Atrial flutter
Atrial flutter
Atrial flutter is an organized atrial tachyarrhythmia due to macro re-entry typically with saw tooth shaped flutter waves in the ECG. Atrial flutter can be classified into isthmus dependent and non-isthmus dependent. In the right atrium it is the cavotricuspid isthmus. In the left atrium there is mitral isthmus.
Non isthmus dependent flutters are the scar related flutters and caval mediated flutters. Isthmus dependent flutter can be typical and reverse typical depending on whether the re-entry is counter-clockwise or clockwise.
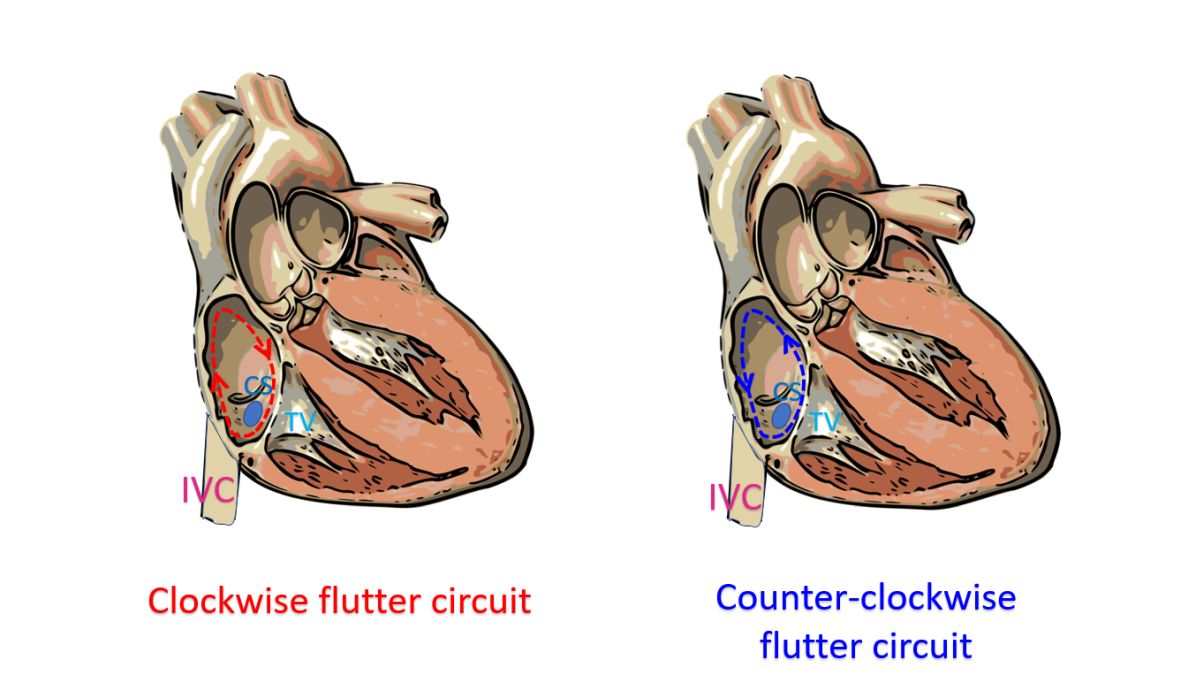
The direction of the less sharp component of the flutter wave is taken as the direction of the wave. If the waves are positive in inferior leads, it is clockwise loop and if negative, the re-entry loop is counter-clockwise.
Atrial flutter is usually associated with a fixed ratio AV block. If there is 1:1 conduction, the ventricular rates will be very high. A typical situation of atrial flutter is with 2:1 conduction, atrial rate of 300/min and ventricular rate of 150/min. Hence a narrow QRS tachycardia with a rate of 150/min, which appears to be SVT is likely to be atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction.
Close scrutiny of the baseline for saw-tooth like flutter waves, especially in the inferior leads is needed to exclude atrial flutter. Since atrial flutter is due to a macro re-entry, it is the arrhythmia which is most sensitive to cardioversion at low energies. Carotid sinus massage is useful in bringing out a diagnosis of atrial flutter because the increase in the grade of AV block makes the flutter waves more evident. Similar effect can be obtained with adenosine.
