What is Ross procedure?
What is Ross procedure?
Ross procedure is done for the treatment of aortic valve disease. Aortic valve is the valve between the aorta and left ventricle. Left ventricle is the lower muscular chamber of the heart which pumps blood to the whole body. Aorta is the great vessel arising from the left ventricle, which takes blood to the whole body. Ross procedure was initially used in children and later in adults as well. In Ross procedure, pulmonary valve along with a part of the main pulmonary artery is taken and used instead of the damaged aortic valve (pulmonary autograft for aortic position). Pulmonary valve is the valve between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery. Right ventricle is the lower muscular chamber of the heart which pumps blood to the lungs for oxygenation. Pulmonary artery takes this blood to the lungs.
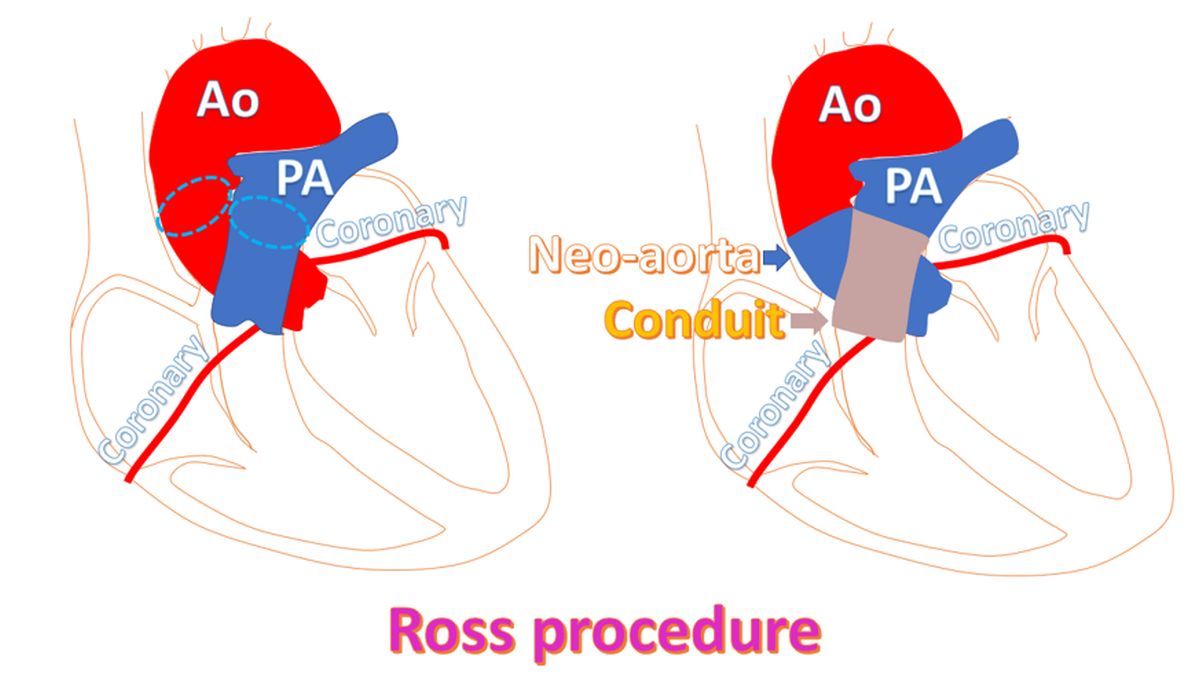
Another valve obtained from a deceased donor or an animal valve (cryopreserved homograft or xenograft) is placed in the position of the pulmonary valve. Sometimes a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) conduit is used in the pulmonary position to bridge the gap produced by removal of a part of the pulmonary artery. The advantage of the autograft in children is that it would grow in size as the child grows, unlike an artificial valve (prosthetic valve). A study has reported 90.7% ten year survival after Ross procedure in adults.
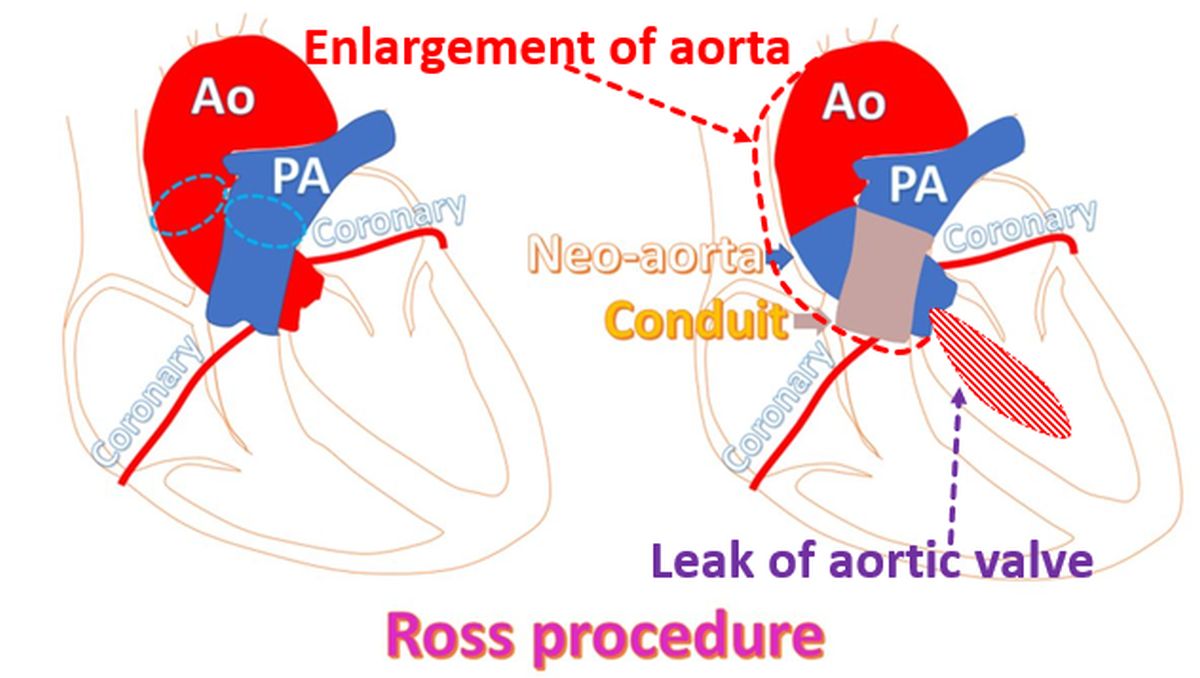
Aorta can enlarge and produce a leak in the aortic valve in some cases in the long run, after Ross procedure. Xenografts taken from animals are more likely to fail than cryopreserved homografts (human valve from a deceased donor) in the pulmonary position. But the availability of homografts is often limited in most centers. Freedom from pulmonary valve reoperation at 15 years was 100% with homografts while it was around 80% with stentless xenografts.
Long term freedom from stroke or major bleeding episodes was better after Ross procedure compared to mechanical aortic valves. This is because clots can form on mechanical valves and they need long term medications to prevent clots. Clots on the valve can break off and travel along blood circulation to block blood vessels elsewhere. Hence they are prone for strokes by blocks in brain blood vessels and bleeds due to the medication used to prevent clots.

