What is cath test?
What is cath test?
Cath test is short for cardiac catheterization test. Cardiac catheterization is a test in which small tubes known as catheters are introduced into the heart through the blood vessels. The test is done in a special procedure room known as cardiac catheterization laboratory (cathlab). The catheters are guided through the blood vessels into the heart using live X-ray imaging (image intensifier fluoroscopy). Sometimes echocardiography (ultrasound imaging of the heart) may also be used to guide the catheter within the heart. Bedside cardiac catheterization can be done using special flow directed catheters which have a balloon at the tip. When the balloon is inflated while in the right upper chamber of the heart (right atrium), the catheter takes the course of the blood flow into other chambers. This method is usually used to measure the blood pressure in the pulmonary artery (blood vessel of the lungs).
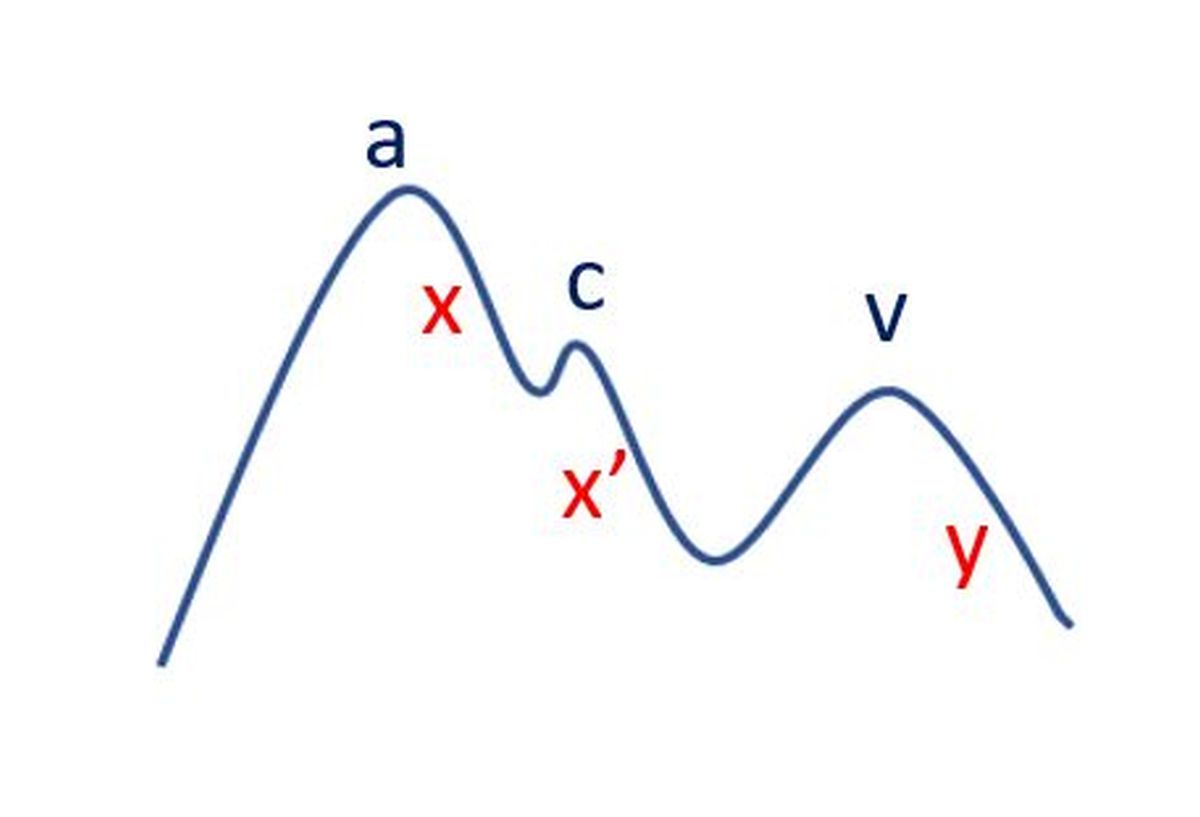
Basic principle of cardiac catheterization is that in which ever chamber the catheter is introduced, pressure and oxygen saturation is measured. Continuous monitoring of the pressure at the tip of the catheter is done to obtain the pattern of the pressure tracings. The pattern of the tracing varies between the various heart chambers and also depending on disease conditions. It is usually higher in the ventricles when the heart contracts and lower when the heart relaxes. Pressure in the ventricles (lower chambers) are higher than that in the atria (upper chambers). Pressure in the left sided chambers are higher than on the right side. Aorta, the major blood vessel arising from the left ventricle, has a much higher blood pressure than the pulmonary artery which arises from the right ventricle, normally. These relationships can change in disease conditions.
