Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral Regurgitation
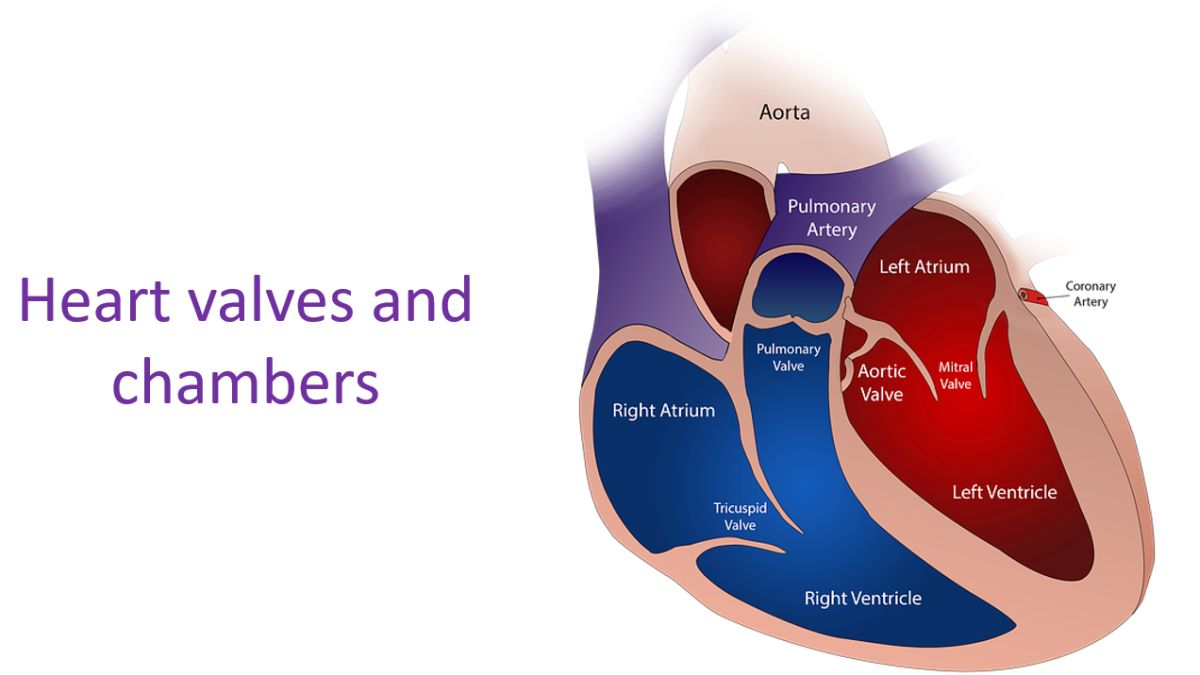
Mitral regurgitation or leak in the mitral valve, can occur as a result of damage to the valve leaflets or due to papillary muscle dysfunction. It can also occur when the left ventricular cavity is dilated. In developing countries rheumatic fever is an important cause of MR as a result of mitral valvulitis. In developed countries rheumatic fever is rare and MR is seldom of rheumatic etiology. More common would be mitral valve prolapse and degenerative mitral valve disease. The severity of MR is quantified by the regurgitant fraction. The fraction of the end diastolic volume which regurgitates into the left atrium is known as the regurgitant fraction. It can be estimated by Doppler echocardiography as well as angiocardiography.
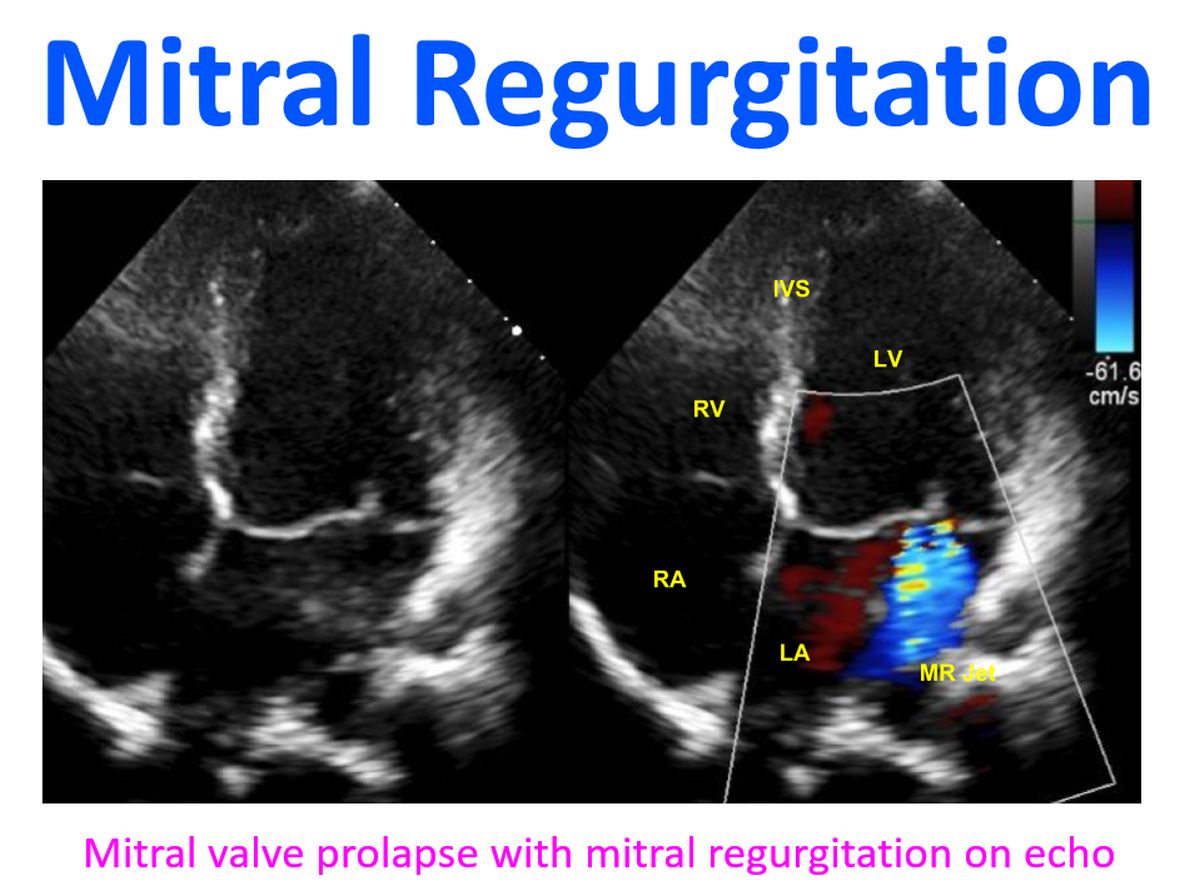
Left ventricle and left atrium dilates gradually with increasing MR. As the left ventricle dilates, the mitral annulus enlarges and allows more regurgitation. This is why it is often mentioned