What is cryoablation?
What is cryoablation?
Cryoablation is a method used to treat heart rhythm disorders by freezing the abnormal region using a cryoprobe at the tip of the cryocatheter. While radiofrequency ablation (RF ablation) removes an abnormal region or pathway by heating up the cells, cryoablation does the same by cooling the cells to sub-zero temperature. Currently the cryocatheter is much more expensive than the radiofrequency ablation system and is not as widely available.
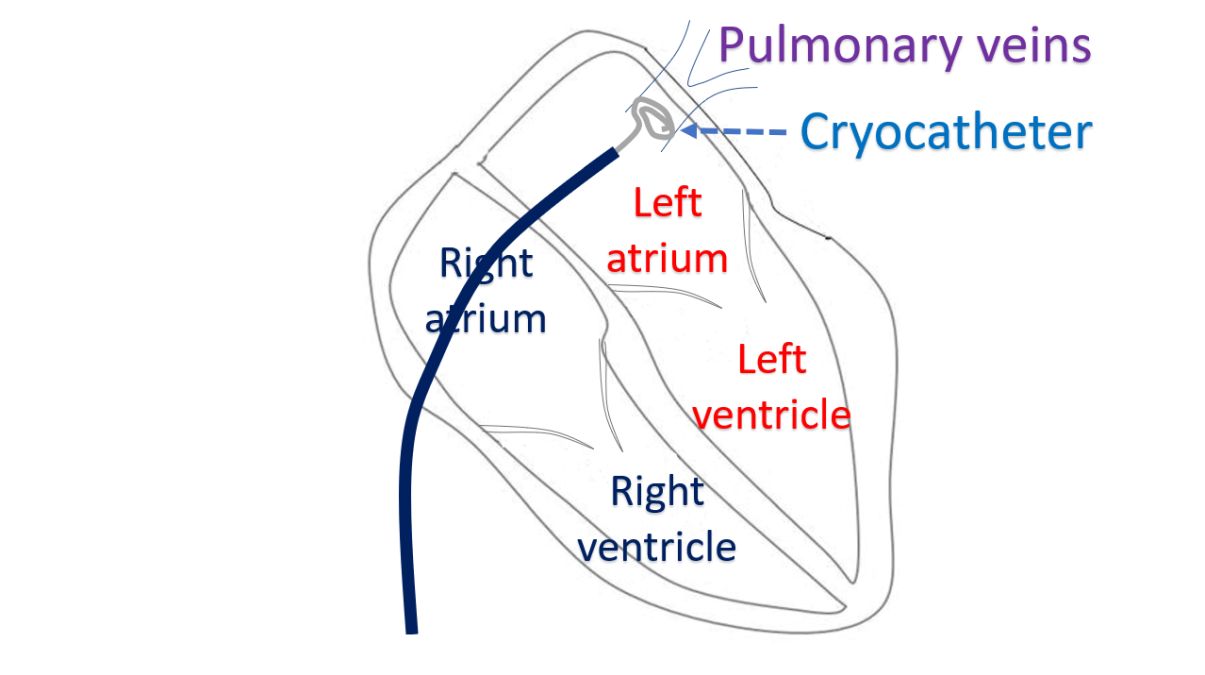
The advantage of cryoprobe is the reversibility while treating abnormalities near to critical heart structures. Initial slow and partial cooling, typically to – 30°C for 80 seconds blocks the electrical conduction and helps to assess whether the treatment will be effective and whether any nearby critical structure will be damaged. If any collateral damage is detected, all you have to do is to rewarm to undo the damage done.
