What is coarctation of aorta?
What is coarctation of aorta?
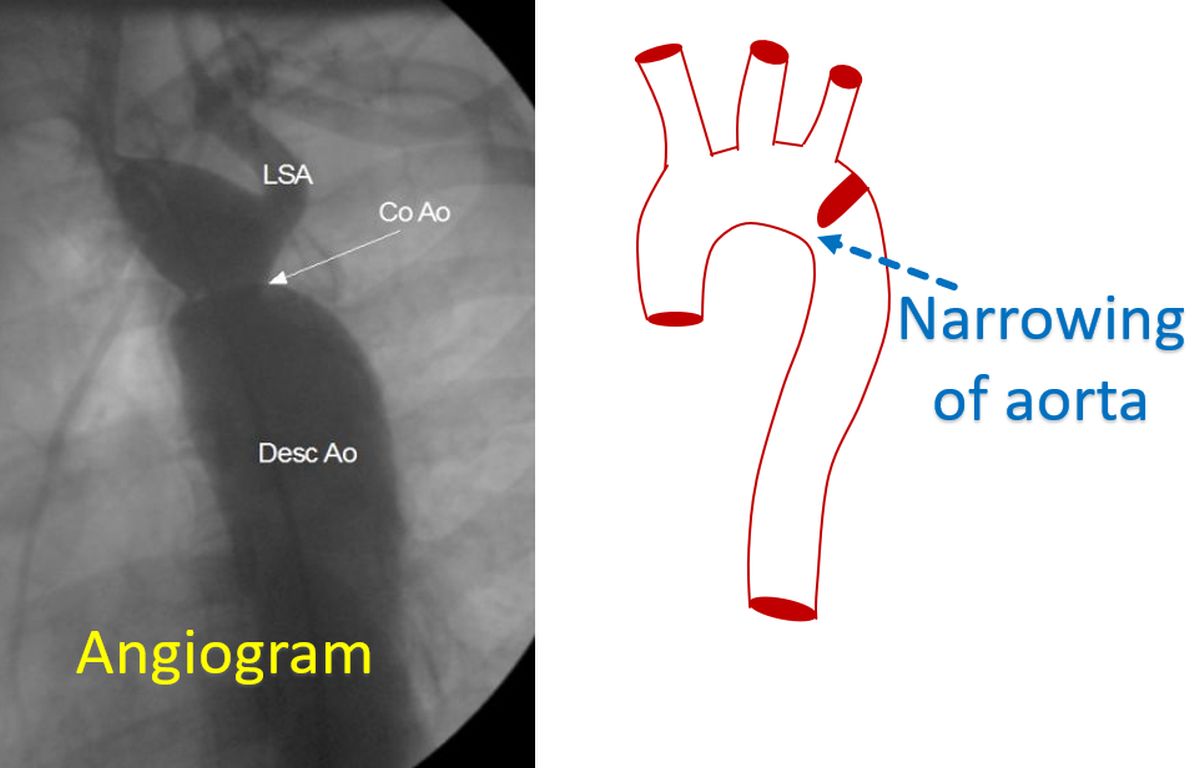
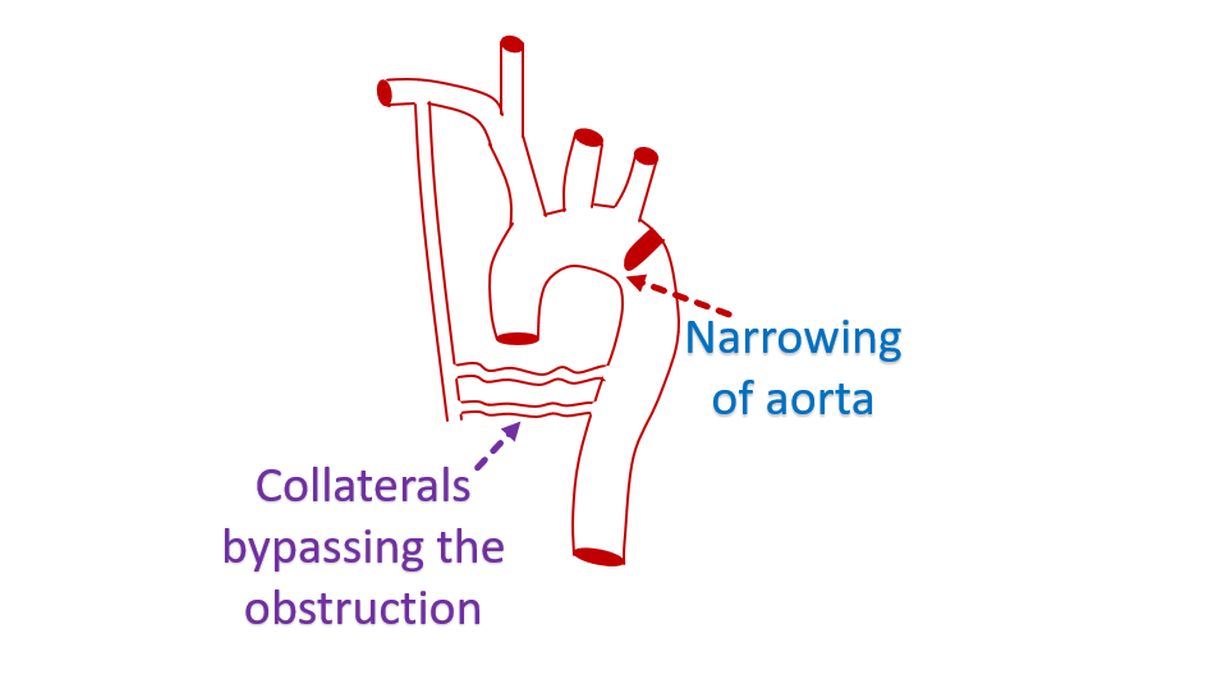
Coarctation of aorta is a birth defect of the aorta, the largest blood vessel supplying oxygenated blood to the whole body. It is a narrowing, which typically occurs at the end of the arch of aorta, after the origin of the blood vessel to the left arm. Occasionally it can occur before the origin of the blood vessel to the left arm as well. In the typical situation when the narrowing is beyond the origin of the blood vessel to the left arm, blood pressure in the upper limbs are much higher than in the lower limbs.
When the blood pressure in the initial part of the aorta is high, it causes resistance to the pumping of the left ventricle which pumps blood to the aorta. Left ventricle is the lower left chamber of the heart. In order to overcome the resistance, the left ventricular muscle gets thickened. Though it is successful in the beginning, in the long run the left ventricle may fail leading to heart failure symptoms.
As coarctation is present at birth, the blood supply to the lower limbs (legs) is lower in severe coarctation of aorta. This can lead on to lower growth in the lower part of the body. In a child coarctation of aorta can be suspected if the pulse in the lower limbs is checked. The pulse is weaker and delayed compared to the upper limbs (arms) due to the obstruction of the aorta.
An important association of coarctation of aorta is the weakening of the blood vessels of the brain which cause them to bulge out. These bulges in the blood vessels of the brain with weakened walls are called berry aneurysms. Berry aneurysms can rupture later and bleed between the coverings of the brain. Sometimes this can result in a stroke as well.
Other associations of coarctation of aorta are bicuspid aortic valve, aortic stenosis, ventricular septal defect and patent ductus arteriosus. Aortic valve at the origin of the aorta normally has three semilunar cusps. If it has only two cusps by birth, it is known as bicuspid aortic valve. Such valves can get narrowed later, and then it is known as aortic stenosis. Ventricular septal defect is a hole in the wall between the lower chambers of the heart.
Patent ductus arteriosus is a connection between the aorta and the pulmonary artery. Pulmonary artery is the blood vessel carrying blood to the lungs for oxygenation. Usually the ductus arteriosus, a connection between the aorta and pulmonary artery which is normally present in all individuals while in the womb closes off soon after birth. If it does not close, it is called patent ductus arteriosus.
