What is TAPVC?
What is TAPVC?
TAPVC stands for total anomalous pulmonary venous connection. It is also known as TAPVD or total anomalous pulmonary venous drainage. Normally, pulmonary veins join the left atrium. When it drains to the right atrium through one of the blood vessels leading to the right atrium, it is known as TAPVC. If only some of the four pulmonary veins join the right side of the heart, then it is called PAPVC or partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection. Pulmonary veins are the blood vessels returning oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. Right and left atria are the upper chambers of the heart.
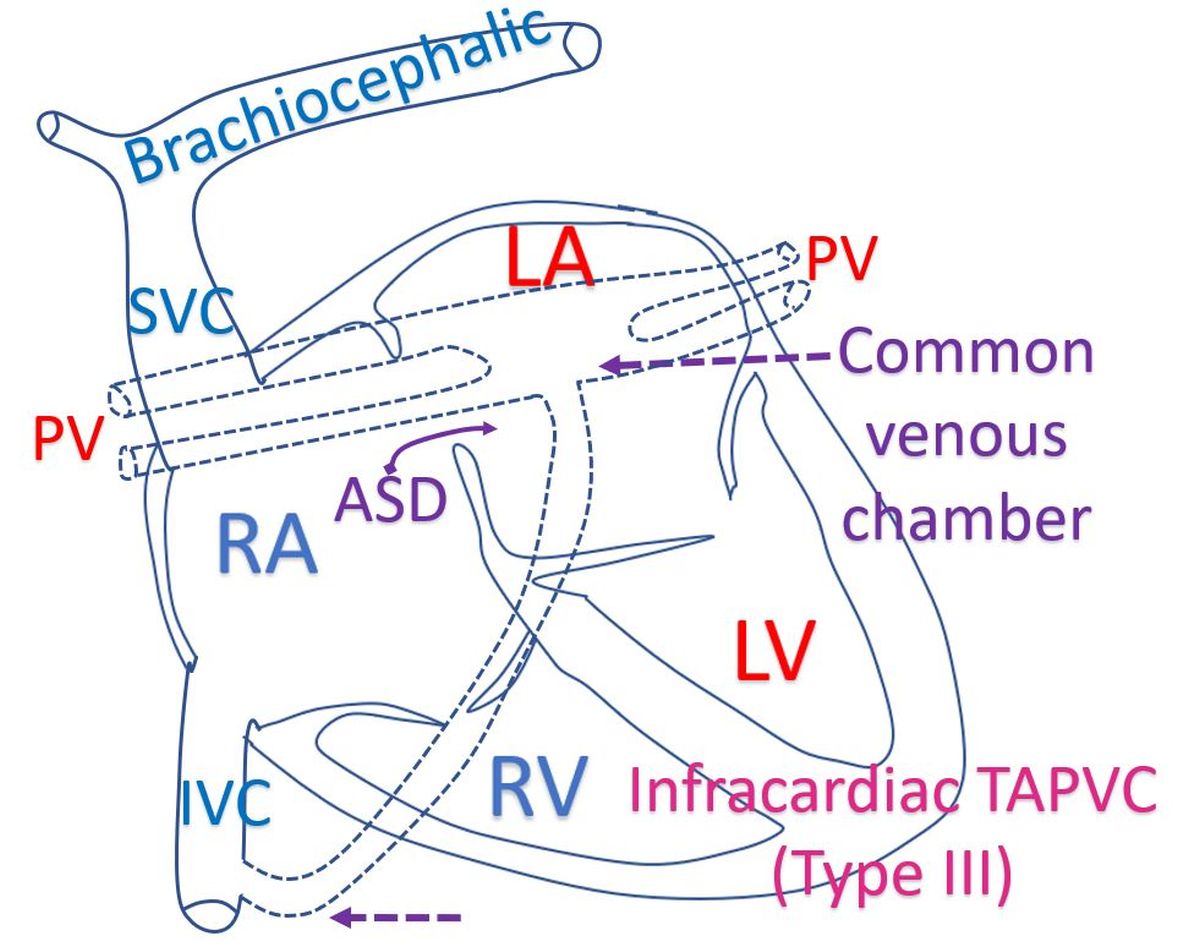
When all the pulmonary veins join the right side of the heart instead of the left side, a defect in the wall between the upper chambers of the heart known as atrial septal defect (ASD) is needed to maintain life. Otherwise body will not get any oxygenated blood. Oxygenated blood returning from the lungs to the right side of the heart gets pumped back to the lungs. If there is no ASD, the left ventricle may not get any blood to pump at all! Blood returning from the body to the right side of the heart also will get pumped to the lungs.
