What is left ventricular aneurysm?
What is left ventricular aneurysm?
Left ventricular aneurysm is a bulge in the wall of the lower left chamber of the heart when the rest of it contracts. It is usually seen as a complication to a heart attack. In that heart attack, the blood vessel to the bulging region is totally blocked and there is very little collateral blood supply. The affected region of heart muscle is scarred and thinned out so that it bulges out when the rest of the left ventricle contracts and pressure inside rises.
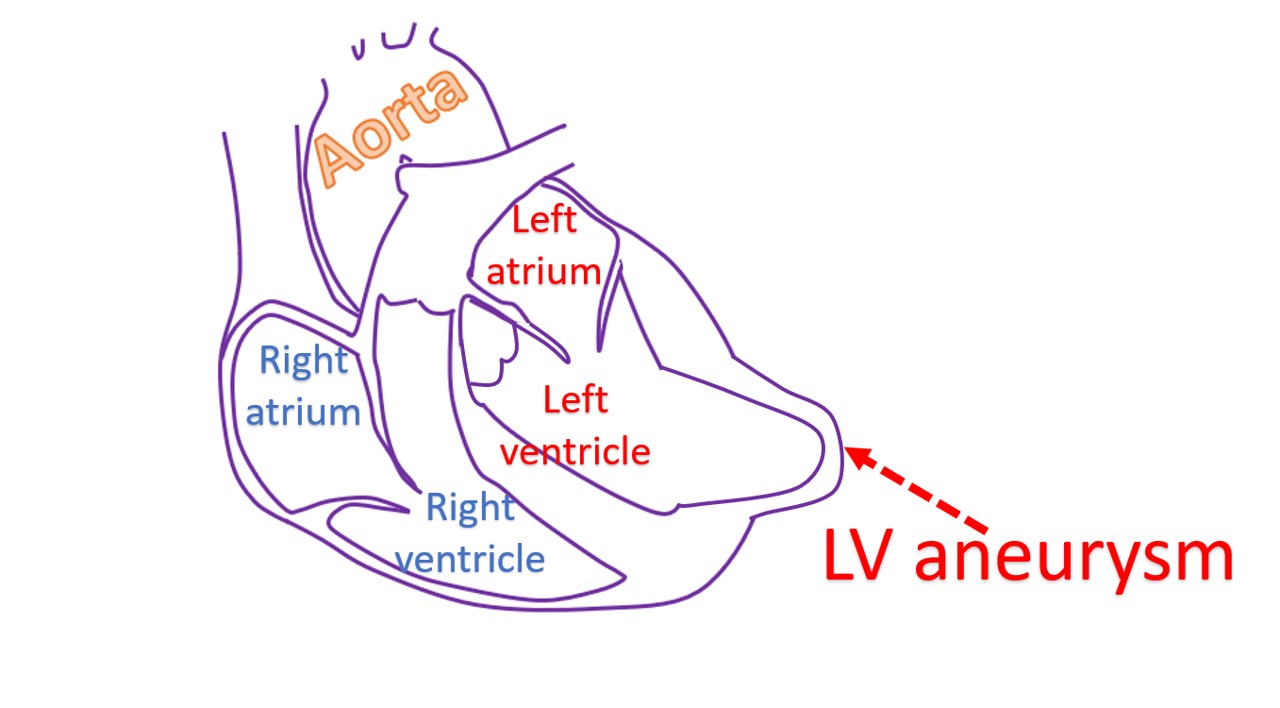
The bulge causes a wastage of the effort of rest of the heart muscle as it bulges out. Hence it can cause heart failure which could be refractory to medical treatment. Blood stagnates in this pouch of the left ventricle and clots can form there. Clots can break off and get carried away by blood circulation. If the break-away clot gets lodged elsewhere, it can cause a block of that blood vessel.
Clots travelling from one region to another through the blood circulation is known as embolism. If the clot is lodged in the blood vessels of the brain, it is known as cerebral embolism and can cause a stroke with weakness of one side. This can be prevented to some extent by giving medications which prevent clot formation known as anticoagulants.
Another problem with aneurysm is that the border zone of the aneurysm with normal muscle contains partially viable muscles. This could be a focus for life threatening heart rhythm disorders (cardiac arrhythmia). Medications can be used to control heart rhythm disorders. Another option is to implant an automatic implantable cardioverter defibrillator (AICD), which detects and automatically treats heart rhythm disorders electrically.
Opening up the blocked vessel supplying the region of the aneurysm or bypassing it may not be very useful as the region is usually irreversibly damaged. Any blood vessel supplying nearby viable heart muscle may be opened up or bypassed. Surgeries are available for the aneurysm, used as a last option sometimes. Medications for prevention of blocks in other blood vessels are routinely needed as secondary prevention.
