What is the difference between dextrocardia and dextroposition?
What is the difference between dextrocardia and dextroposition?
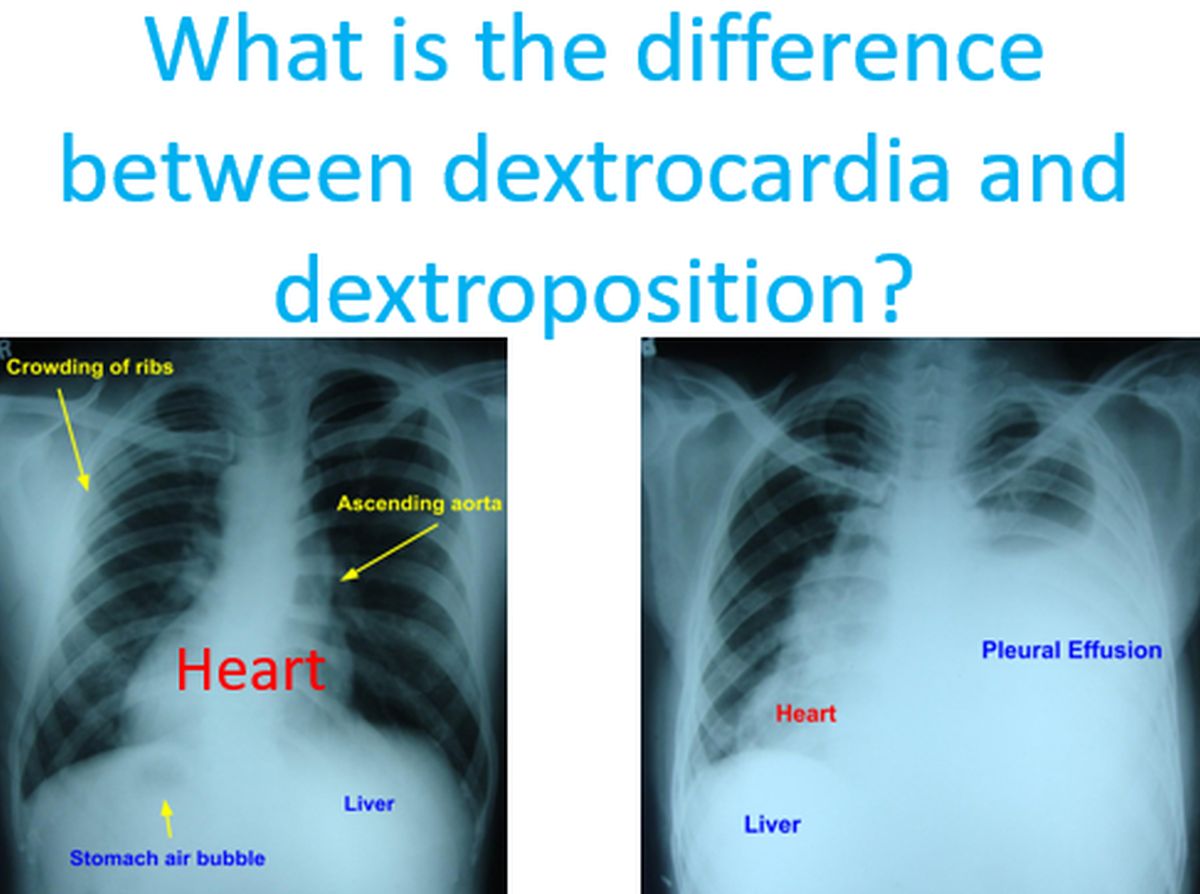
Dextrocardia means heart is situated in the right side of the chest instead of the left, as a birth defect. In dextroposition, the heart is either pushed to the right or pulled to the right by another abnormality, usually in the lungs. Heart can be pulled to the right when the right lung is collapsed due to some reason, leaving more space on the right side of the chest. Here we have two X-rays illustrating dextrocardia and dextroposition. First one is true dextrocardia while the second is dextroposition due to collection of fluid in the left side of the chest, known as pleural effusion.
In the first one, along with the heart, other internal organs have also switched position, in a condition called situs inversus. Stomach is on the right side and the liver is on the left side, the opposite of normal. Location of stomach is usually identified on X-ray by the presence of air in it. It may be noted that while taking X-ray, the body is between the X-ray source and the X-ray film or sensor. This type of dextrocardia is also known as mirror-image dextrocardia as it appears as if viewing in a mirror.
In this chest X-ray, there is massive pleural effusion on the left side pushing the heart to right side producing a dextroposition. Pleural effusion is collection of fluid in the pleural cavity, between the two layers of the covering of the lungs, known as pleura. The liver shadow is on the right side indicating that there is no situs inversus. Stomach air bubble is not visible well in this X-ray. In usual X-rays, air appears as black and fluid appears as white. Hence lungs appear black and heart appears as white. Air transmits X-rays well while fluid reduces transmission of X-rays from the X-ray tube to the X-ray film or sensor in case of modern digital X-rays.



