Basics About Resistors
Basics About Resistors
Resistors are passive elements in electronic circuits meaning that they do not need a power supply unlike active devices which need a power supply for them to function. Other common passive elements used in electronic circuits are capacitors and inductors. Resistance of a resistor is expressed in Ohms. Higher values may be expressed as Kilo Ohms or Mega Ohms. Kilo Ohms meaning 1000 Ohms and Mega Ohms meaning million ohms.
Resistors come in different wattages depending on their size, indicating heat dissipation capacity. The resistors shown in the picture are quarter Watt resistors while half Watt and one Watt resistors are also available. Higher and smaller denominations are also used in specific applications depending on the circuit demand.
The value of the resistor is indicated on the resistor with a colour code. The resistors shown here have a four band colour code, which is the most common one in use. First two bands indicate the resistance value which has to be multiplied by the code on the third band. Fourth band indicates the tolerance.
All the resistors shown here have a golden band for the tolerance indicating 5% variation above or below the coded value. If there is no tolerance band, the tolerance is presumed to be 20%.
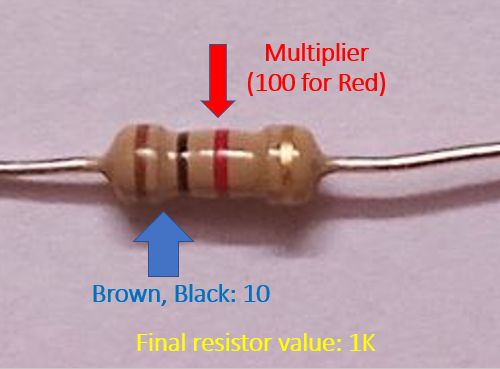
Colour code values are as follows: Black 0, Brown 1, Red 2, Orange 3, Yellow 4, Green 5, Blue 6, Violet 7, Grey 8, White 9. Golden colour is for 5% tolerance while Silver colour is for 10% tolerance. As mentioned above if there is no tolerance band, it implies 20% tolerance. Third band is used as multiplier for the first two bands. Multiplication is by ten to the power of the third band colour code. Multiply by 1 if it is black, by 10 if it is brown, by 100 if it is red etc.
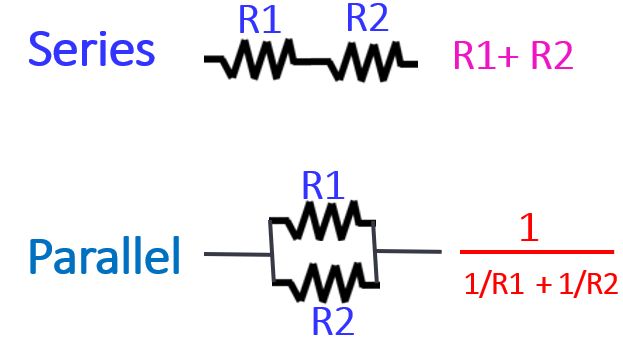
This is the symbol of a resistor used in circuits and indicated by the letter R. Resistors can be connected in parallel or series.
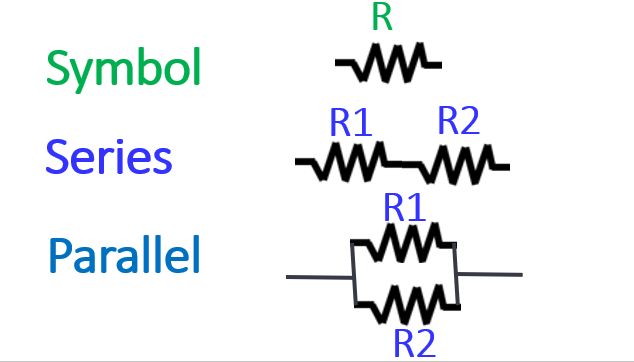
When the resistors are connected in series, the total value is the sum of the individual values. When they are connected in parallel, it is a complex calculation as shown here.