What is arterial switch operation?
What is arterial switch operation?
Arterial switch operation is the ideal corrective surgery for transposition of great arteries (TGA). It was described by Jatene and colleagues in 1976. Normally aorta originates from the left ventricle and pulmonary artery originates from the right ventricle. This is reversed in TGA, so that pulmonary artery arises from the left ventricle and aorta originates from the right ventricle. Arterial switch operation normalizes this relationship, by moving the aorta and pulmonary artery back to their expected positions. Aorta is the large blood vessel carrying oxygenated blood to the body. Pulmonary artery carries blood to the lungs for oxygenation. Left ventricle is the lower left chamber and right ventricle the lower right chamber of the heart.
When the blood vessels are switched, the coronary arteries are also repositioned to arise from the new aorta which is connected to the left ventricle. Coronary arteries are blood vessels carrying oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Arterial switch operation has to be done very early in life, typically before 2-3 weeks of age. Beyond that the left ventricular muscle becomes thinner as it is connected to the pulmonary artery. Pulmonary artery has much lower pressure than the aorta. So if the left ventricle is connected to the pulmonary artery for a long period, its muscle mass comes down. Later, if it is connected to the aorta, it will not be able to pump at the higher pressure needed in aorta.
Though arterial switch operation is the best one for TGA, some long term issues have been noted later. As the pulmonary artery has to be switched, distortion in the vessel can cause narrowing of the vessel in the long run. This narrowing can be enlarged using balloons attached to small tubes known as balloon catheters. But occasionally this can produce leaks, which can be dangerous. The newly placed coronary arteries may be close to the narrowed pulmonary arteries and can get compressed during balloon dilatation and stenting of pulmonary artery. Stent is a spring like metallic material inserted into the pulmonary artery after balloon dilatation to prevent recoil. Fracture of the stents can also occur later in some cases.
Another problem noted is the enlargement of the root of aorta in the long run, along with leak in the aortic valve. Aortic valve is the valve between the aorta and left ventricle, preventing backflow when the left ventricle relaxes after a contraction. Though these problems have been noted in the long run, till date, arterial switch is the best operation for correction of TGA if done early in life. Arterial switch still gives better long term results than other previous corrective surgeries for TGA.
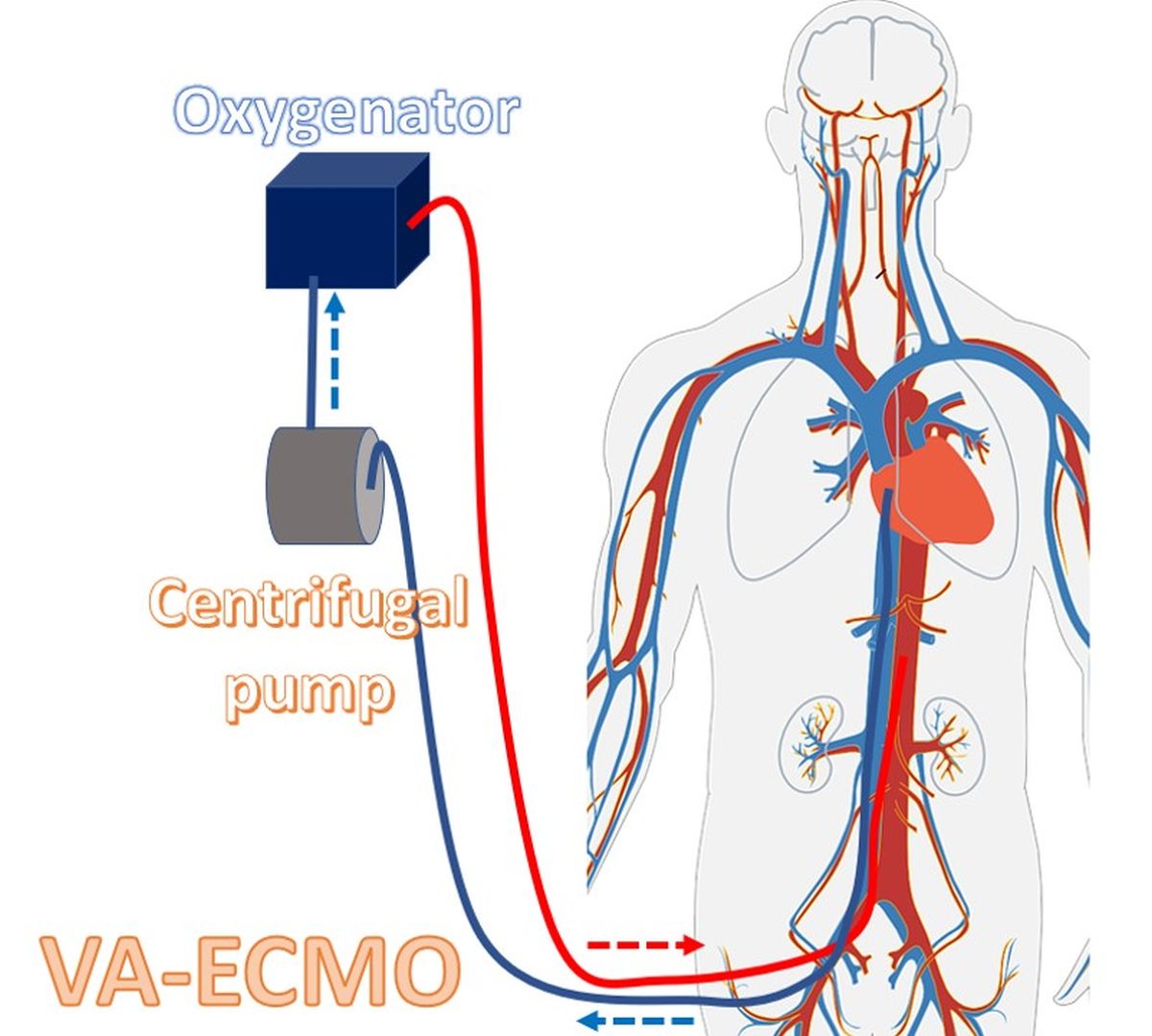
Some reports of successful delayed performance of arterial switch has also been reported. These babies had to be operated beyond 8 weeks. They needed support of breathing machine (ventilator) for periods ranging from 1 to 16 days. Half of the patients needed special heart lung support known as ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation). In ECMO, machine takes over the function of both heart and lungs temporarily. Ventilators only inflate and deflate the lungs allowing air entry. But ECMO does both pumping of blood as done by the heart and oxygenation of blood as done by the lungs. That report showed that good results for arterial switch can be obtained even beyond 8 weeks if ECMO support and excellent expert intensive care is available.