Alcohol Ablation of Vein of Marshall for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
Alcohol Ablation of Vein of Marshall for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
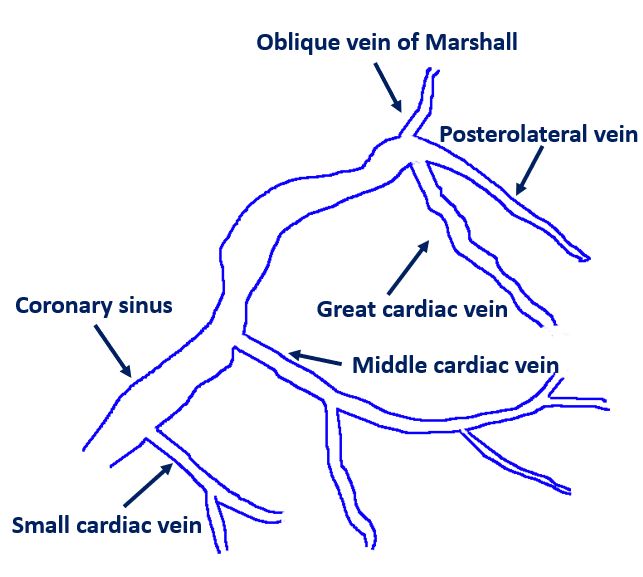
Vein of Marshall (VOM) is a tributary of the coronary sinus with abundant sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation. It has been implicated in the genesis and maintenance of atrial fibrillation (AF). Three reasons described are the myocardial extensions into the structure, node like remnants within the vein and the rich autonomic innervation surrounding it [1] It is anatomically related to the mitral isthmus. Mitral isthmus is the region between the left inferior pulmonary vein ostium and the mitral annulus. Oblique vein of Marshall is the residua of the embryonic left superior cardinal vein [2].
Though pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) is effective in the treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, the role in persistent atrial fibrillation is suboptimal [3]. A common form of ablation failure is recurrence as peri-mitral flutter. VOM is in the re-entrant circuit of peri-mitral flutter and VOM ablation can abolish peri-mitral flutter. Effect on sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation is another important aspect of VOM ablation.
VENUS (Vein of Marshall Ethanol for Untreated Persistent AF) trial enrolled patients undergoing their first catheter ablation for AF, while MARS-AF enrolled patients undergoing ablation after previous ablation failure. Both were National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) funded randomized controlled trials. The trials were to test the safety and efficacy of VOM ethanol infusion added to PVI in patients undergoing either de novo ablation of persistent AF or after a previous ablation failure.
VENUS trial was a single-blinded trial conducted in 12 centers in the United States [4]. 158 patients were assigned to catheter ablation alone and 185 patients to combined catheter ablation with VOM ethanol infusion. Higher number of patients were randomized to VOM ethanol infusion to accommodate for the possibility of 15% technical failure. VOM procedure was done prior to catheter ablation. VOM was identified by coronary sinus venography. If the vein of Marshall was present, the vein was cannulated with an angioplasty wire and over-the-wire balloon. Ethanol infusion was given distal to an inflated balloon. A bolus injection can reach the left atrium. One ml of 98% ethanol was delivered over 2 minutes. Up to 4 infusions from distal to proximal were given depending on the size of VOM. After ethanol injection, a repeat voltage map was obtained to identify the ethanol induced scar.
VOM ethanol infusion was successfully delivered in 155 of the 185 patients. Freedom from AF/atrial tachycardia was 49.2% in VOM plus catheter ablation group vs 38% in catheter ablation alone group. The assessment was based on absence of these events on monitoring at 6 months and 12 months.
Vein of Marshall Alcohol in Repeat Ablation of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation (MARS-AF) trial did not show significant benefit in those with previous failed AF ablation [5]. There were 80 patients across 11 centres in this trial.
References
- Habib A, Lachman N, Christensen KN, Asirvatham SJ. The anatomy of the coronary sinus venous system for the cardiac electrophysiologist. Europace. 2009 Nov;11 Suppl 5:v15-21.
- Harikrishnan S, Nair K, Tharakan J. Oblique vein of Marshall. Heart. 2005 Feb;91(2):e16.
- Valderrábano M, Peterson LE, Bunge R, Prystash M, Dave AS, Nagueh S, Kleiman NS. Vein of Marshall ethanol infusion for persistent atrial fibrillation: VENUS and MARS clinical trial design. Am Heart J. 2019 Sep;215:52-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2019.04.022. Epub 2019 May 11. PMID: 31279972; PMCID: PMC6692654.
- Valderrábano M, Peterson LE, Swarup V, Schurmann PA, Makkar A, Doshi RN, DeLurgio D, Athill CA, Ellenbogen KA, Natale A, Koneru J, Dave AS, Giorgberidze I, Afshar H, Guthrie ML, Bunge R, Morillo CA, Kleiman NS. Effect of Catheter Ablation With Vein of Marshall Ethanol Infusion vs Catheter Ablation Alone on Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: The VENUS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2020 Oct 27;324(16):1620-1628. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.16195. PMID: 33107945; PMCID: PMC7592031.
- Adi Lador, Miguel Valderrabano. Vein of Marshall Alcohol in Repeat Ablation of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation (MARS-AF). Heart Rhythm 2021; 18(8 supplement): S398.