Aortic stent grafting (EVAR)
Aortic stent grafting (EVAR)
Most of you will be familiar with insertion of stents after coronary angioplasty. A similar procedure for disease of the aorta is known as aortic stent grafting. It is different from simple stenting for obstruction of aorta which can occur as a birth defect. The stent graft is a metallic stent covered with fabric so that it can be used to prevent leakage of blood from the stented region. Stent grafts are used for treatment of localized enlargements of the aorta known as aortic aneurysms. Aorta is the largest blood vessel carrying oxygenated blood to the whole body.
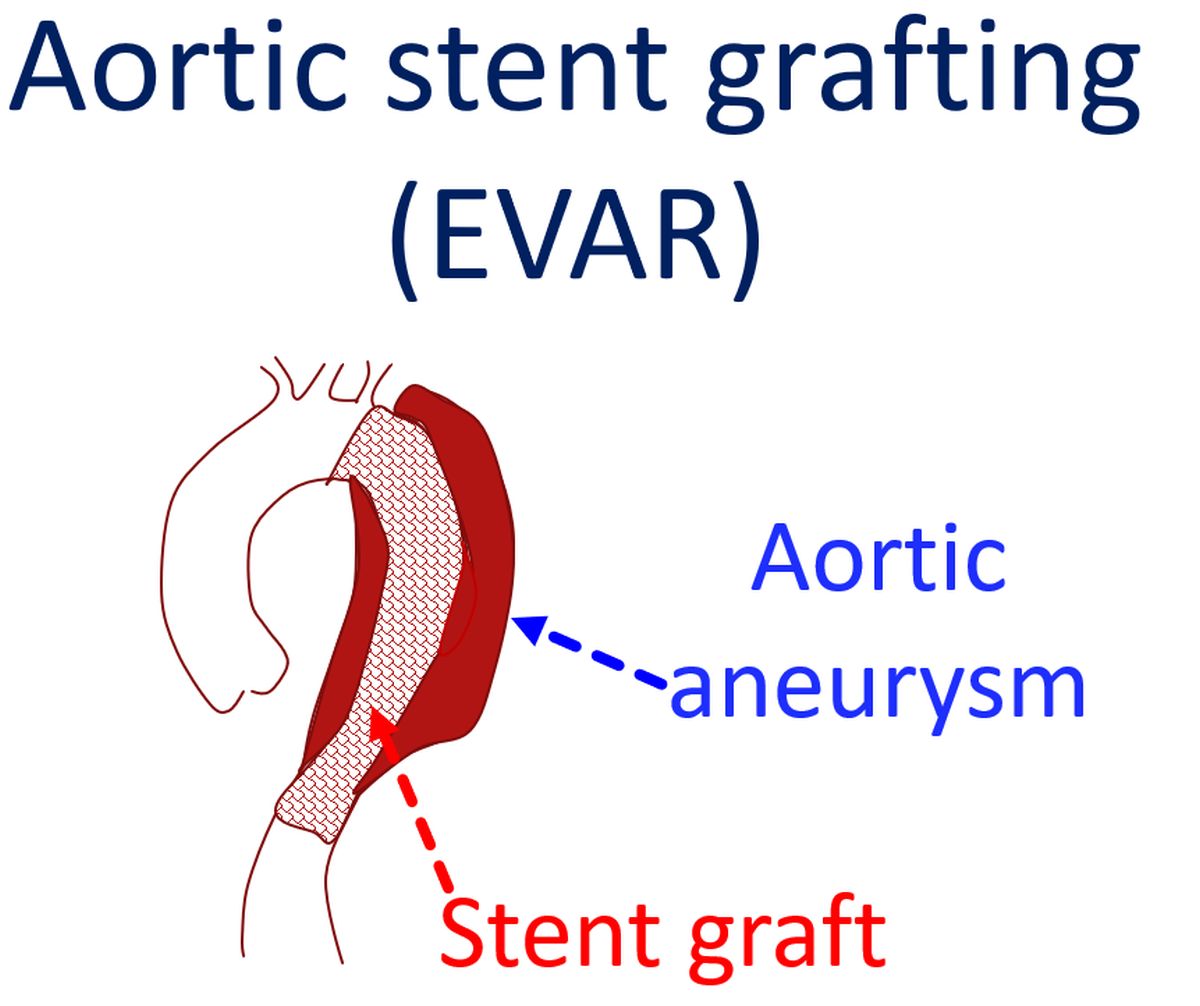
The chance for development of aneurysm of aorta increases as age advances. In many countries, screening for aneurysm of aorta in the tummy by ultrasound scanning at regular intervals after about 65 years of age is common practice. Aortic stent grafting is called by the technical name endovascular aortic repair (EVAR). Endovascular repair means repairing from within the blood vessel without opening it and stitching up as was done previously by surgery. The folded stent graft is mounted on a tubular device and introduced through the blood vessel in the groin.
The device is guided to the desired location using continuous X-ray imaging. Once the device is across the diseased region of the aorta, it is released. The fabric coated stent excludes the enlarged portion of aorta from the blood circulation. Blood flows from the normal segment above to the normal segment below only through the stent graft. The enlarged portion of the aorta outside the stent graft develops blood clots and gets occluded. Stent grafting prevents progressive enlargement and potential rupture of the aortic aneurysm, which is a dreaded and often fatal outcome of aortic aneurysm.
Advantage of stent graft is that it avoids a major open surgery in these patients who often have high surgical risk due to other associated diseases common in the elderly. Detailed computed tomographic (CT) imaging of the region to be stented is done for planning the procedure. Correct size of the stent graft is decided based on the evaluation of CT images. Exact sizing is important to ensure a good fit inside the blood vessel, without side leaks. As the device is expensive, meticulous pre-procedure planning is usual. Periodic follow up with CT imaging after procedure is also done.