that “MR begets MR”. Left ventricular end diastolic pressure may increase when the left ventricle fails in severe MR. This is more likely in acute MR than in chronic mitral regurgitation. Rise in left ventricular end diastolic pressure also leads to elevation of left atrial pressure and pulmonary venous pressure. This in turn can lead to elevated pulmonary capillary pressures and pulmonary edema. Reactive pulmonary arterial hypertension can also occur in chronic severe mitral regurgitation.
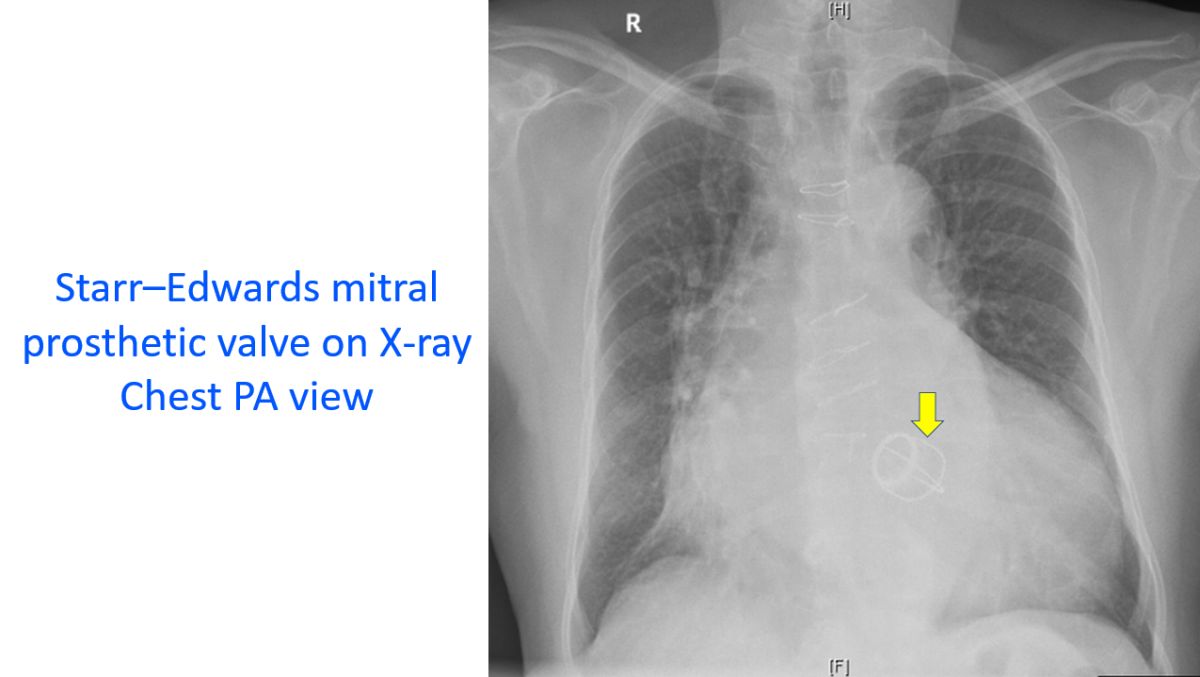
Severe mitral regurgitation can be surgically treated by mitral valve repair as well as mitral valve replacement. The scarred mitral valve of rheumatic mitral regurgitation is often not suitable for repair and requires replacement. Percutaneous techniques for mitral valve repair are also being used, though currently more expensive. Once the mitral valve is replaced by a mechanical prosthesis, life long anticoagulation is mandatory, with its attendant problems and need for regular monitoring of clotting function with prothrombin time estimation.