What is a subcutaneous ICD?
What is a subcutaneous ICD?
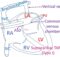
ICD stands for implantable cardioverter defibrillator in cardiology. It is a device which monitors the heart rhythm and automatically treats it with electrical signals which could be a high voltage internal shock if needed. They are also called AICD or automatic implantable cardioverter defibrillators. In usual ICD, the device is implanted under the skin and the leads are introduced into the heart through the blood vessels. In purely subcutaneous ICD, both the lead and the device are implanted under the skin. Subcutaneous means under the skin.
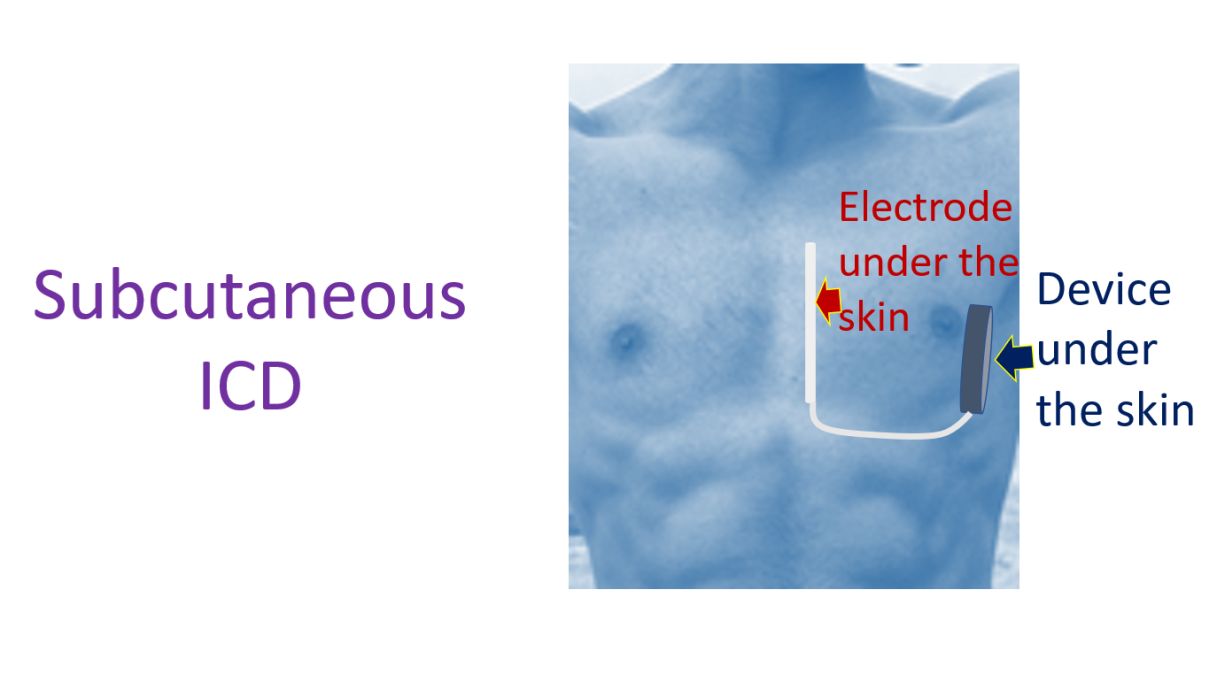
For the usual ICD, its lead is sometimes called as its Achilles heel, because more problems like infections, lead displacement and lead fracture occur with the lead than with device as such. It was for this reason that an ICD without a lead introduced into the heart was developed, as a purely subcutaneous ICD. As the shock is delivered outside the heart, under the skin, it requires higher power output to be effective. Hence the device is bulkier, to include a more powerful battery. This also reduces the battery longevity as the energy needed for each shock is more.
Most important advantage of the subcutaneous ICD is that no lead needs to be introduced into the heart. So it avoids many of the lead related problems like lead displacement as mentioned initially. The procedure for introducing the leads into the heart is not without risk, though it can be reduced by careful techniques by an experienced operator. But subcutaneous ICD is a trade off as you need much larger battery with bigger sized device, still having lesser battery life if it is used frequently for the higher output shocks.
Another disadvantage of a subcutaneous ICD is that it cannot be used for giving pacing signals to the heart on a regular basis. It can give a short period of backup pacing after shock, but that will not be very effective as the signals are delivered outside the heart and not inside the heart. Pacing from under the skin requires higher voltage and can be painful. Another disadvantage is that it cannot be combined with a cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), which is also known as a heart failure device. CRT paces both lower chambers and one upper chamber of the heart in selected cases of heart failure.
Still, subcutaneous ICD can be considered in those with inherited heart rhythm abnormalities with propensity for life threatening ventricular arrhythmias and in birth defects of the heart with limitations on internal lead placement due to poor access to appropriate blood vessels. They may also be considered in those with deficiency of immune system who are more likely to have infections in leads placed in blood vessels and in young and active persons who have a higher chance of conventional ICD lead failure.