What is the difference between CRT-P and CRT-D?
What is the difference between CRT-P and CRT-D?
CRT-P, CRT-D എന്നിവ തമ്മിലുള്ള വ്യത്യാസം എന്താണ്?
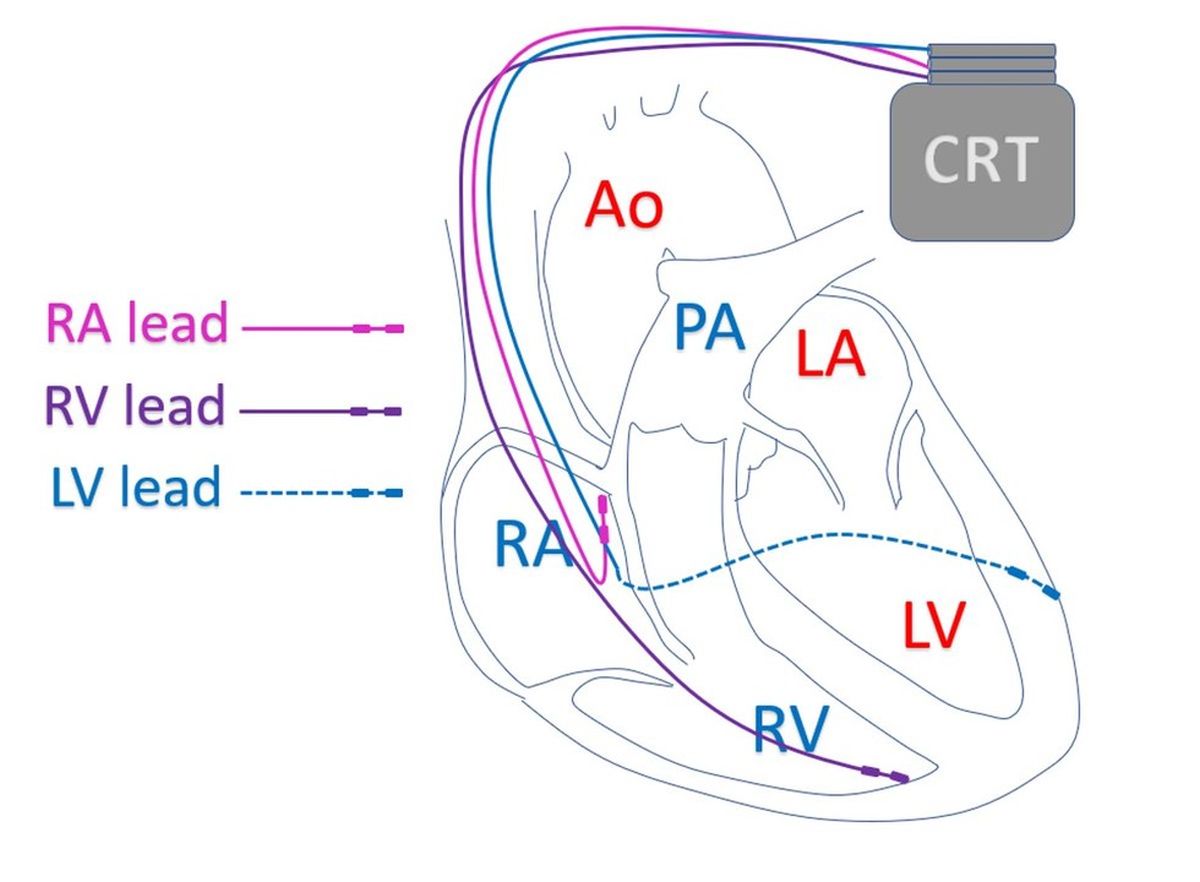
In cardiology, CRT stands for cardiac resynchronization therapy. CRT is used in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, is a type of heart failure in which the pumping function of the left ventricle is reduced. Left ventricle is the lower left chamber of the heart. CRT is a type of pacemaker in which electrical leads are placed in three chambers of the heart, right upper chamber (right atrium), right lower chamber (right ventricle) and the left ventricle.
