What is Takayasu arteritis?
What is Takayasu arteritis?
Takayasu arteritis is an inflammatory disease involving mainly the large blood vessels, usually the aorta and its major branches. Aorta is the largest blood vessel arising from the left ventricle, the lower left chamber of the heart. It has various other names like aortoarteritis and pulseless disease. It is called pulseless disease because upper limb blood vessels are often occluded and the pulses are not easily felt. It can also involve the heart sometimes. Aortoarteritis means inflammation of the aorta. Arteritis means inflammation of arteries, the blood vessels which carry oxygenated blood to the various organs. High blood pressure can be associated, though it may be difficult to document because upper limb blood vessels are blocked.
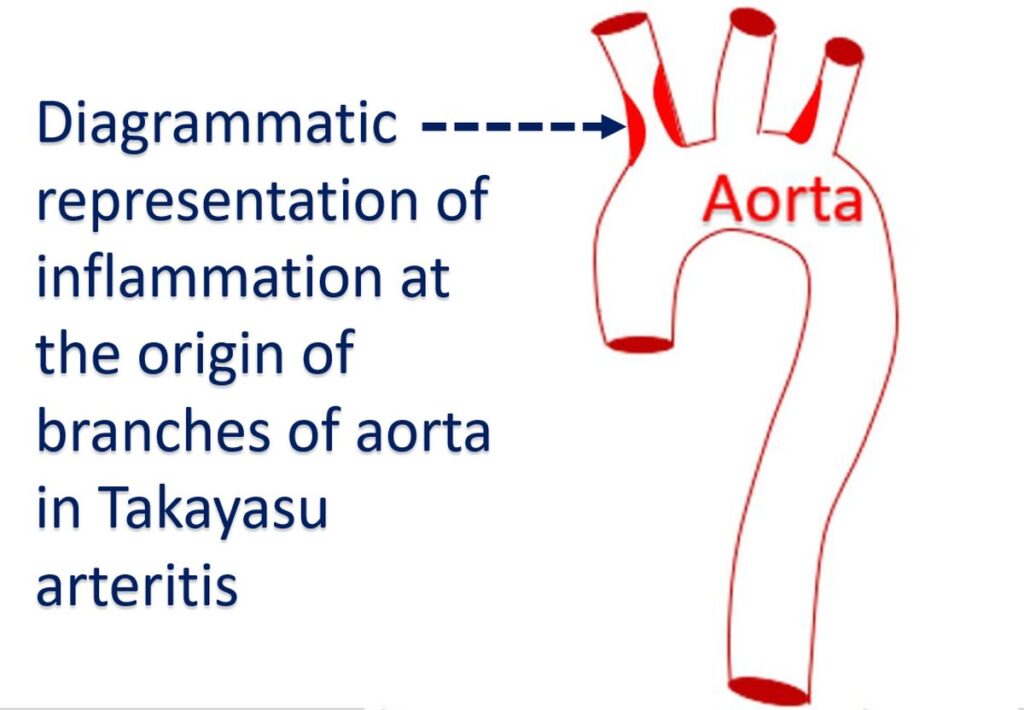
Arteritis leads to thickening of blood vessel wall, scar formation, narrowing of the blood vessel and formation of clots inside the blood vessels. Severe inflammation may weaken the wall of the blood vessel and lead to the formation of localized bulges known as aneurysms. Takayasu was an ophthalmologist (eye specialist), who noted abnormalities in the blood vessels of the eye in a young lady in 1905. Two others noted similar abnormalities and associated absence of pulses at the wrist. That is how the disease came to be known as Takayasu arteritis.
Persons with Takayasu arteritis can have narrowing of multiple blood vessels including that of the kidneys. This is one reason why they can have high blood pressure. Blood vessels of the heart may also be affected. Heart failure has been noted in about a quarter of those with Takayasu arteritis. Narrowing of the blood vessels can be demonstrated by injecting radiocontrast medications into them and taking X-ray images. Narrowing of superficial blood vessels can also be documented by a special ultrasound study known as Doppler evaluation.