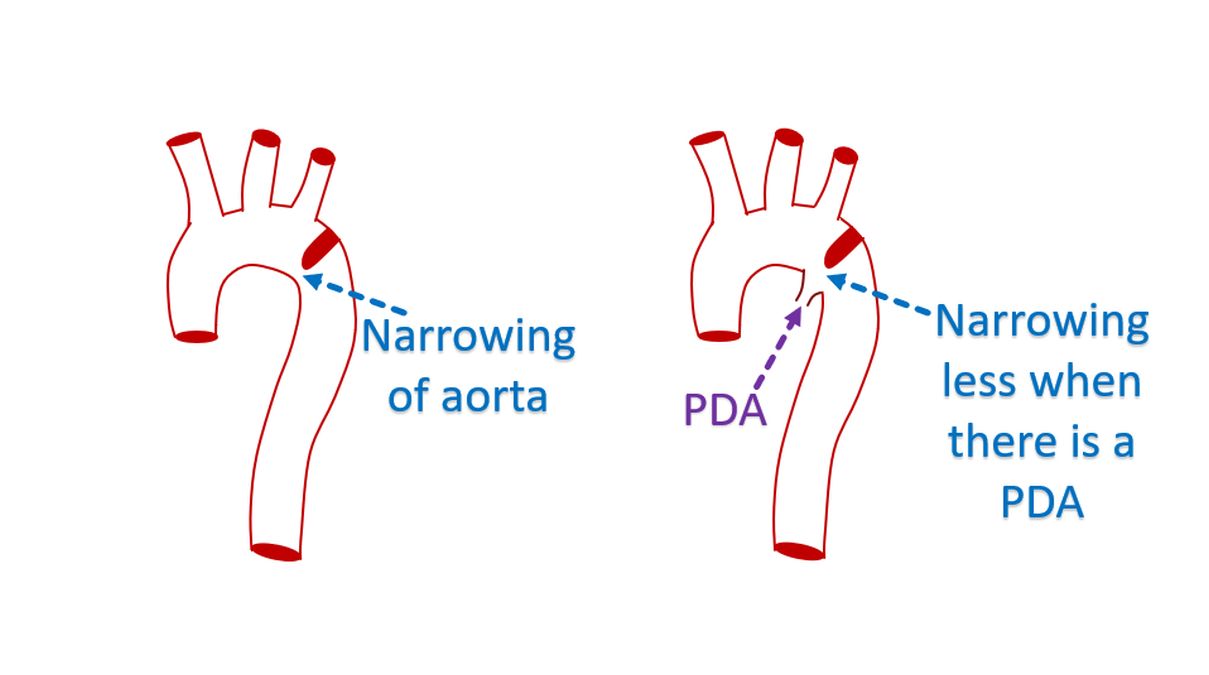
When a patent ductus arteriosus joins the aorta just at the region of the coarctation, assessment of coarctation may be erroneous. This is because part of the patent ductus arteriosus also helps in the blood flow. If the patent ductus arteriosus closes after some time, the coarctation appears to have rapidly worsened.
Coarctation of aorta can cause development of collateral blood flow the lower part of the body through circuitous routes. This causes enlargement of the blood vessels over the back of the chest, which may be felt as pulsations in the back. When large number of collaterals are present, the volume of pulse in the lower limbs may improve, though they are still delayed because of the circuitous route of blood flow.
Simplest way of detecting a coarctation of aorta is by checking the pulses in the groin and comparing them with those in the arm. The difference in pulse volume can be documented better by recording the blood pressure in upper and lower limbs. The lower limb blood pressure is usually higher in normal individuals. But in coarctation of aorta, it is significantly lower than in upper limbs. This is one of the reasons why it is taught that in the initial examination of high blood pressure, blood pressure in the lower limbs should be checked.