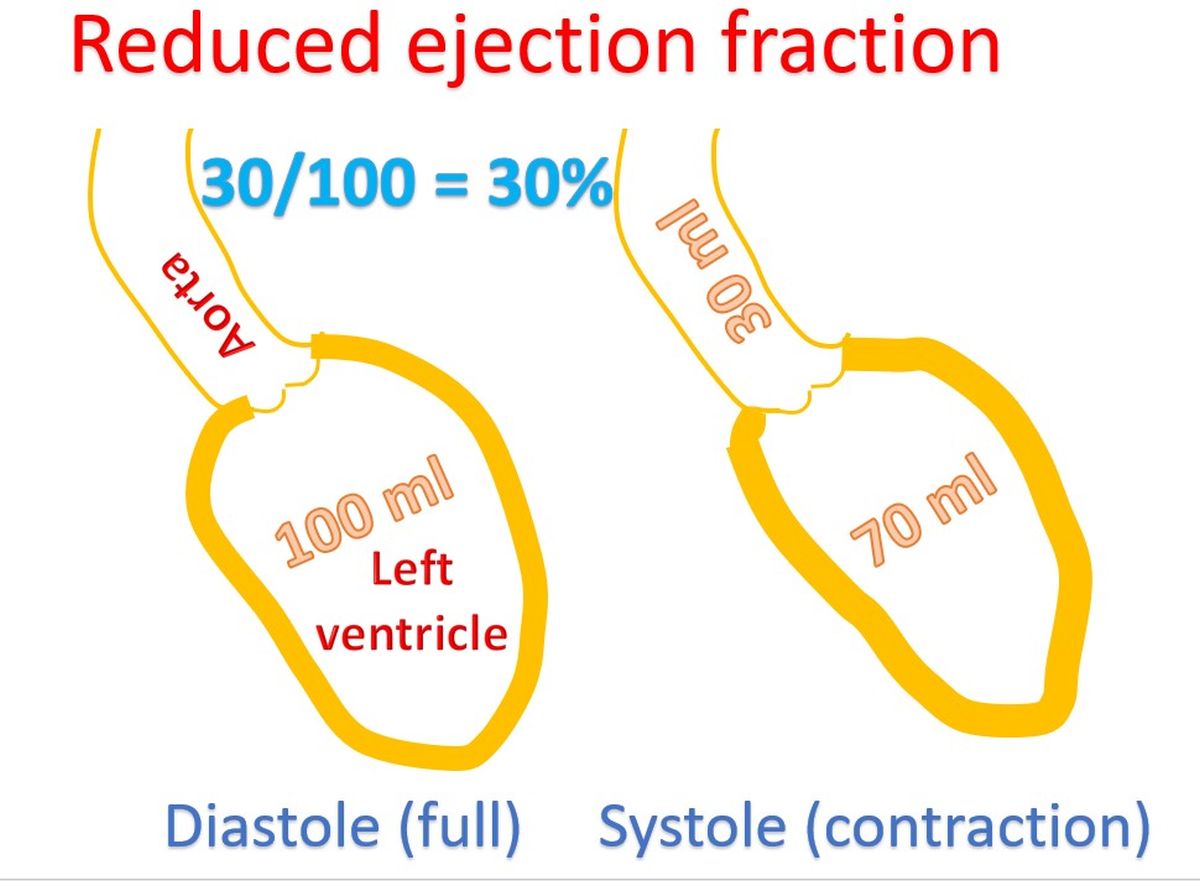
This picture illustrates what reduced ejection fraction means. Ejection fraction is the fraction of the blood which is pumped out from the left ventricle when it contracts after filling up. The period of relaxation is known as diastole, in which the ventricle fills and contraction is known as systole. Normal ejection fraction is around 60 to 70%. When it is reduced below 40%, it is known as heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
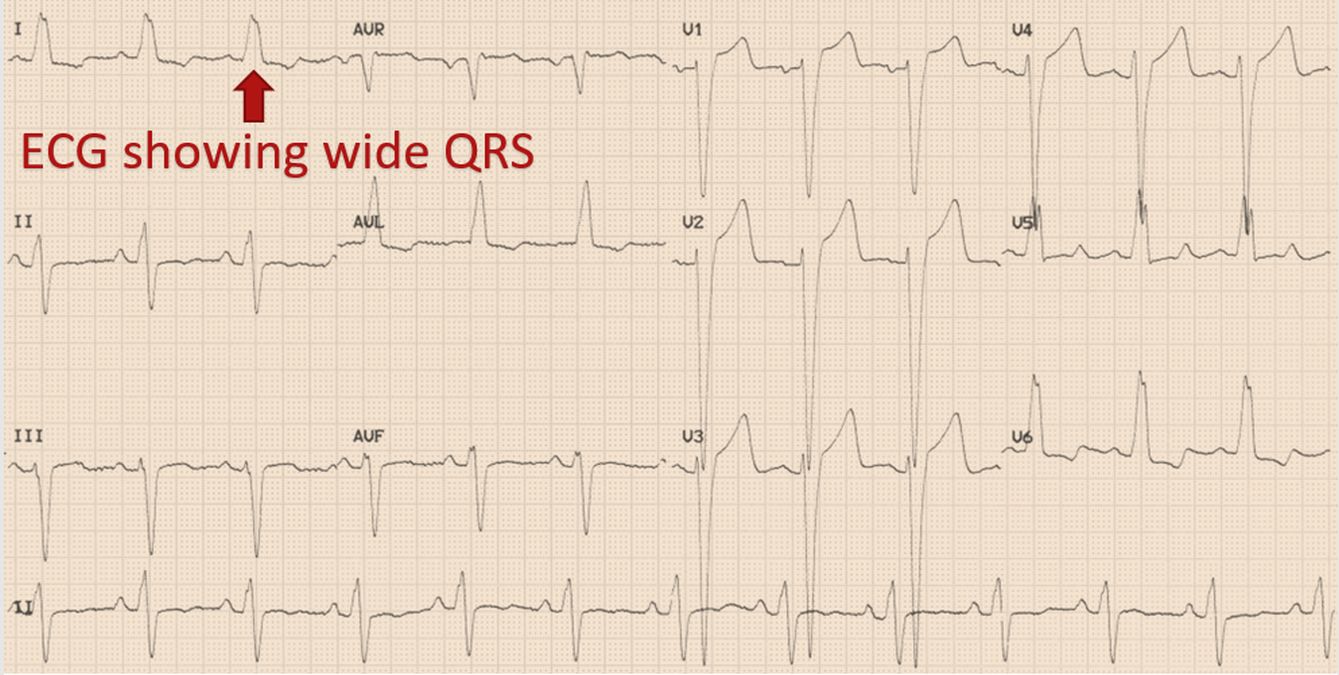
In some persons with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction, contraction of different parts of the left ventricle loses its natural synchrony, so that part of the contractile effort is wasted. This can be inferred from ECG, the electrical recording of the heart. ECG will show a wide QRS complex with a left bundle branch block