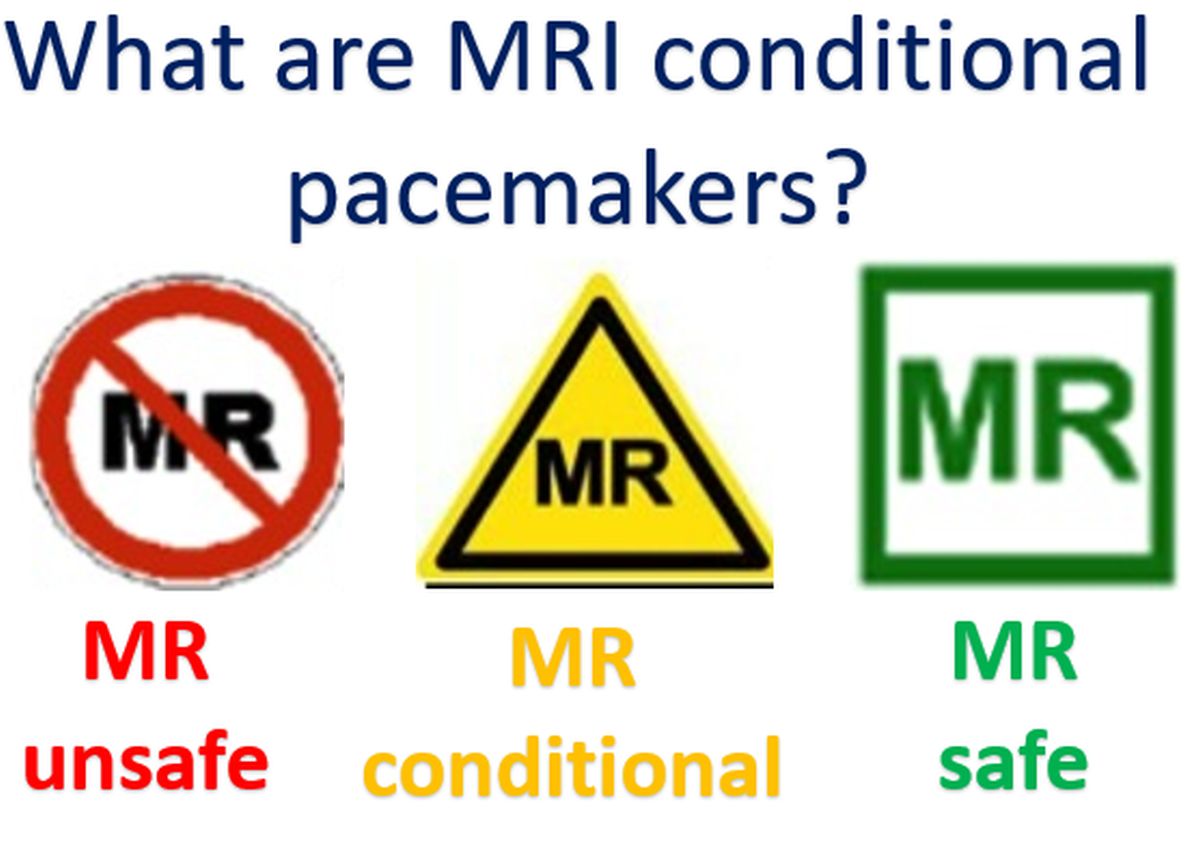
What are MRI conditional pacemakers?
What are MRI conditional pacemakers?
Usually devices containing metallic components are considered to be unsafe during an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) procedure. Pacemakers are devices which give regular electrical pulses to the heart when the electrical system of the heart is not functioning well and the heart rate has gone down. Usual pacemakers have a pulse generator circuit with battery implanted under the skin of the chest.