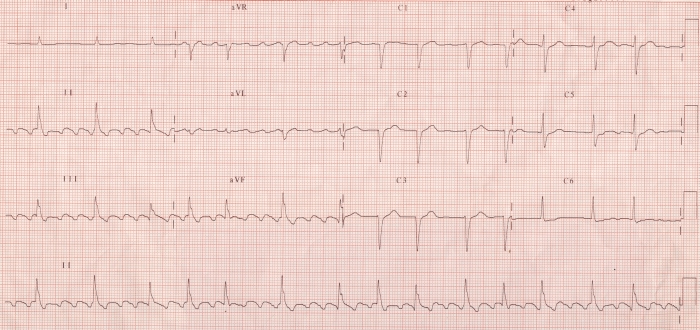
ECG showing atrial flutter with varying conduction (4:1 and 3:1). The flutter waves are seen at a rate of around 300 minute and ventricular rate varies between 75 – 100 / minute. The flutter waves are inverted in leads II, III and aVF, suggestive of typical atrial flutter.
If quinidine is given as a single drug for atrial flutter, it can increase the ventricular rate since it reduces the flutter rate to around 200 per minute and the conduction become 1:1. Hence an additional AV nodal blocking drug is needed when quinidine is given for the treatment of atrial flutter. Digoxin can convert atrial flutter to atrial fibrillation.
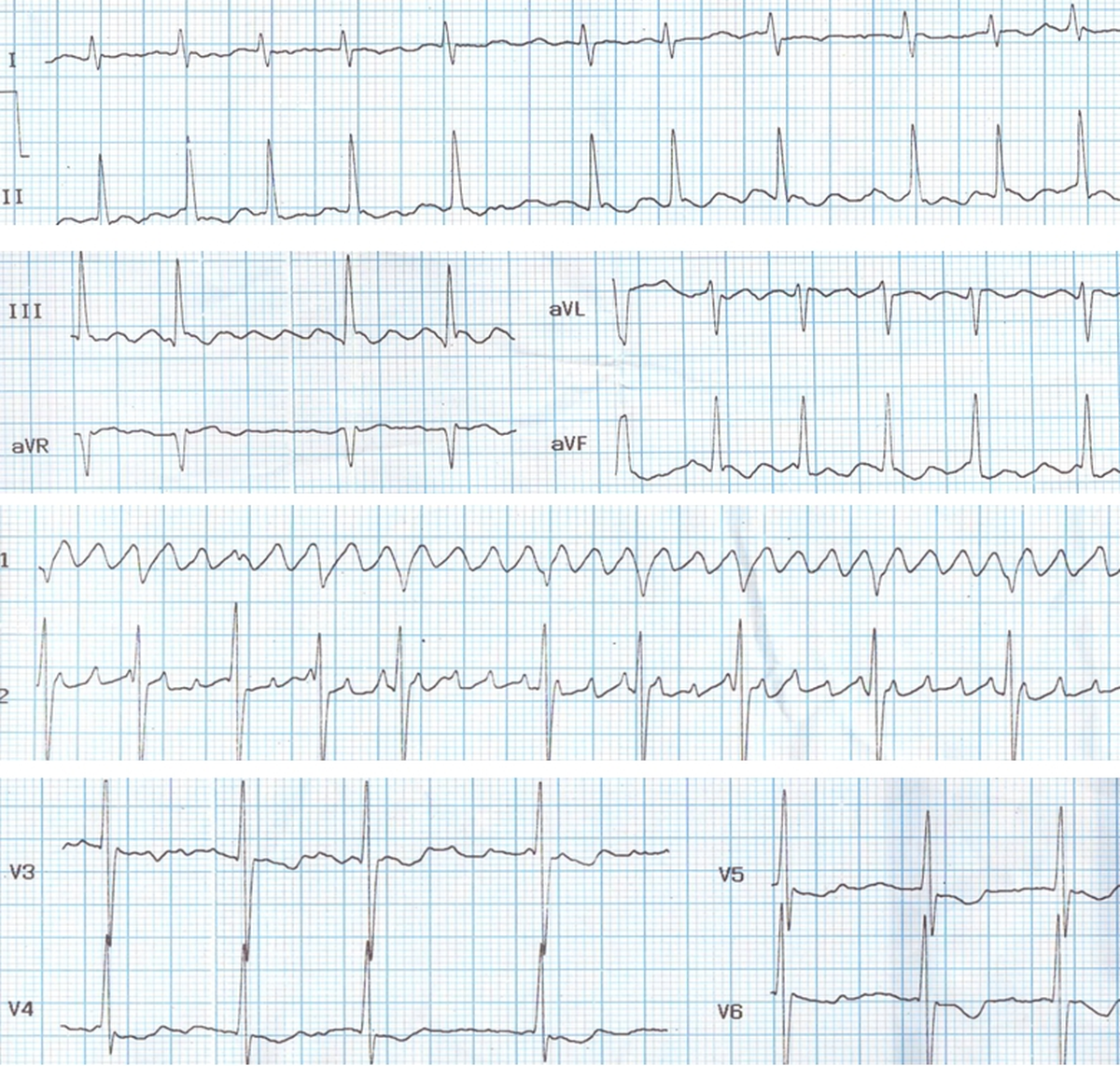
Atrial flutter is less common than atrial fibrillation in mitral stenosis. In this ECG the flutter waves are seen well in inferior leads and V1 as typical sawtooth waves while it is also seen in other leads. Such an organized flutter is rare in mitral stenosis. In most cases of mitral stenosis, the coarse fibrillary waves resemble flutter waves in some leads, but not in others. Such impure rhythms are sometimes called flutter-fibrillation, flitter, or fib-flutter. In those cases, the waves are irregular. In this ECG the waves are regular, suggesting true atrial flutter. The conduction ratio is varying so that the ventricular rate is irregular and resembling atrial fibrillation. The large atria in this case helps the maintenance of this flutter circuit. Both left and right atria are enlarged as there is severe pulmonary arterial hypertension secondary to severe mitral stenosis.