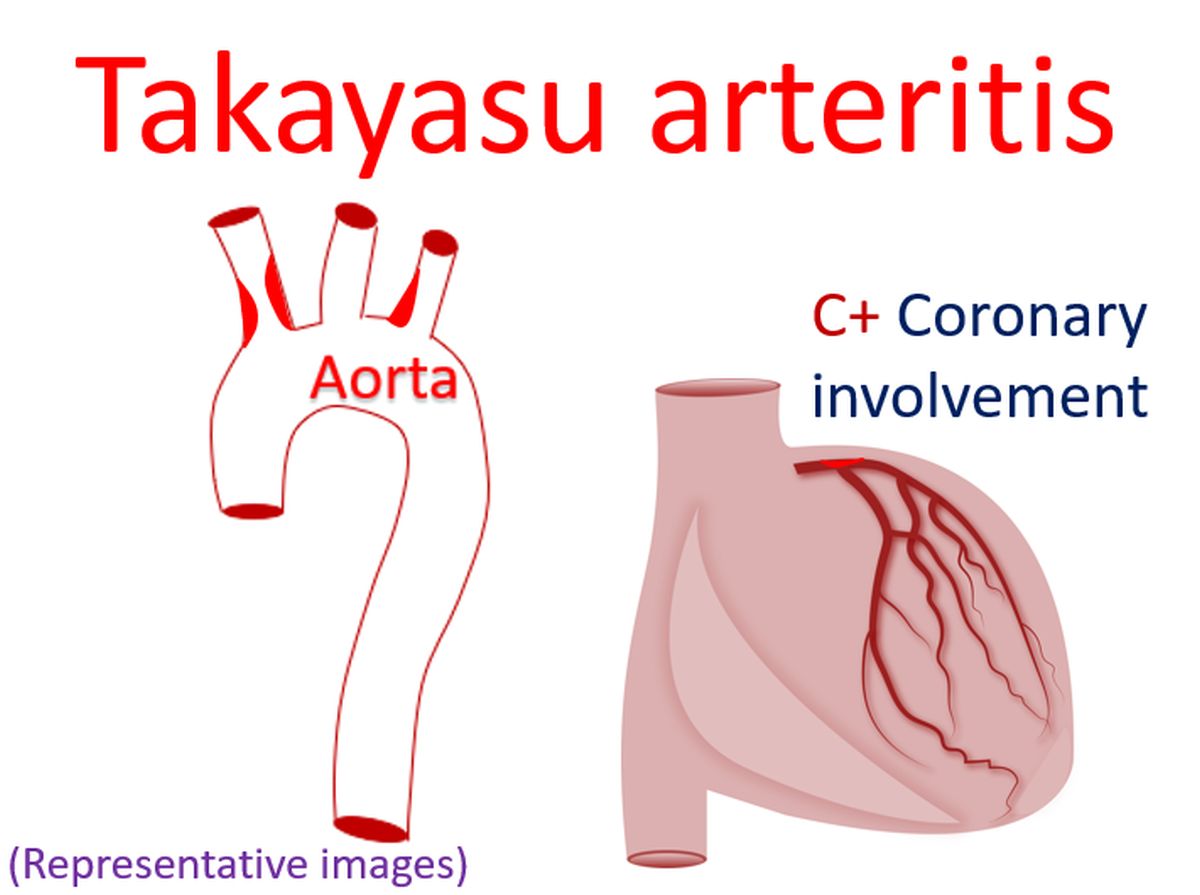
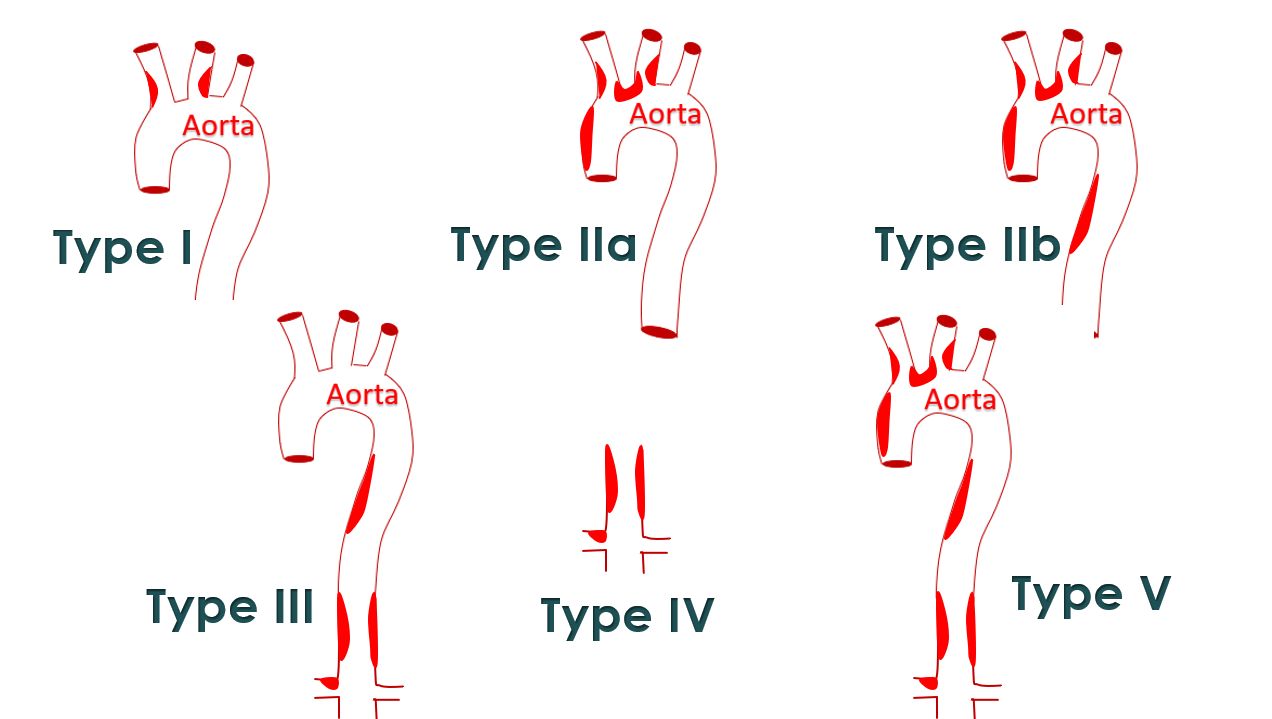
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can also show the involvement of various blood vessels in the body. Blood vessels of the lungs can also be involved in Takayasu arteritis. The disease has been classified into various types based on the extend of involvement of blood vessels noted on angiography. Brain attacks (stroke) can also occur as a complication of Takayasu arteritis. Those with higher number of complications have a lesser survival, as expected.
Another test which is useful in Takayasu arteritis is positron emission tomography (PET). It can be combined with computed tomography (CT) in a test known as PET CT. PET CT can show the extent of involvement of the blood vessels in the body as a whole and show regions which are inflamed. Thus it can assess the extent and activity of the disease. Presence of inflammation shows that the disease is in its active phase.


