Amiodarone and thyroid – Wolff-Chaikoff effect and Jod-Basedow phenomenon
Amiodarone and thyroid – Wolff-Chaikoff effect and Jod-Basedow phenomenon
It is well known that amiodarone, a commonly used anti-arrhythmic drug can cause thyroid dysfunction due to its iodine content. Now what are Wolff-Chaikoff effect and Jod-Basedow phenomenon in this connection? Hypothyroidism is mediated by the Wolff-Chaikoff effect and hyperthyroidism by Jod-Basedow effect [1].
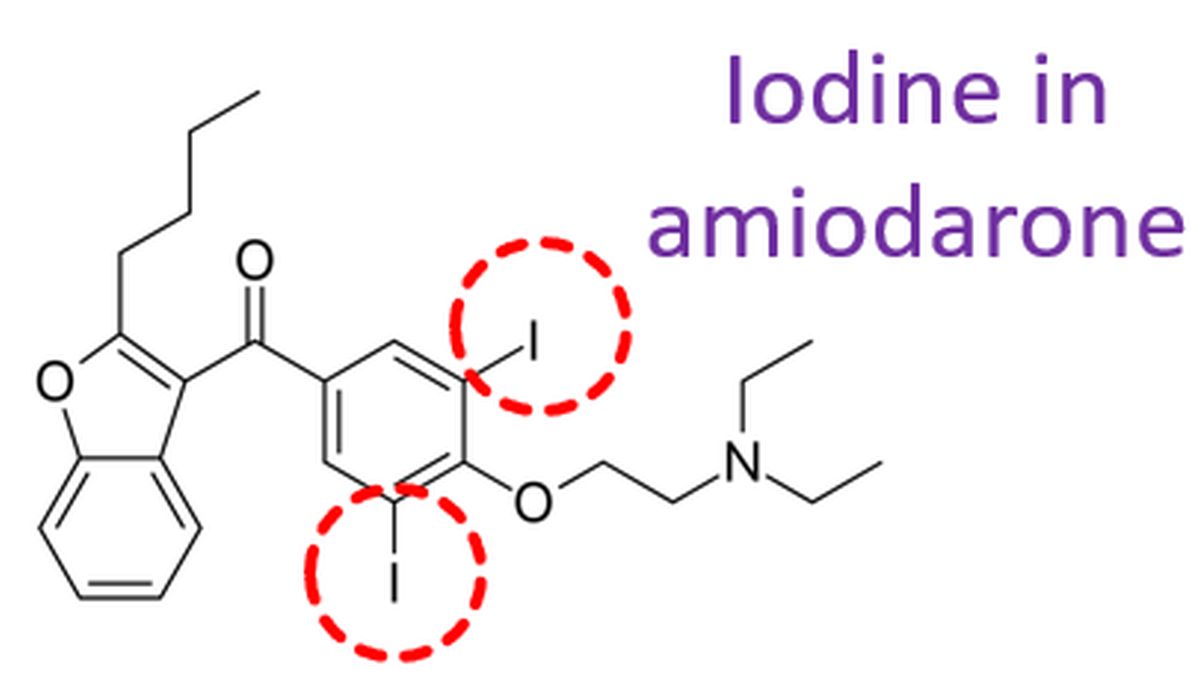
Iodine is an essential for the synthesis of thyroid hormone and amiodarone has a high iodine content. Thyroid gland has the mechanism to handle iodine efficiently when the availability of iodine is scarce as well as when iodine is available in excess. Thyroid can acutely inhibit organification of iodine by the acute Wolff-Chaikoff effect. It has been proposed that iodopeptides are formed that temporarily inhibits thyroid peroxidase (TPO) mRNA and protein synthesis and, thereby thyroglobulin iodination. Thus Wolff-Chaikoff effect is a means of rejecting iodine when large quantities are given and thereby preventing the thyroid from synthesizing large quantities of thyroid hormones. The acute Wolff-Chaikoff effect lasts for few a days and then an escape from this effect can occur so that organification of iodine resumes leading to normal synthesis of thyroid hormones [2]. Wolff–Chaikoff effect has been used as a treatment principle against hyperthyroidism, especially for thyroid storm, by infusion of a large amount of iodine to suppress the thyroid gland.
Jod-Basedow phenomenon occurs due to either overactivation of the entire thyroid gland or, more often, autonomous nodules within the gland after iodine repletion. This escape from the protective Wolff-Chaikoff effect is called the Jod-Basedow phenomenon [1]. This can occur naturally when persons with endemic goiter due iodine deficiency relocate to iodine abundant geographic areas. Same effect can occur with administration of iodinated contrast and amiodarone. Jod–Basedow hyperthyroidism usually develops in 2 to 12 weeks after iodine exposure as iodine is used as a substrate for new thyroid hormone synthesis. It typically occurs in persons with nodular goiter, the elderly among whom the prevalence of nodular goiter is high and in people living in areas of iodine deficiency [3].
References
- Vargas-Uricoechea H, Sierra-Torres CH. Thyroid hormones and the heart. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2014 Apr;18(1):15-26. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2013-0059. PMID: 25389997.
- Markou K, Georgopoulos N, Kyriazopoulou V, Vagenakis AG. Iodine-Induced hypothyroidism. Thyroid. 2001 May;11(5):501-10. doi: 10.1089/105072501300176462. PMID: 11396709.
- Dunne P, Kaimal N, MacDonald J, Syed AA. Iodinated contrast-induced thyrotoxicosis. CMAJ. 2013 Feb 5;185(2):144-7. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.120734. Epub 2012 Nov 12. PMID: 23148056; PMCID: PMC3563887.

