What is cardiac sarcoidosis?
What is cardiac sarcoidosis?
എന്താണ് കാർഡിയാക് സാർകോയിഡോസിസ്?
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disorder which can involve multiple organs like skin, lymph nodes, lungs, eyes and brain in addition to the heart. Involvement of the heart can occur in about one fourth of those with sarcoidosis. Exact cause of sarcoidosis is unknown though it is thought to have an immunological basis.
Biopsy of the heart using small tubular devices introduced through the blood vessels known as endomyocardial biopsy have been used to confirm cardiac sarcoidosis. But the results are not always positive in clinically suspected cases. Non-invasive tests which can give a clue to the presence of cardiac involvement are positron emission tomographic scanning and magnetic resonance imaging. Elevated blood level of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) is an indicator of sarcoidosis in general. ACE is an enzyme produced mainly in the tiny blood vessels of the lungs.
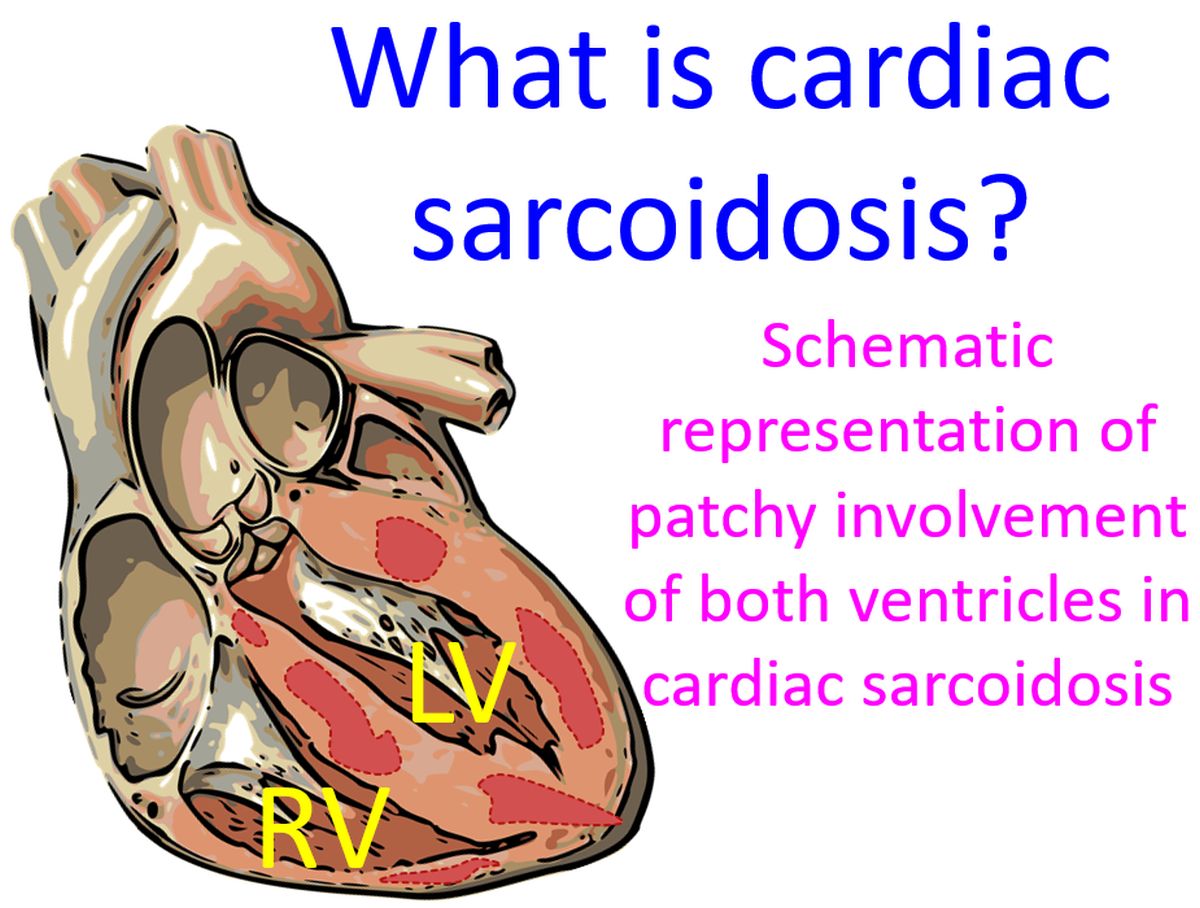
Important manifestations of cardiac sarcoidosis include electrical conduction abnormalities, heart rhythm abnormalities, heart failure and rarely sudden death. Important heart rhythm abnormality is ventricular tachycardia, a dangerous fast rhythm originating from the lower chambers of the heart. Electrical conduction abnormality can cause complete heart block and slow heart rate.
Swelling and inflammation which occur in regions of the heart muscle can cause scarring and act as a focus for the generation of heart rhythm abnormalities. Involvement of the heart and lungs can cause enlargement of the upper chambers of the heart. This in turn can cause abnormal rhythms originating from the upper chambers sometime. One such heart rhythm abnormality is atrial fibrillation, a fast irregular rhythm.
Several medications have been tried for the treatment of sarcoidosis. Corticosteroid group of medications have been in use for a long time, though definite clinical trial data is not available. Due to the multiple potential adverse effects of long term steroid usage like diabetes, obesity and high blood pressure, several other steroid-sparing medications have also been used. But successful reports are mainly in the form of case reports and case series rather than large scale clinical trials.
Permanent pacemakers are useful when the heart rate is unduly slow due to electrical conduction abnormalities of the heart. When there are frequent episodes of fast rhythms from the lower chambers of the heart, implantable cardioverter defibrillator can be life saving. Final option in those with severe damage to heart and lungs due to sarcoidosis could be a heart-lung transplant.