pattern (LBBB) in those with dyssynchrony. QRS complex denotes the electrical activation of the lower chambers of the heart. Left bundle branch is that part of the electrical conduction system of heart which takes signals to the left ventricle.
The timing of the electrical signals given by the pacemaker is adjusted to produce synchrony of contractions of the heart. The right atrium is paced first and the ventricles after a short delay. Pacing of the left and right ventricles are timed in such a way that the left ventricle contracts in a synchronized fashion to improve the pumping function. As the name suggests, CRT is implanted in those heart failure patients in whom the synchrony of the left ventricular contraction has been lost.
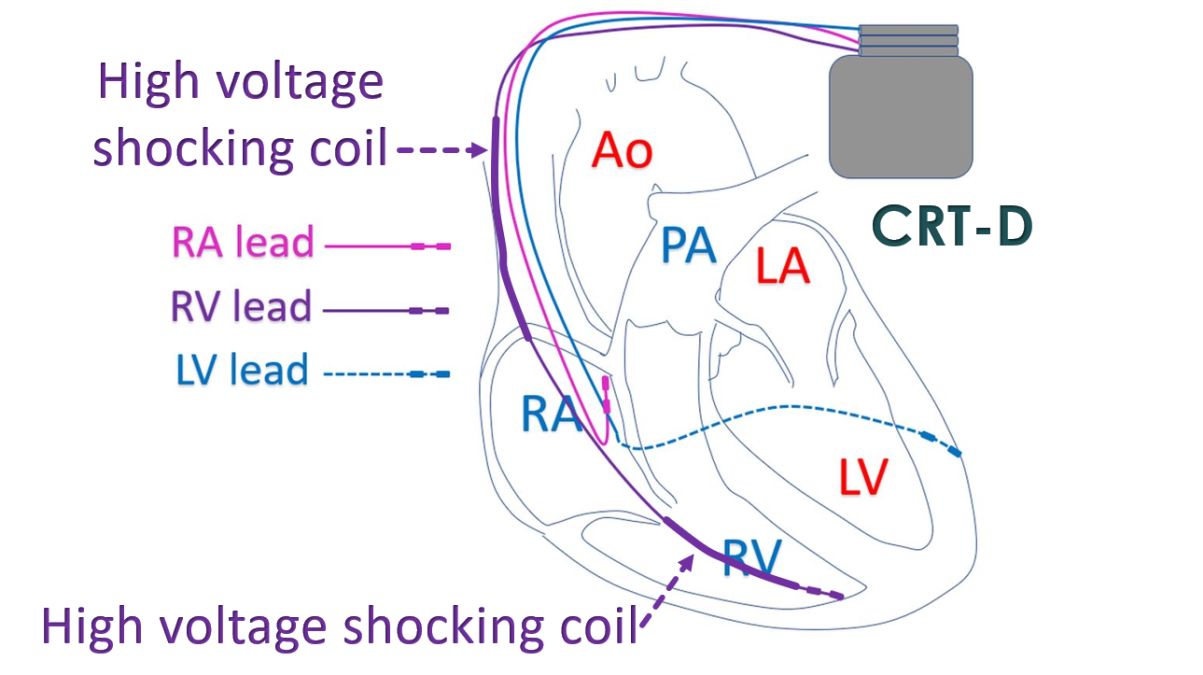
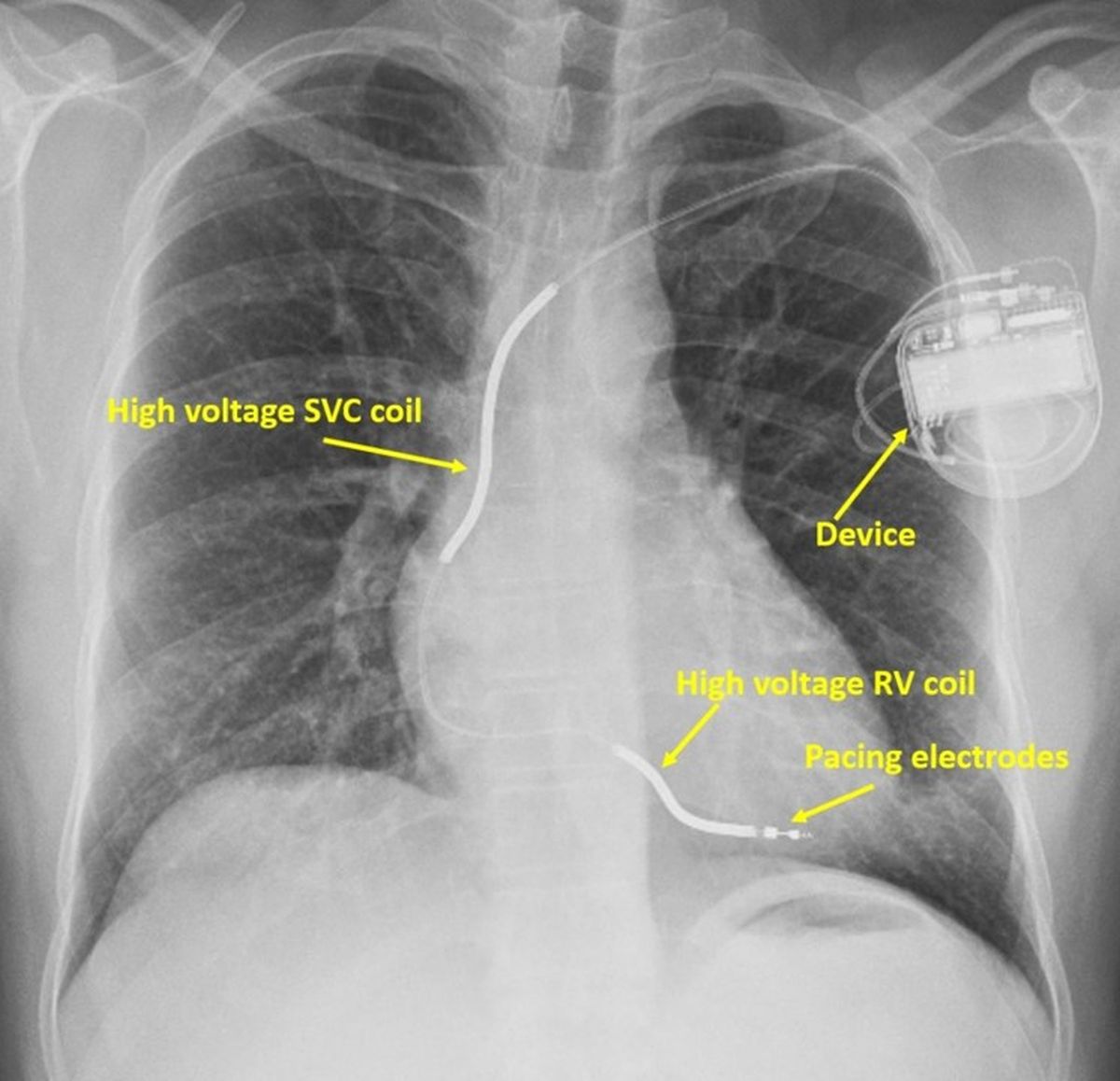
CRT alone is now re-designated as CRT-P or CRT with pacing alone. This is because there is another device known as CRT-D in which a CRT is combined with an ICD. ICD is short form for implantable cardioverter defibrillator, used to automatically shock back the heart into action in case of life threatening heart rhythm disorders. This X-ray shows an ICD with high voltage shocking coils within the heart. In CRT-D, shocking leads which are thicker high voltage leads are included along with the pacing leads of CRT-P.
Battery capacity has to be more for CRT-D because a large amount of electrical energy is needed for the shocks. Naturally, the longevity of CRT-D battery is lesser than that of CRT-P. Moreover, the internal shocks given by CRT-D can be painful, though essential to save life in case of major heart rhythm disorder. CRT-D is needed in some heart failure patients who have a high risk of life threatening heart rhythm disorders.