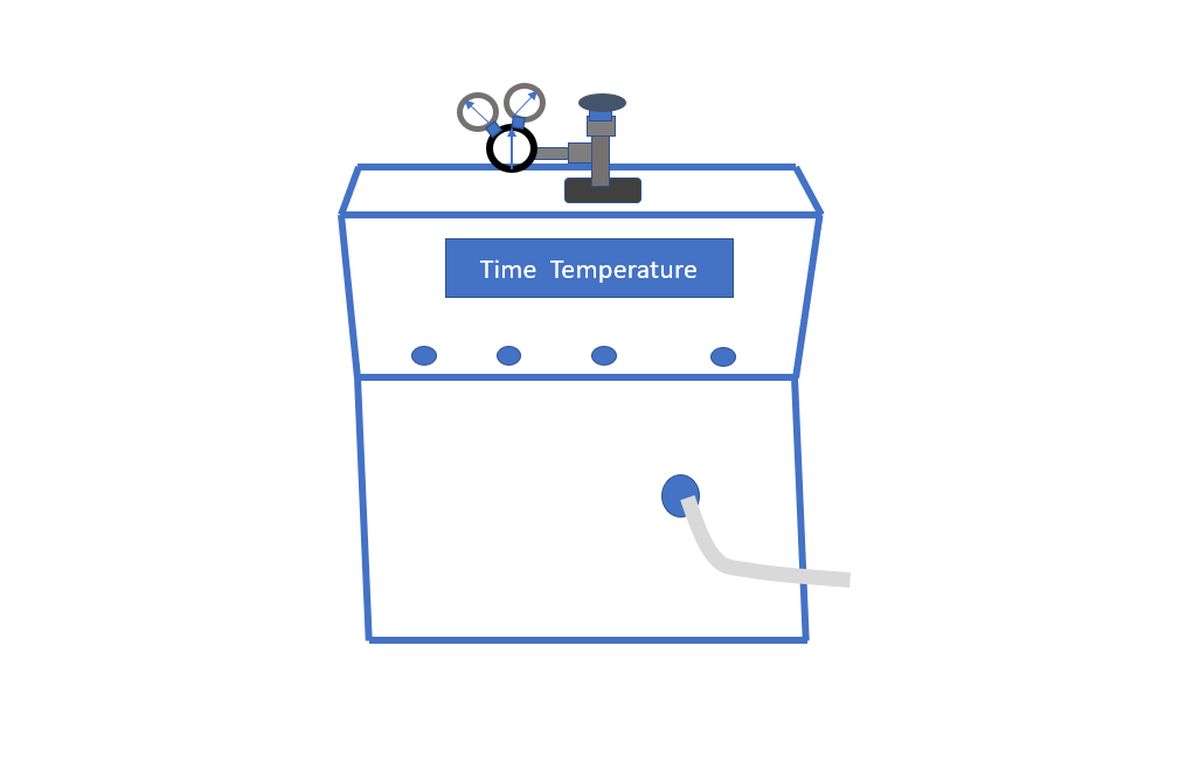
The cooling console for the cryocatheter is placed near the procedure table and connected to the cryocatheter using tubes. Tank of liquid nitrous oxide used for cooling is located in the console. The nitrous oxide returning from the cryocatheter is removed by a scavenging hose into the vacuum system of the procedure room.
If no collateral damage is detected, further faster cooling, typically to –75°C for up to 480 seconds produces a permanent treatment effect. Though the chance for collateral damage is less, the efficacy also may be a little lower than radiofrequency catheter ablation because of the slightly higher chance for recurrence. It may be noted like radiofrequency ablation, cryoablation is also used in other disciplines like cancer therapy.
