Risk factors for heart disease
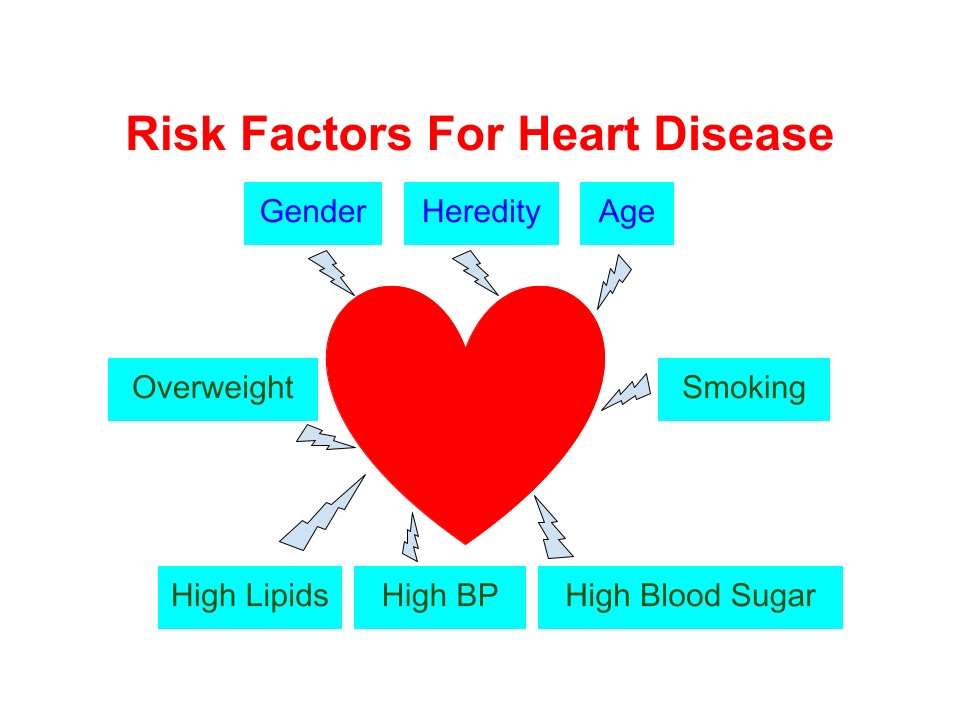
What are the important risk factors for heart disease?
In general, when we talk about risk factors for heart disease, we tend to think about the most common variety of heart disease in adults – coronary artery disease. Risk factors for heart disease can be divided into modifiable and non modifiable ones. The non modifiable ones are age, gender, ethnicity and family history. The risk of coronary artery disease increases as age advances.
So also, the risk is more in males compared to pre-menopausal females. A strong family history of premature heart disease is an important risk factor. Some races are more prone to coronary artery disease than others. Obviously, all these risk factors cannot be modified.
We are more concerned about the modifiable risk factors because that is where the individual and the community can act to reduce the risk. Important modifiable risk factors are smoking, high blood pressure (hypertension), high blood sugar (diabetes mellitus), high body weight (obesity), high levels of lipids in the blood (dyslipidemia) and chronic kidney disease.
There are other risk factors as well, though not always checked for – increased levels of homocysteine, fibrinogen, C-reactive protein (CRP) and lipoprotein (a) [Lp(a)] in the blood. Though Lp (a) levels carry significant risk, there are no well established ways of reducing the risk due to it.

