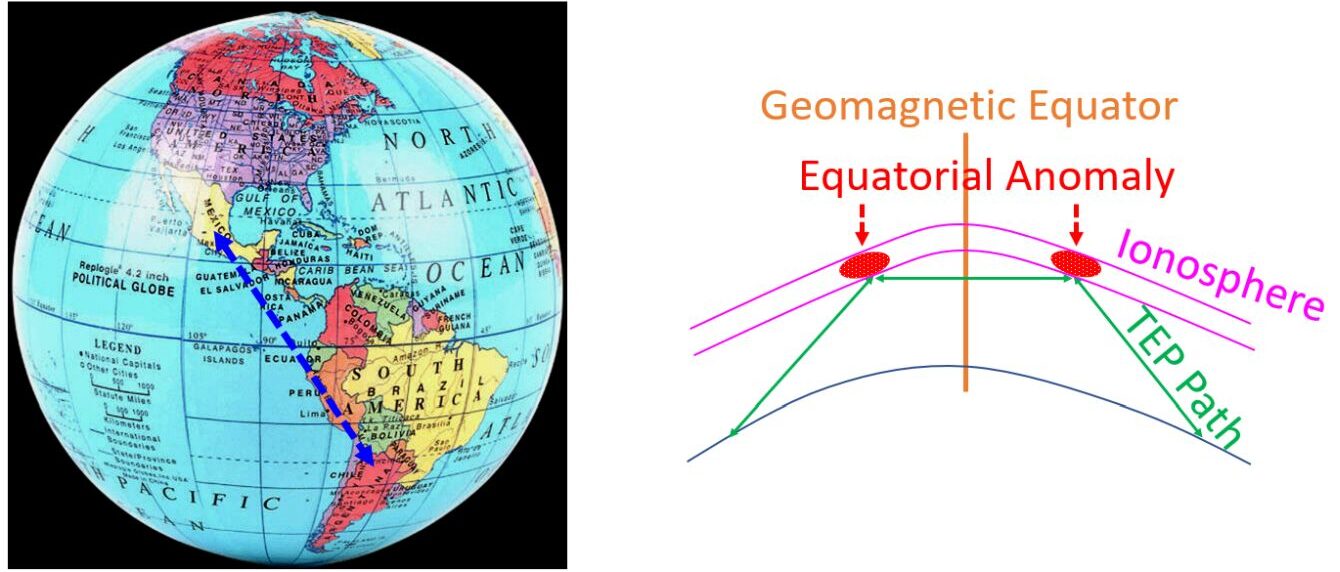
Another special type of propagation near solar cycle maximum in 6 m band is the Transequatorial Propagation which can enable communications at 6000 km, between stations equidistant from the equator. Mechanism by which transequatorial propagation occurs is the presence of equatorial anomaly, which is a high concentration of electrons on either side of the equator in the region of 10 to 20 degrees latitude. The signals are reflected by one anomaly to the other and then back to the ground on the opposite side of the equator.