Oxygen saturation is measured by withdrawing small samples of blood from the concerned chamber. The samples are analyzed in an equipment known as blood gas analyzer which gives the amount of oxygen in blood as well as other important information. Usually, oxygen levels are lower in the right sided chambers and pulmonary artery and higher in the left sided chambers and aorta. But this can change in birth defects of the heart when the origin of the blood vessels and position of the heart chambers can be abnormal. There could be also mixing of blood from both sides of the heart when there is a defect in the wall between the chambers of the heart. This mixing of blood is called shunts. It could be a left to right shunt, right to left shunt or bidirectional shunt, depending on the type of birth defect.
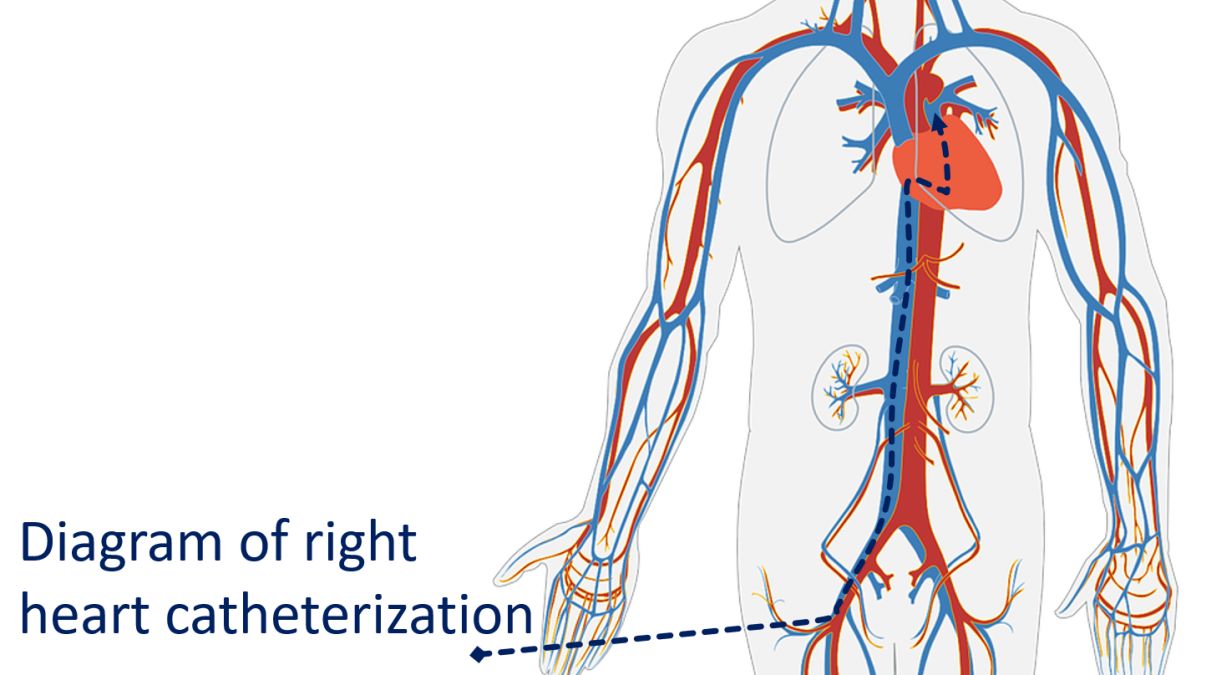
Catheterization of right side of the heart (right atrium, right ventricle and pulmonary artery) is called right heart catheterization. This is done by introducing catheters through the veins, the blood vessels carrying oxygen poor blood to the heart.
