What is Standing Wave Ratio (SWR)?
What is Standing Wave Ratio (SWR)?
Standing wave occurs when there is impedance mismatch between the transmission line and the load, which is the antenna. When there is an impedance mismatch, part of the signal is reflected back to the transmitter. This reduces the effective power transmitted and thereby the efficiency. Standing wave can be considered as resultant of forward and reflected waves together. Standing wave ratio or SWR is the ratio between the maximum and minimum amplitudes of the standing wave.
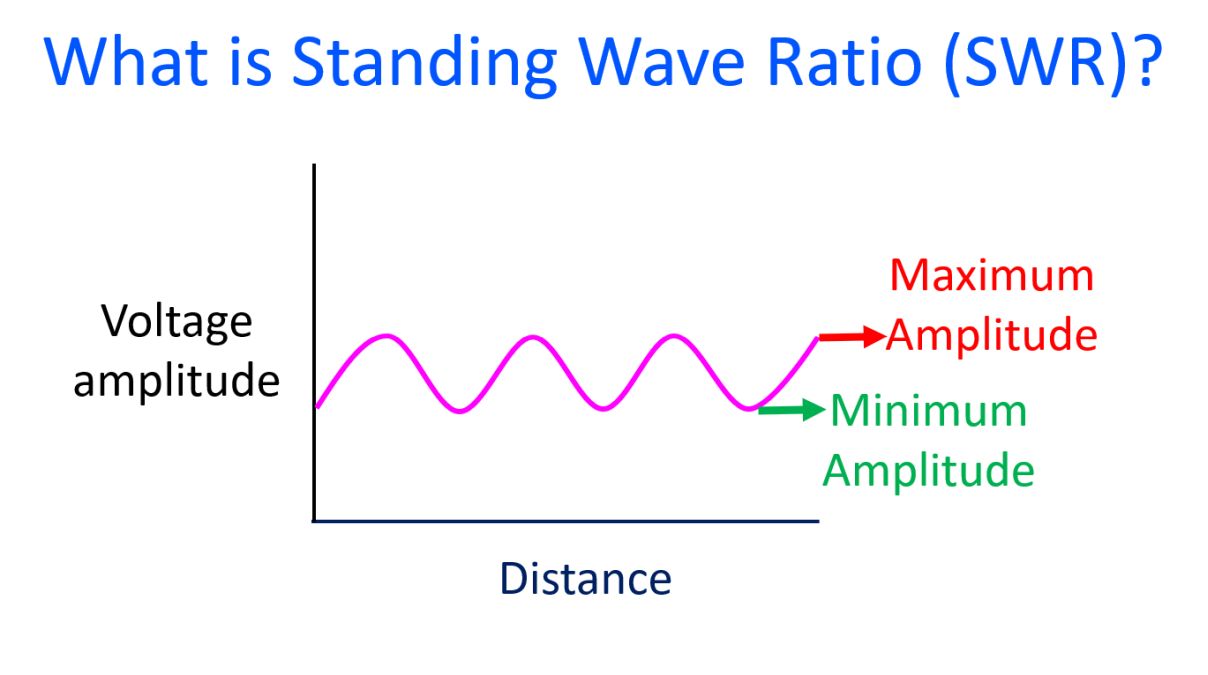
Highest level of SWR occurs when the antenna is not connected (open circuit) or when there is short circuit in the transmission line. SWR can be in terms of voltage known as voltage SWR and current, known as current SWR. Usually it is the voltage SWR that is measured using an SWR meter. Ideal SWR is 1 and high SWR above 2 can cause heating of the transmission line and final power amplifier of the transmitter circuit, and likely to cause severe damage.