What is Laser Angioplasty?
What is Laser Angioplasty?
Simple balloon angioplasty removes the plaques in blood vessels by plastering the plaque on to the artery wall. It also enlarges the vessel a little bit, so that final lumen is better than the initial lumen. Laser angioplasty, also known as laser atherectomy, is a novel technique in which a laser beam from a small tube like device is used to vaporize the block within the blood vessel. A small tube known as catheter is introduced through a small nick in the skin of the groin and guided to the location of the block using X-ray imaging. Once the block is removed, the device is taken out.
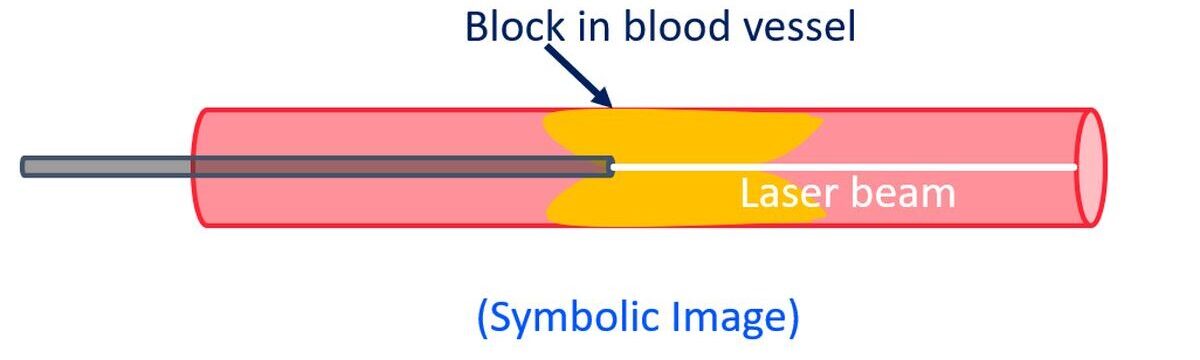
Laser atherectomy can be used for removing blocks within previously implanted stents and to create a path when conventional angioplasty balloon cannot cross a long standing block. An important advantage of excimer laser atherectomy over other atherectomy devices is delivery on a standard 0.014-inch angioplasty guidewire. The technique can be mastered after a short period of training.
Major limitation is in the presence of heavy calcification, which requires rotational atherectomy, a procedure which uses a diamond burr rotating at high speed, for clearance of the block. But when there is inability to pass a rota wire which is thicker, laser may be useful in creating an upstream channel to permit rota wire passage. Laser device works by producing monochromatic light energy to cause heat and shock waves which lead to disruption of plaque and thrombus.