Due to the mixing of oxygenated and oxygen poor blood in the right atrium, the blood pumped out into the body has less oxygen than normal. This produces bluish discoloration of lips, tongue and skin, known as cyanosis. Thus TAPVC is a cyanotic congenital heart disease (birth defect of the heart with cyanosis). Part of the blood returning from the lungs can get recirculated to the lungs, increasing the pulmonary blood flow. Increased pulmonary blood flow can increase the blood pressure in the lungs in the long run.
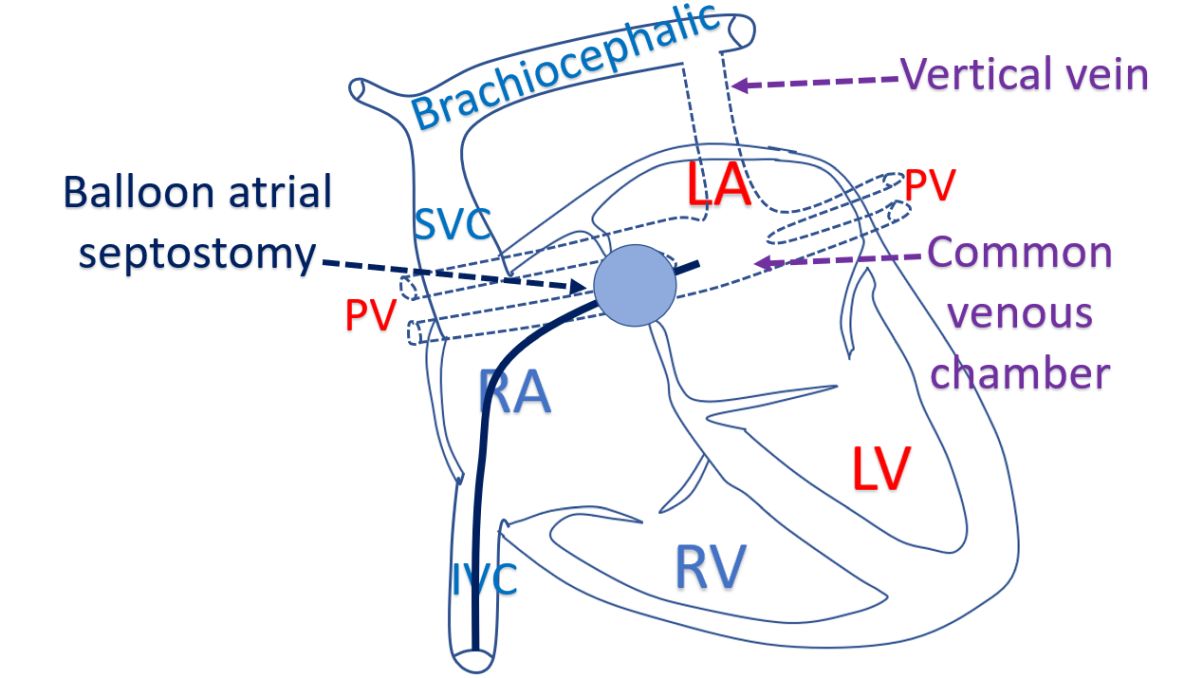
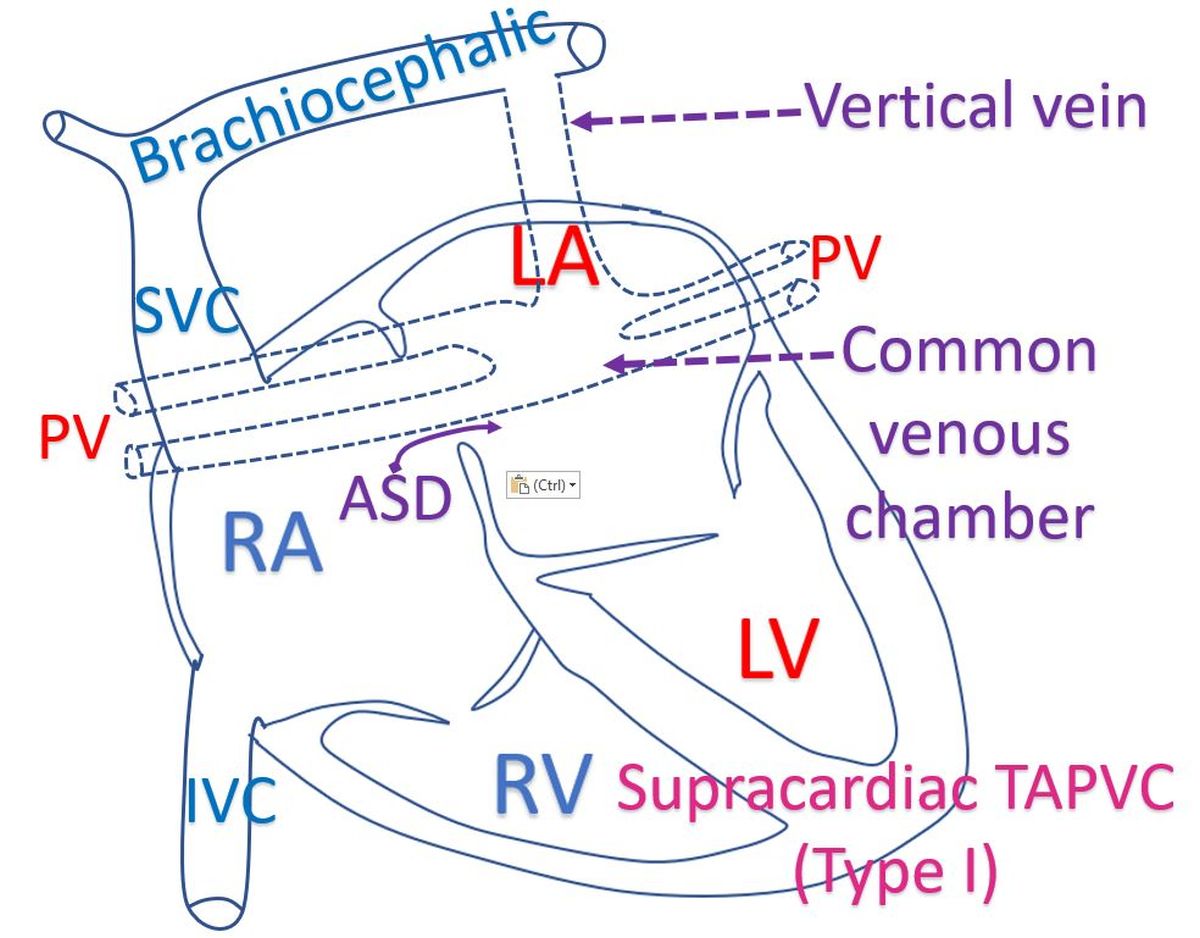
There are basically four types of TAPVC. Most common variety is supracardiac, meaning, above the heart. In supracardiac TAPVC, four pulmonary veins from the two lungs join together and drains upwards in a vertical vein. As the name implies, it runs vertically upwards from behind the heart, to a blood vessel returning blood from the upper part of the body known as brachiocephalic vein. This vein then joins the superior vena cava (SVC), a large vein draining blood from the upper part of the body. SVC in turn drains to the right atrium, the right upper chamber of the heart.
