Tumours of the heart
Tumours of the heart
ഹൃദയത്തിന്റെ ട്യൂമറുകൾ – മിക്കപ്പോഴും ക്യാൻസറല്ല
Tumours of the heart are most often secondaries from cancer of breast, lungs, or other organs. Primary tumours of the heart are rare and most often benign, meaning non-cancerous. Half of the primary tumours are of a type called as myxomas. Cancerous or malignant primary tumours of the heart come to about a quarter of the primary heart tumours. Commonest primary tumour of the heart is a sarcoma. Persons with tumours of the heart can have symptoms of heart disease or general symptoms. Occasionally it is an incidental detection during ultrasound study of the heart known as echocardiography, done for some other reason.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging can give additional information during the evaluation of tumours of the heart. CT has better spatial resolution than MRI and is useful for staging and treatment planning, especially for surgical removal of the tumour. CT also provides information on the blood flow to the tumour and about calcium deposits within the tumour. MRI also provides information about blood flow, gives better information on the nature of the tumour and has no radiation risk.
About 10% of all cancers spread to the heart. But it seldom manifests as a problem of the heart. Symptoms are most often due to the primary cancer in the other organs. Areas of spread within the heart are usually small and could be multiple, preventing good removal by surgery.
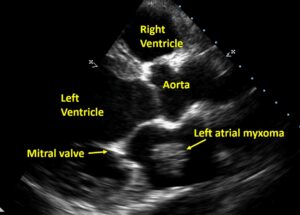
About three fourths of myxomas arise in the left upper chamber of the heart called left atrium, while about a fifth arise in the right atrium. Myxomas in the lower chambers of the heart called ventricles are still rarer. Myxomas usually have a long stalk so that a left atrial myxoma can move into the left ventricle in diastole as demonstrated in the YouTube video here. Diastole is the period during which the ventricle fills after a contraction. Majority of myxomas are not familial and do not recur after a complete surgical removal.
Familial myxomas can occur as a part of a group of disorders called Carney complex. They may be associated with dark spots in the skin, myxomas of skin and increased production of some hormones. It is linked to mutation on chromosome number 17.
Commonest primary tumour of the heart in children is called rhabdomyoma, which is rare in adults. They occur often in the left ventricle or the wall between the two ventricles. Spontaneous decrease in size and even total cure is common and can occur in about half of them. In a report of heart tumours in children over a thirty year period from a center, 20 children with rhabdomyomas were managed without surgery.