Neonatal atrial flutter is a rare arrhythmia of the newborn. Neonatal atrial flutter will have a much higher atrial and ventricular rate. Often the fast heart rate in the fetus is considered a sign of fetal distress. In this ECG the ventricular rate is over 200 per minute. The ‘saw tooth’ shaped flutter waves are seen well in the lead II rhythm strip.
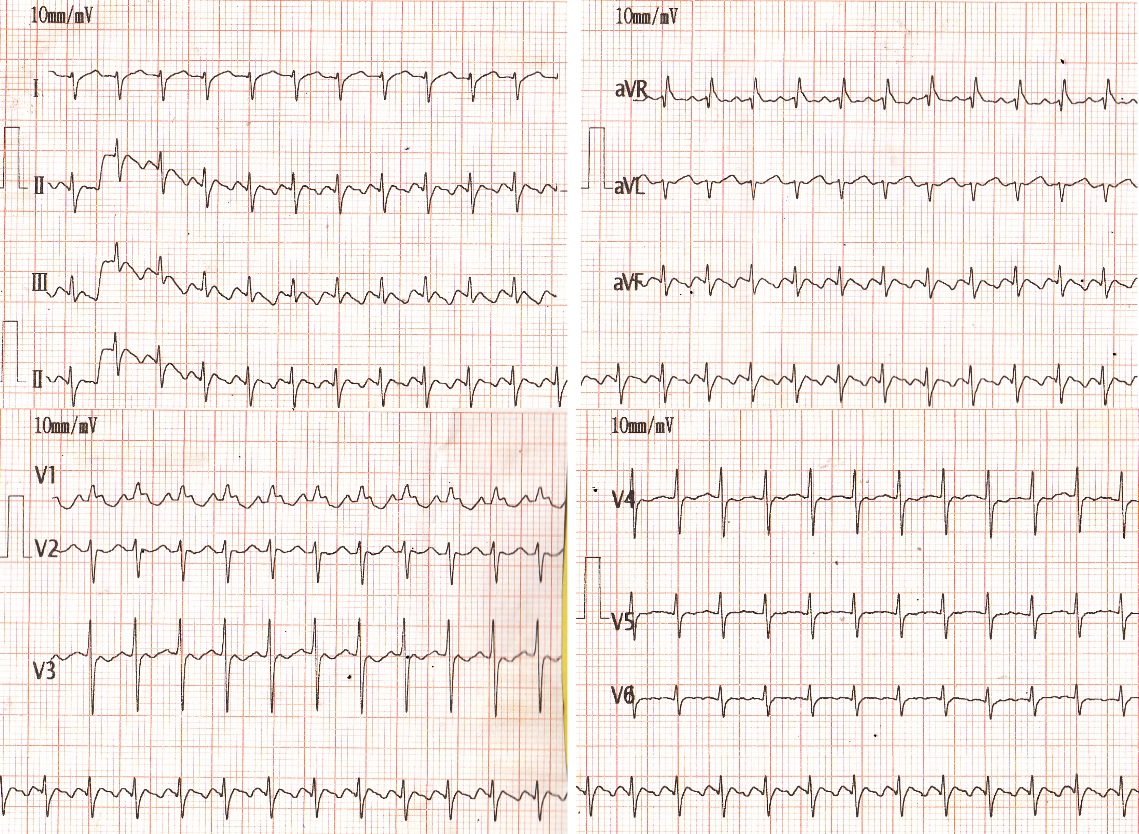
The negative flutter waves suggest typical atrial flutter with counter-clockwise re-entry loop. There is one QRS complex for every two flutter waves. Hence the conduction ratio is 2:1, indicating atrial rate over 400 per minute. Dominant R wave in V1, right axis deviation and clockwise rotation in the frontal plane QRS pattern are suggestive of neonatal ECG pattern.
