What is ETCO2 monitoring?
What is ETCO2 monitoring?
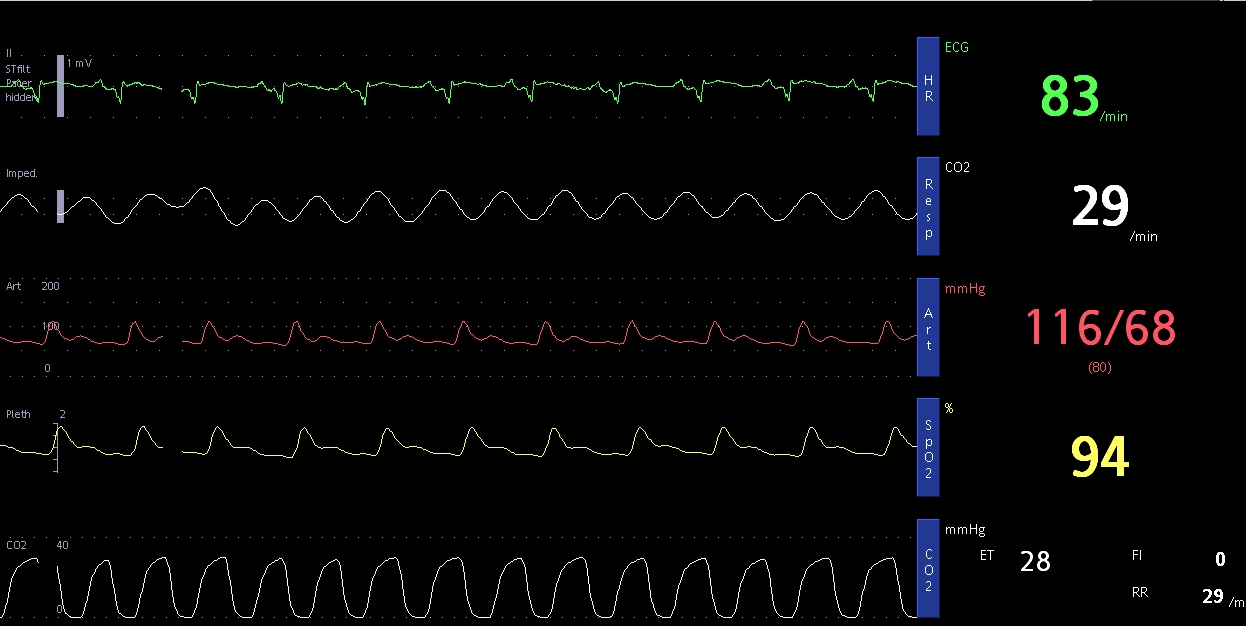
End tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO2) is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (CO2) in exhaled air at the end of expiration. In simple terms, it measures the carbon dioxide content in the air which is breathed out. Carbon dioxide monitoring is also known as capnography. The graphical representation of CO2 is known as capnogram. In the monitor screenshot shown above, the capnogram is at the bottom. Here the ETCO2 is shown as 28 mm Hg.
Respiratory rate (breathing rate) drawn from the capnography is 29/min. Top most tracing is the electrocardiogram (ECG), which shows normal sinus rhythm at 83/min. Invasive blood pressure monitoring, using a small tube inserted into the blood vessel at the wrist shows a blood pressure of 116/68 mm Hg. The remaining tracing is of pulse oximetry which shows an oxygen saturation of 94%.
Capnography is useful after endotracheal intubation (putting a tube in the wind pipe) to confirm the position of the tube in the trachea (wind pipe) and is used routinely in most modern centres in the emergency department. A tube is put in the wind pipe for giving artificial breaths either using a bag and mask or with a breathing machine (ventilator). It could also be used to give anesthetic agents to the lungs.
ETCO2 monitoring is common place in the operating room and most of the state-of-the-art intensive care units. Capnography provides instantaneous information on ventilation, blood flow into the organs and cellular respiration, all of which are important in maintaining ETCO2 values in the normal range. Hence ETCO2 monitoring is also useful in assessing the effectiveness of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is given as emergency care for a person whose heart has suddenly stopped beating (cardiac arrest).



