Diagnosis of coronary heart disease
How is coronary heart disease diagnosed?
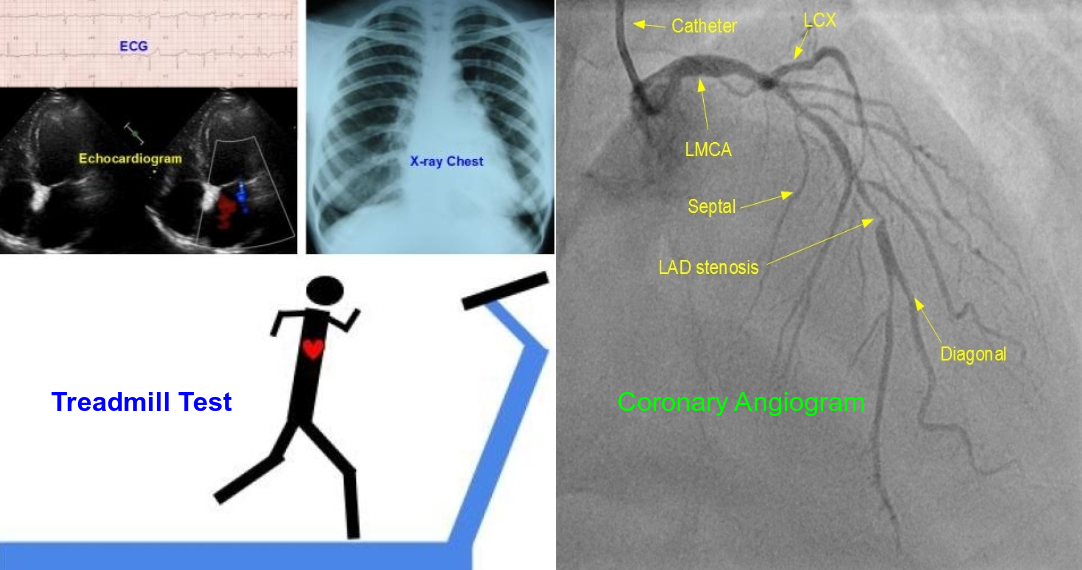
Coronary heart disease (coronary artery disease, coronary artery heart disease, ischemic heart disease) is usually suspected by the symptoms. Typically it is a central chest pain or discomfort induced by exercise and relieved by rest. But this need not be the case always. Pain of heart attack may appear all of a sudden and does not get relieved by rest. Still it is an important manifestation of coronary heart disease. Other symptoms associated with chest pain could be pain in the jaw or arms, excessive sweating along with pain or sometimes breathlessness or dizziness. First investigation to be done is usually an ECG (electrocardiogram). When a heart attack is suspected, other investigations done in the emergency department are a bedside echocardiogram and a blood test for Troponin, which is released into the blood when heart muscle is damaged. Finally an emergency coronary angiogram may be done if there is evidence of a heart attack. In the outpatient setting, a treadmill exercise ECG (treadmill test) can be done in stable patients resting ECG does not give a diagnosis. Other advanced tests are coronary CT angiogram and nuclear scan of the heart.