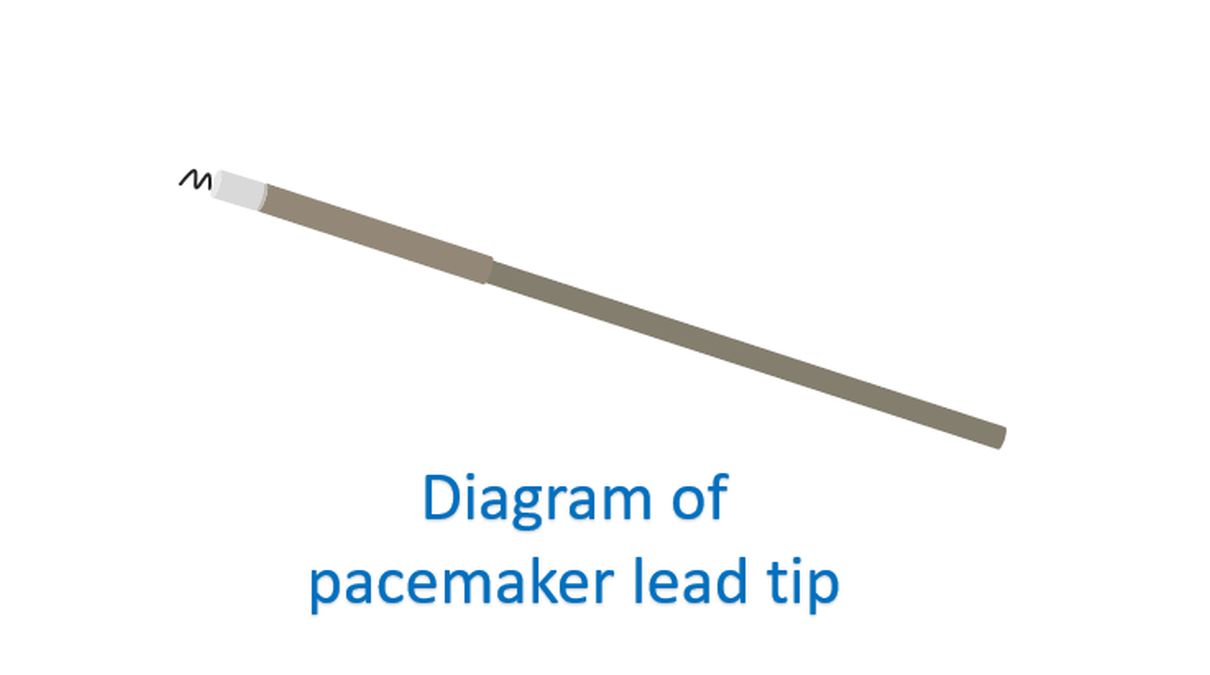
The device is connected to the heart using electrode wires known as leads, introduced through blood vessels. Intense magnetic fields used for MRI can interfere with the function of the pacemaker. The pacemaker lead can act like an antenna and absorb a lot of electromagnetic energy which could heat up the cells where it makes contact within the heart.
MRI conditional pacemakers are devices which can be used in the MRI environment following certain precautions advised by the manufacturer. MRI conditional pacemakers were first introduced in 2008. They have less ferromagnetic material and lead design reduces the chance for heating. Reduction of ferromagnetic material also reduces the potential for artifacts induced by the pacemaker system in the MR images.
The winding pattern of the filament of inner lead coil and geometric design of the leads have been changed to avoid resonance at the MR signal frequency to avoid heating. It may be noted that MRI conditional devices should be connected to MRI conditional leads only. Otherwise the system will not be MRI conditional.
Reed switch is replaced by a solid state Hall effect sensor which perform better within the MR console, by avoiding unpredictable reed switch behaviour. Reed switch behaviour will vary with the strength of the magnetic field and the orientation of the reed switch in the field. Magnetic reed switch was used in pacemakers to control their mode of function externally using a magnet.
Easily programmable MRI mode is available in these devices. This will prevent inappropriate pacemaker inhibition and competing rhythms. These devices have special circuitry to prevent damage to internal power supply when exposed to MRI signals.
Initially MRI scan was permitted only with 1.5 Tesla scanners. But later studies have shown that even 3 Tesla MRI scanners may be used without much adverse events. Yet the chance of adverse events increases as the strength of the magnetic field in the MRI scanner increases. Pacemaker programming is done before and after the scan to ensure that function is not affected.