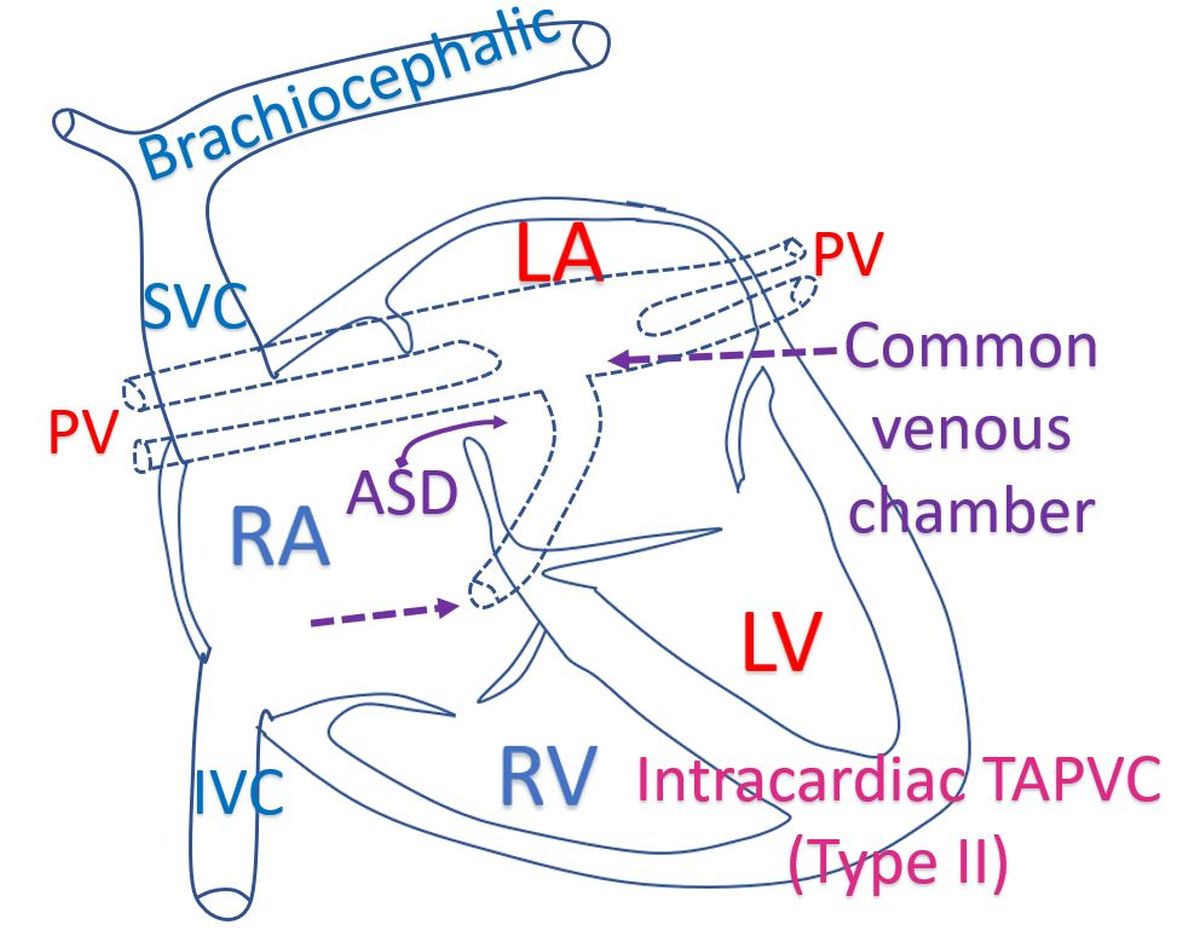
Intracardiac variety drains into coronary sinus, the vein returning blood from the heart into the right atrium. Intracardiac means within the heart as all pulmonary veins are draining directly to the vein of the heart itself, and not outside the heart as in other varieties.
Next is the infracardiac variety, in which pulmonary veins go below the diaphragm, the breathing muscle separating the chest cavity and the tummy. The pulmonary veins then join portal vein in the liver and drains to the inferior vena cava. Inferior vena cava is the blood vessel draining blood from the lower part of the body to the heart. Infracardiac, means below the heart. There is also a fourth mixed type, which is much less common.
In the infracardiac variety, as the blood return from the lungs passes through the liver, the flow is partially obstructed (obstructed TAPVC). This causes back pressure in the lungs and collection of fluid within the lungs. Collection of fluid in the lungs is known as pulmonary edema and causes severe breathlessness in the baby, in addition to blue colour. That will be a life threatening situation needing emergency treatment.
TAPVC with large ASD can survive long without much symptoms, but those with small ASD need emergency surgery. Initial procedure can be enlargement of the ASD by a procedure known as balloon atrial septostomy. Balloon atrial septostomy uses balloons attached to small tubes, introduced through blood vessels, to enlarge the defect in the wall between the upper chambers. The baby is then considered for corrective surgery after stabilization of medical status. Those with infracardiac variety will need emergency corrective surgery because of severe breathlessness.