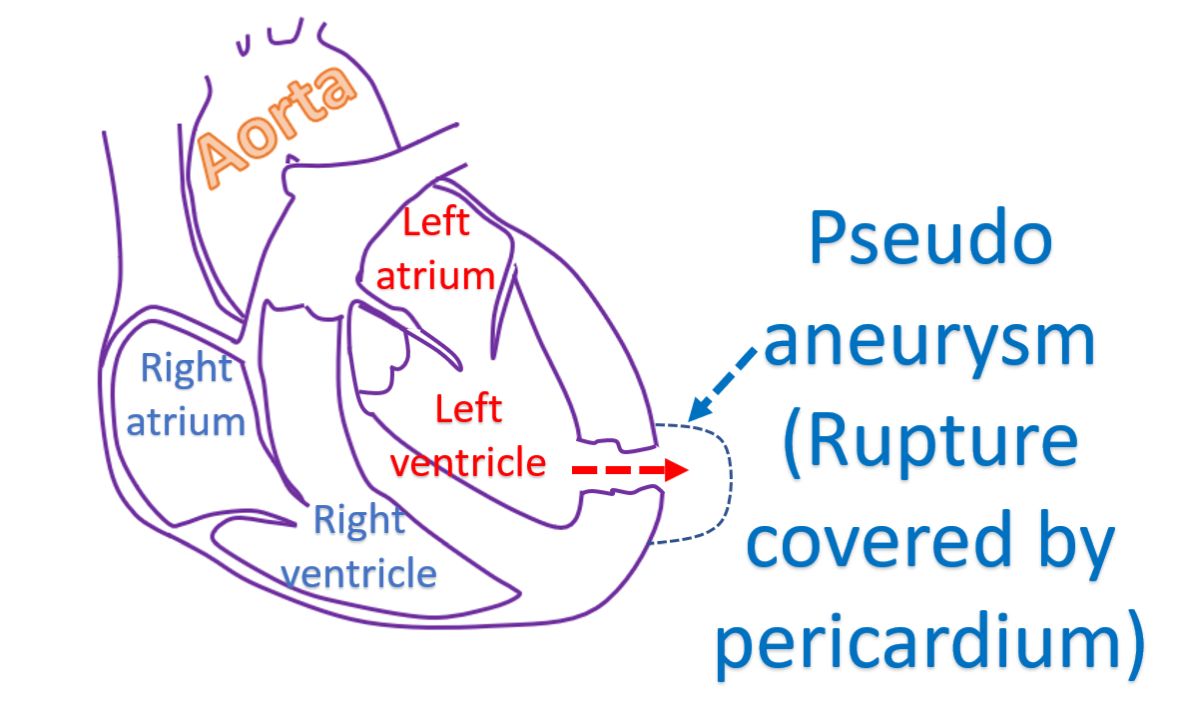
Another related condition is a pseudo aneurysm, which is a very dangerous situation requiring urgent surgery. It is a contained rupture of the left ventricle, which is sealed off by the outer covering called as pericardium. As the pericardium is a very thin structure, a pseudo aneurysm can rupture any time when the heart contracts, leading to a lot of bleeding. Pseudo means false, quite different from the true aneurysm. True aneurysm is very unlikely to rupture.
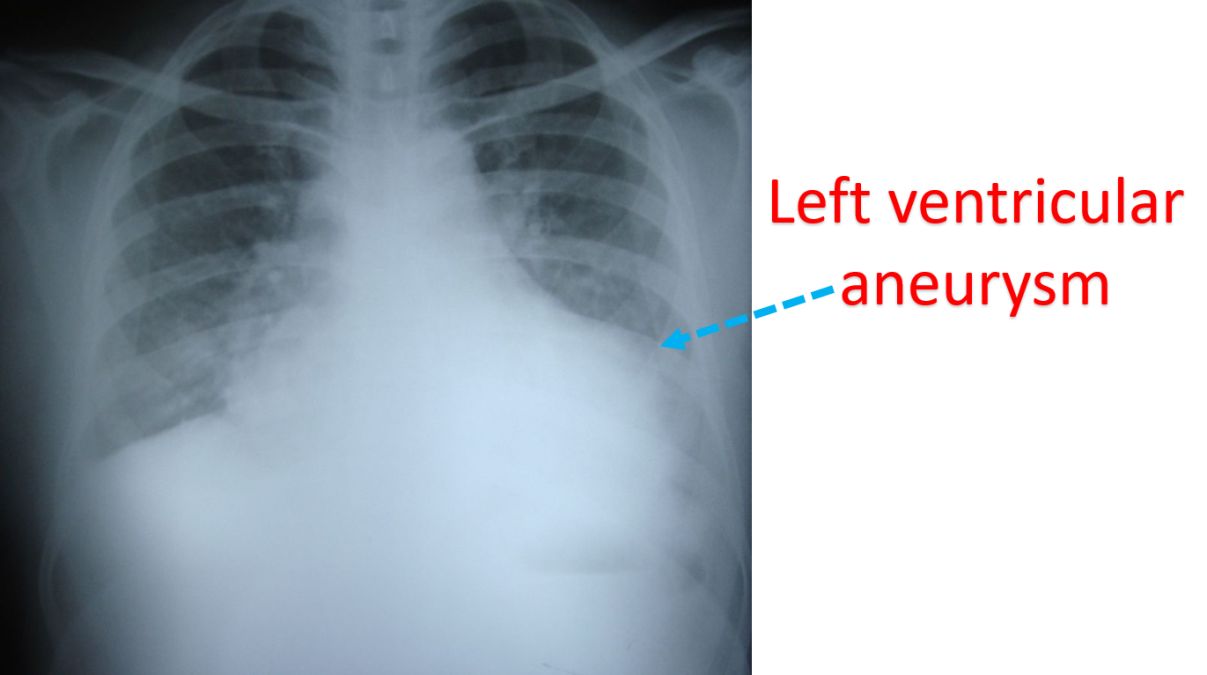
Left ventricular aneurysm will be seen on X-ray as a bulge on the contour of the heart shadow. It can also be identified easily on ultrasound study of the heart known as echocardiography. In earlier era it was documented by injecting radiocontrast medication into the heart and obtaining continuous X-ray imaging, known as left ventriculography, which is seldom needed now. Other imaging modalities like computed tomography (CT scan), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) also can show the aneurysm very well.