Initial tests done in coarctation of aorta includes ECG, X-ray of chest and echocardiogram. ECG is the electrical recording of the heart which can show evidence of thickening of the left ventricle in coarctation of aorta. X-ray of chest can show enlargement of the heart and notching of the ribs. Notching of the ribs occur due to the pressure from the collateral blood flow. Echocardiogram will show thickening of the left ventricle as well as the narrowing of the aorta. The pressure gradient across the narrowing can be measured by Doppler echocardiogram, an additional mode available in all echo machines.
The narrowing of the aorta can be further documented by an angiogram in which cine X-ray imaging is done after injecting a radiocontrast material into the aorta. Another mode of imaging is computed tomography (CT scan). CT scan obtained after injecting contrast medication will visualize the coarctation well. In addition it will show the collateral blood vessels in great detail and is useful in planning treatment.
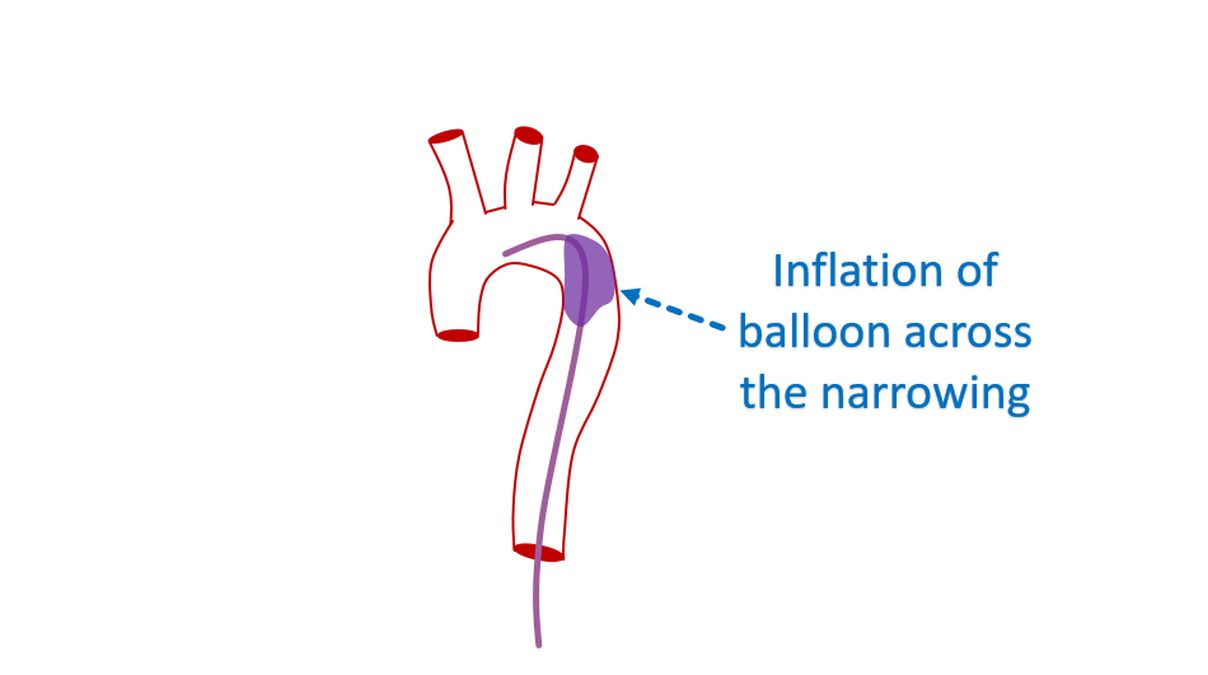
High blood pressure if present will be treated with medications. But a significant narrowing of the aorta has to be corrected to prevent long term damage. The narrowed region can be repaired by surgery. Enlarging the narrowed segment using a balloon catheter and implanting a stent is another option. Balloon catheters are small tubes with a sturdy balloon at the tip, introduced through the blood vessel of the groin. Balloon placed across the narrowed segment can be inflated to relieve the obstruction. Stent is a spring like metallic device which is implanted after expanding the narrowed segment to prevent recoil.