What is atrial flutter?
What is atrial flutter?
Atrial flutter is a fast but organized arrhythmia originating from the upper chambers of the heart. In this way it is different from the commoner atrial fibrillation which is quite fast but irregular rhythm originating from the upper chambers of the heart. It shares the risk of clot formation in the upper chambers of the heart and needs additional medications to prevent clot formation, like atrial fibrillation. Atrial flutter commonly arises from the right upper chamber of the heart known as right atrium. It can also arise from the left atrium sometimes.
Though the rate in the upper chambers is typically around 300/minute, the whole of it does not get conducted to the lower chambers. The AV node situated in the junction between the upper and lower chambers reduces the number of signals conducted to the ventricles. When there is only 2:1 conduction to the lower chambers, the ventricles beat at 150/minute. At this rate it may be mistaken for other types of fast rhythms originating above the ventricles.
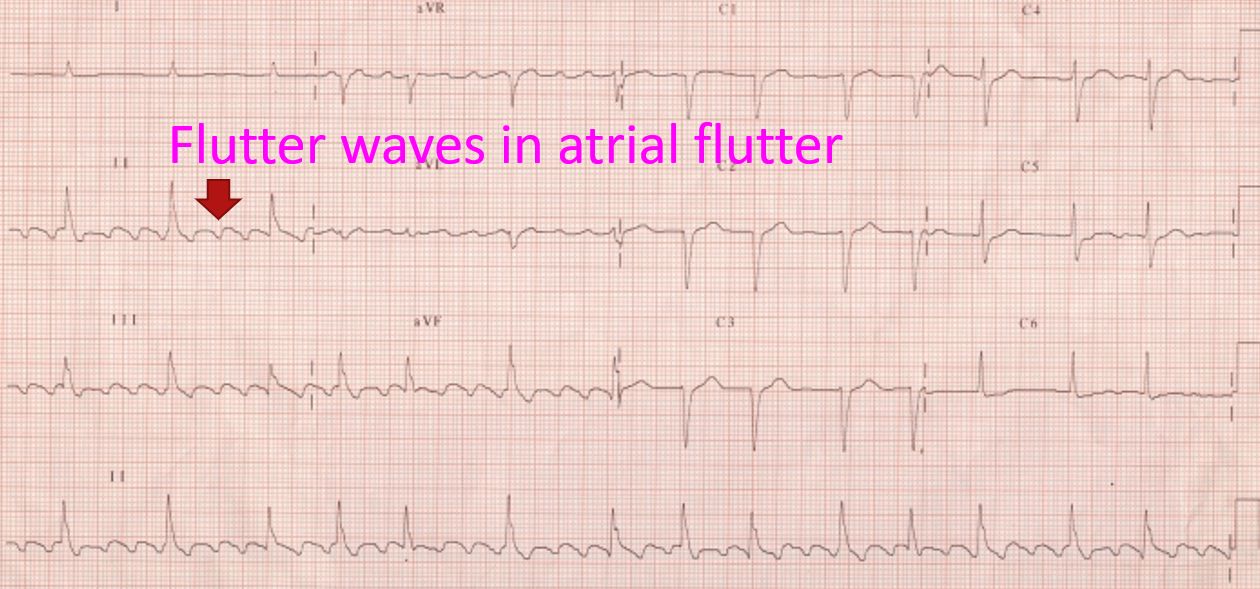
Atrial flutter can be seen in the ECG as ‘saw tooth shaped’ flutter waves representing the activity of the upper chambers. This is easily seen when the conduction block is more than 2:1 so that there is enough space between the QRS complexes and T waves to show the flutter waves. QRS complex and T waves represent the electrical activity of the ventricles in the ECG. Normal electrical activity of upper chambers is known as P wave, which is replaced by flutter waves in atrial flutter.
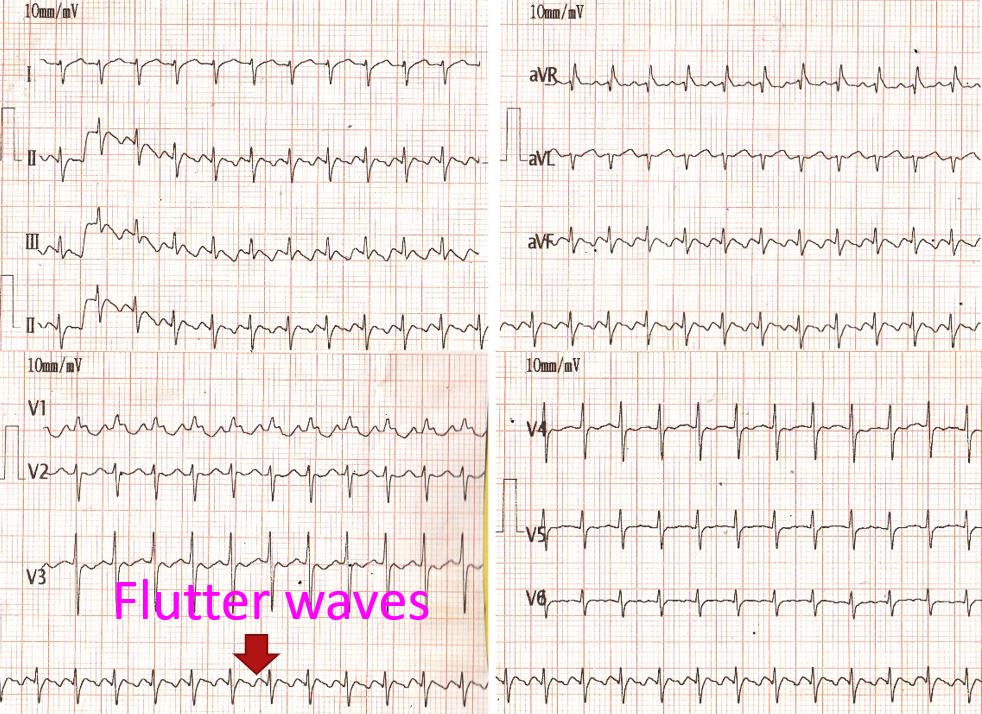
When atrial flutter occurs in a new born baby, the flutter rate is higher, just like the normal heart rate in the baby which is higher than in the adult. In the ECG shown below, the rate in the upper chambers is above 400/minute and that in the lower chambers above 200/minute. This also shows the 2:1 conduction from upper chambers to lower chambers across the AV node. You can also see that it is more difficult to notice the flutter waves in this case.
Atrial flutter can be treated initially with medications given as injections or tablets. If there is no response, it can be easily terminated by giving a controlled electrical shock with a medical device known as defibrillator. Defibrillator is used with ECG monitoring in the emergency department or intensive care room. If there is any underlying structural heart disease or abnormality in the blood electrolytes, it has to be treated. There is an advanced form of treatment known as radiofrequency catheter ablation which can be used to prevent recurrence of atrial flutter in the long term.

