Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) Tissue Oximetry – Novel method of measuring oxygen levels in body
Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) Tissue Oximetry – Novel method of measuring oxygen levels in body
Near- Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) Tissue Oximetry is an emerging noninvasive method used to evaluate tissue oxygenation. It can measure oxygen delivery to the cells of the brain and kidneys, two important vital organs. Though this technology was first described more than 40 years ago, use of NIRS has increased significantly worldwide in the past decade. NIRS is based on the fact that near-infrared light is able to penetrate biologic tissue and can obtain real-time noninvasive information on tissue oxygenation and metabolism. Oxygenation-dependent light absorbing characteristics of hemoglobin in blood is utilised in NIRS.
Cerebral oximetry or measurement of oxygenation of the brain has been studied most widely in the field of cardiac surgery. This is because these operations can lead to significant neurologic complications and associated illness and mortality. NIRS can also monitor oxygenation in muscles. NIRS monitoring in muscles has found application in the field of sports science.
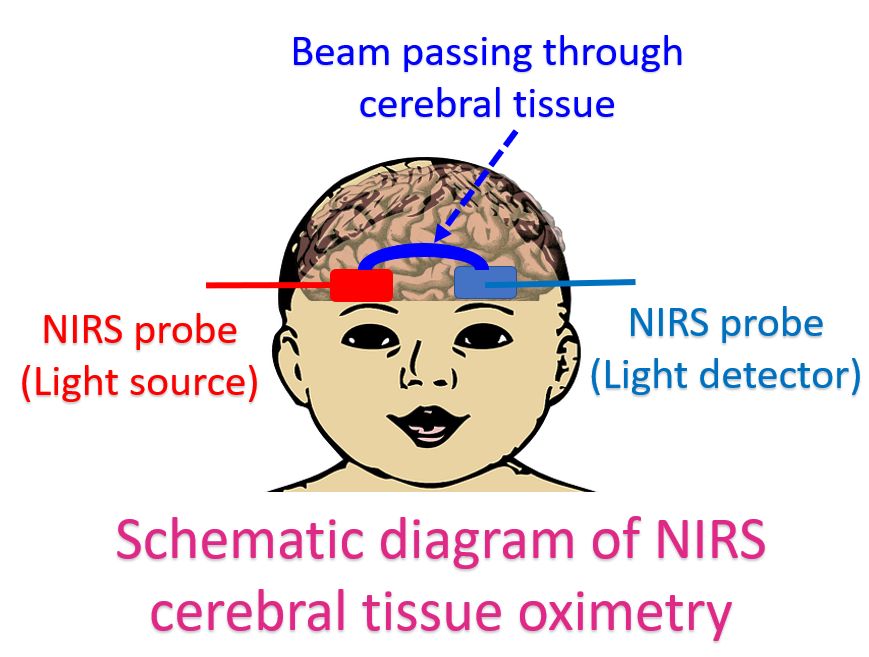
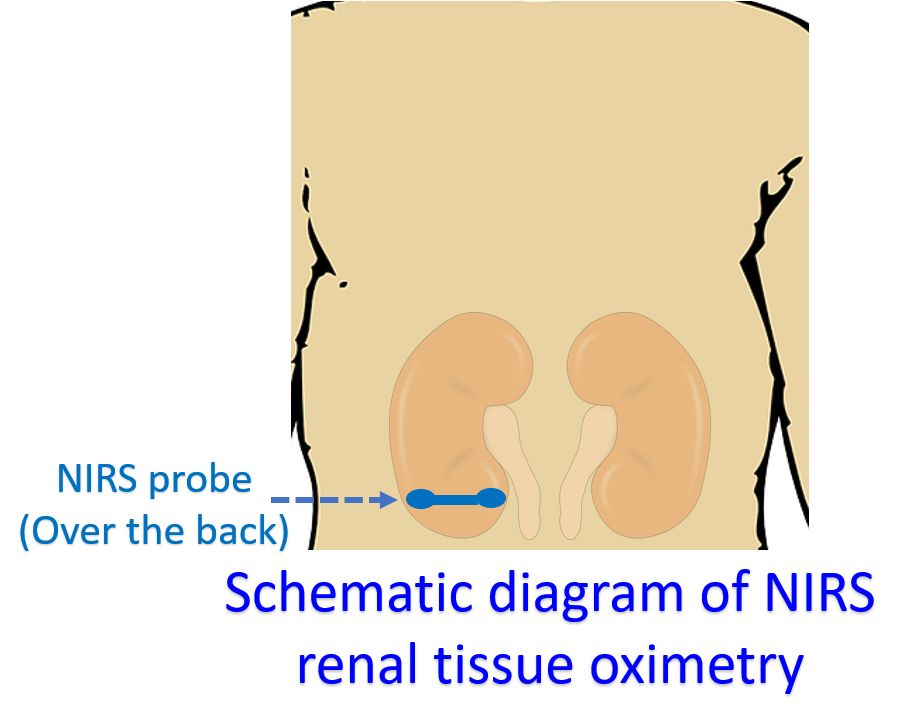
Oxygenation of the brain and kidneys can be monitored during interventions in the cardiac catheterization laboratory. In a study, it was found that when a heart rhythm abnormality or cardiac arrhythmia develops, NIRS values fall simultaneously. When desaturation problem develops, NIRS falls 10-15 seconds earlier than pulse oximetry. On improving saturation, NIRS returns to earlier values 10-15 seconds before pulse oximetry readings. Thus it may provide an early warning. A survey of the Congenital Cardiac Anesthesia Society in 2021 among its members showed the usage of NIRS by 34.7% in the cardiac catheterization laboratory and 97.1% in open heart surgery.
How is NIRS different from pulse oximetry?
Pulse oximetry calculates the percentage of oxygenated hemoglobin in arterial blood. NIRS calculates changes in oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin in the tissue under investigation, which contains both arterial and venous blood.