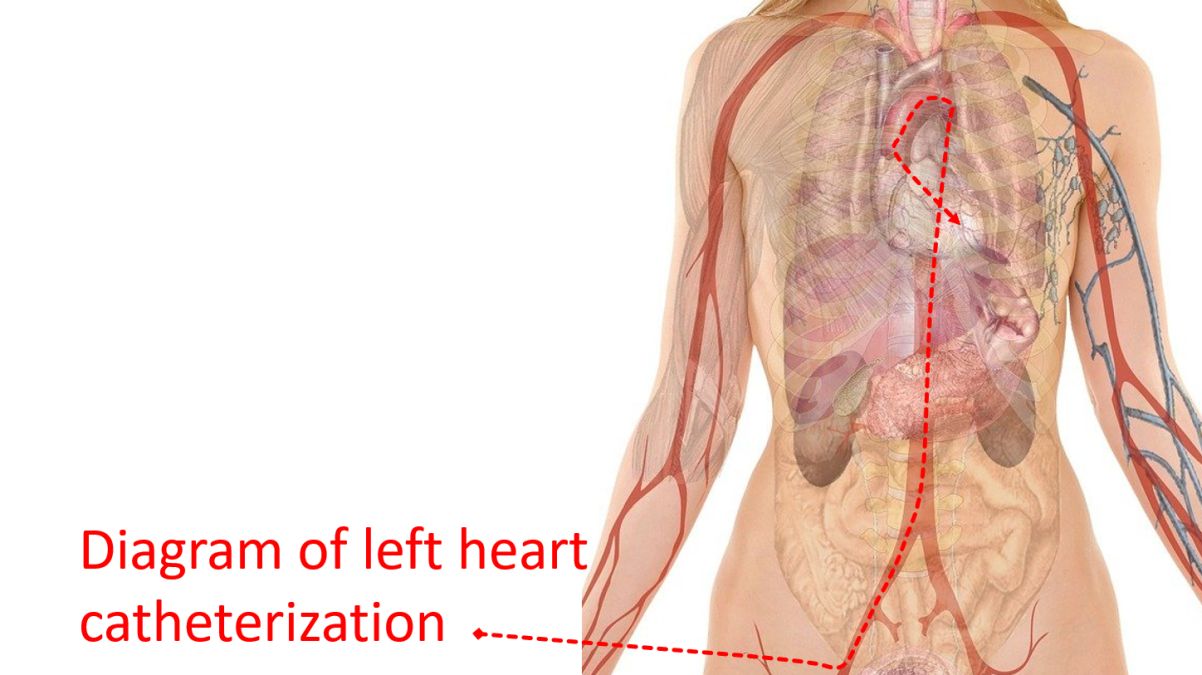
Catheterization of the left side of the heart (left atrium, left ventricle and aorta) is known as left heart catheterization. This is done by introducing catheters into the arteries, the blood vessels carrying oxygenated blood to various parts of the body. In most cases, both are done in the same sitting, often simultaneously. Blood vessels in the groin, arm and neck are chosen for the study. In adults, the test can be done under local anaesthesia. In children, as they are afraid of procedures, general anaesthesia is needed.
A related test known as angiography is also often done along with cardiac catheterization. Angiography is done by injecting radiocontrast medications into the blood vessels or chambers and taking continuous X-ray imaging (cine runs). One of the commonest forms of angiography is coronary angiography, the visualization of blood vessels of the heart. This is used to detect blocks in the blood vessels and to assess their location and severity. Visualization of the lower chambers of the heart by injecting radiocontrast medication is known as ventriculography. Angiogram of the aorta is known as an aortogram. Blood vessels of the lungs are seen on pulmonary angiogram.

