What is pulmonary regurgitation?
What is pulmonary regurgitation?
Pulmonary regurgitation is the leak in the pulmonary valve between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery. Right ventricle is the lower right chamber of the heart which pumps blood returning from the body, to the lungs for oxygenation. Pulmonary artery is the blood vessel which carries the blood pumped out by the right ventricle into the lungs. A minimal leak of the pulmonary valve is common in many normal persons, which can be detected by very sensitive tests like colour Doppler echocardiography, the ultrasound imaging of the heart.
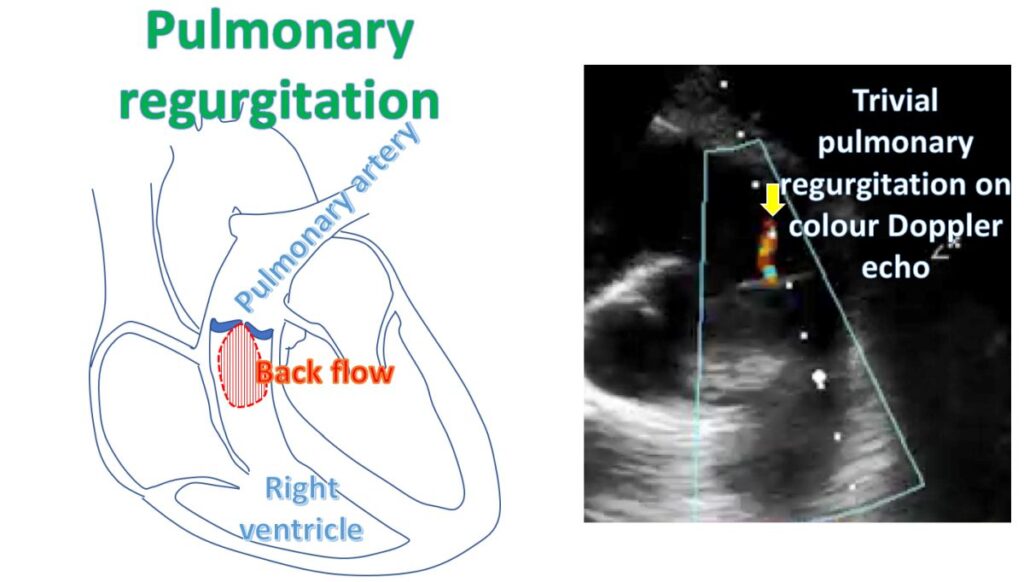
But if the leak is severe, it increases the workload of the right ventricle as it has to pump back this extra load during the next contraction. Right ventricle enlarges in response to this leak and later becomes thickened as well, to pump more blood. Pulmonary artery can also enlarge to accommodate the extra blood being pumped out by the right ventricle.
Commonest cause of significant pulmonary regurgitation is not an abnormality of the valve, but an increase in the pressure in the pulmonary artery. Increase in pulmonary artery pressure can occur as a disease by itself. Then it is called primary pulmonary hypertension. But most often the increase in pulmonary artery pressure is due to transmission of back pressure from the left sided heart disease due to disease there. Conditions like mitral stenosis or narrowing of the valve between the left upper and lower chambers of the heart is well known to produce severe pulmonary hypertension.
In the absence of an increased pressure in the pulmonary artery, pulmonary regurgitation can occur due to problems with the pulmonary valve. The pulmonary valve may even be absent by birth, often associated other more complicated birth defects of the heart. Severe pulmonary regurgitation can also occur after a repair of complex birth defects of the heart in which a narrowed pulmonary valve is opened up by an operation.

Mild and moderate pulmonary regurgitation is usually left alone as they do not cause much problem to the person. But observation is needed to check whether the leak is increasing. Very severe leak can produce progressive enlargement of the right ventricle, which can fail in the long run. A failing right ventricle can also upset the heart rhythm and increase the risk of sudden cardiac death rarely.
Failure of the right ventricle increases the pressure in the right upper chamber, the right atrium, from which the right ventricle receives blood. This increased pressure is in turn transmitted to the great veins superior and inferior vena cava. Veins in the neck get distended. Liver gets congested and enlarged. Fluids collects under the skin of the legs and in severe long standing cases in the tummy. This situation is called right heart failure and needs medical treatment to improve heart function initially.
When there is no response, in selected few cases, the pulmonary valve may be replaced. This is considered often when it is a severe leak which had occurred after a surgery for a complex birth defect of the heart. If the leak is secondary to a disease of the left sided heart valves, it may decrease if that valve is opened up or replaced as in case of mitral stenosis. When the leak is due to isolated increase in pulmonary artery pressure, medications to lower pulmonary artery pressure are given.
Pulmonary valve can be repaired and replaced by an open heart surgery. Non-surgical method in which the valve mounted on a balloon is introduced through a hole in the groin is also there. In this case, the device is guided by X-ray imaging techniques in a special room known as cardiac catheterization laboratory. For this procedure there is no need to open up the chest.