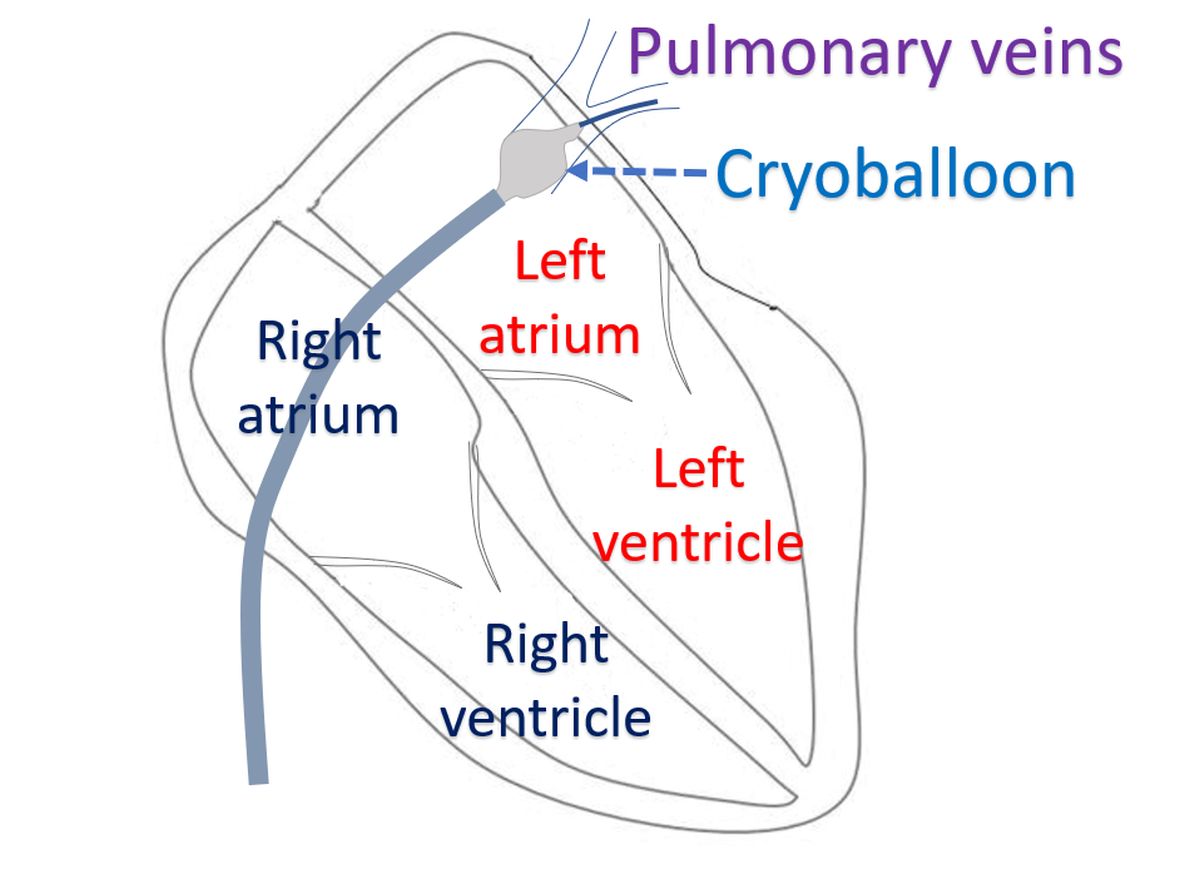
Cryoballoon ablation is a special type of cryoablation in which instead of the usual cryocatheter, a cryoballoon is used for circular cooling. While doing ablation in pulmonary veins for atrial fibrillation, cryoballoon ablation avoids missing of abnormal regions. Pulmonary veins are blood vessels returning oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium. Left atrium is the left upper chamber of the heart. Atrial fibrillation is an irregular fast rhythm of the heart originating from the upper chambers. Recurrent episodes of atrial fibrillation can be initiated by abnormal electrical activity near the opening of the pulmonary veins into the left atrium. This abnormal electrical activity can be abolished by freezing with cryoballoon. As the cryoballoon produces uniform cooling around the opening of the pulmonary vein, the chance for missing a region of abnormal electrical activity is less. Moreover, it is more convenient as multiple ablations using a conventional cryoprobe is not needed.
Atrial fibrillation is the commonest sustained heart rhythm abnormality and the chance for atrial fibrillation increases as age advances. In atrial fibrillation, the upper chambers cannot contract properly, leading to local stagnation of blood and clot formation. These tiny blood clots in the upper chambers can break off and get carried by the blood stream. If these clots get lodged in the blood vessels of the brain, a stroke with weakness of one side of the body can occur.



