Cardiac amyloidosis
Cardiac amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is a group of disorders in which an abnormal protein gets deposited in tissues. Two important types of amyloidosis which can involve the heart are light-chain amyloidosis and transthyretin amyloidosis. They are known in short as AL and ATTR respectively. Earlier terms like primary amyloidosis, secondary amyloidosis, senile amyloidosis and familial amyloid cardiomyopathy are now considered obsolete.
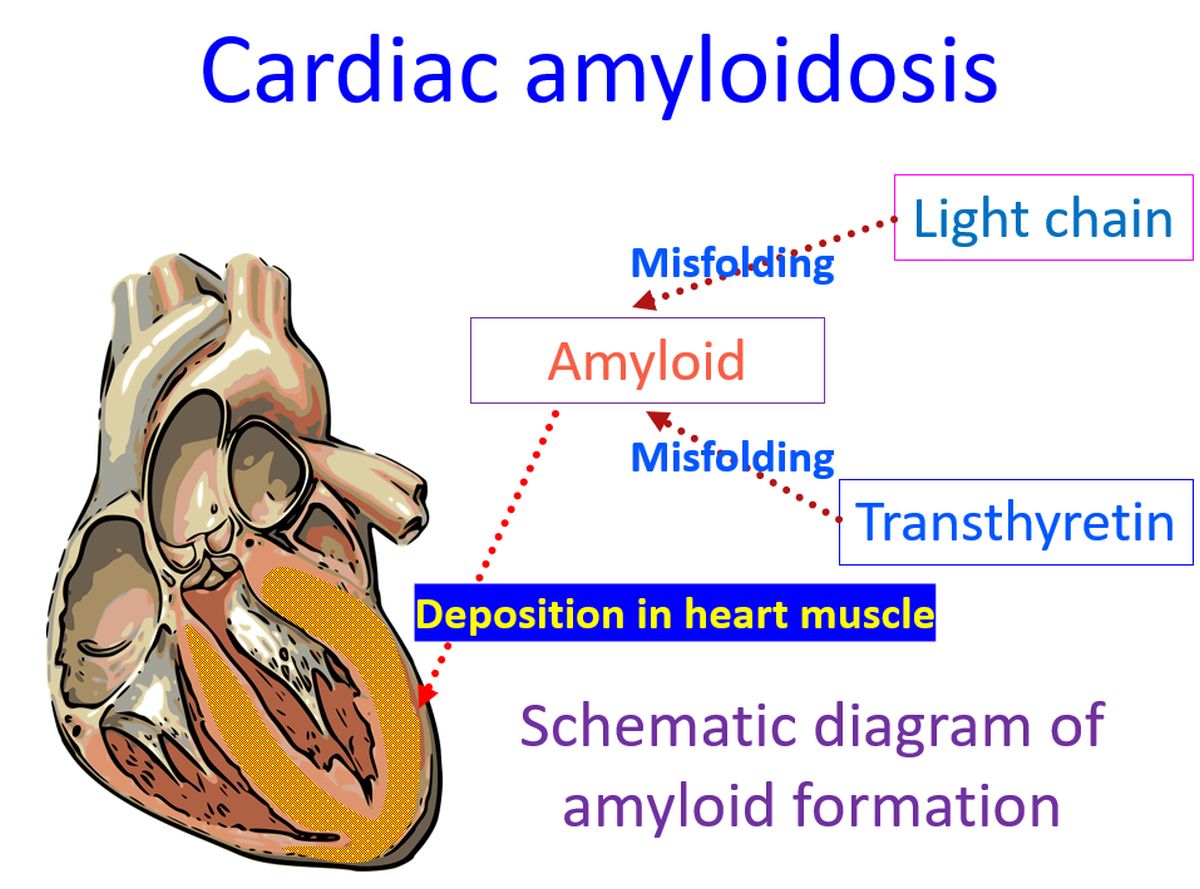
Light chain amyloidosis is the most commonly diagnosed form of systemic amyloidosis. AL amyloidosis is due to clonal proliferation of plasma cells leading to excessive production of light chains of antibodies. In some cases, these light chains are prone for misfolding into beta-pleated sheets. These light chains circulating in blood can get deposited in tissues and cause AL amyloidosis.
Cardiac amyloidosis due to AL amyloidosis can manifest as heart failure with either diastolic dysfunction or systolic dysfunction, of which diastolic dysfunction is more common. Cardiac arrhythmias are another important manifestation of cardiac amyloidosis. Heart failure biomarkers B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP) are elevated in cardiac amyloidosis. Mild elevation of cardiac troponins may also be noted.
Typical feature of cardiac amyloidosis is the disparity between the thickening of the ventricles noted on echocardiography and the low voltage complexes noted on ECG. Both have the same reason, infiltration of amyloid material, which increases the thickness on echocardiography, and reduces the electrical signals recorded from the heart. A restrictive pattern is seen on Doppler studies.
AL amyloidosis being a plasma cell proliferation, responds to chemotherapy targeted against the plasma cell clone. Another option considered is stem cell transplantation. Prognosis is poorer for AL amyloidosis than ATTR amyloidosis.
Transthyretin amyloidosis is due to excessive monomeric form of transthyretin which is prone for misfolding and deposition in tissue. Transthyretin is prealbumin produced by the liver and acts as the transporter for thyroxine and retinol. Dominant form in blood is a homotetramer, though small amounts of monomer may also be found in circulation.
Two types of ATTR amyloidosis are wild-type and mutant type. While the wild-type of ATTR amyloidosis takes a long period for the amyloid deposits to develop, mutant type has a rapid rate of deposition.
Carpal tunnel syndrome has been considered as a potential early, red-flag sign of amyloidosis [1]. Patients classically present with cardiac manifestation several years after being operated on by the surgeon for carpal tunnel release! A study with 538 subjects evaluated the relation between carpal tunnel syndrome and amyloidosis [2].
The study had 166 cases of hereditary ATTR, 107 cases of wild-type ATTR, 197 AL amyloidosis and 69 TTR mutation carriers. Comparison was with a cohort of 14.9 million people, in which prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome had been estimated. It was found that prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome is higher among elderly males with ATTR. Carpal tunnel syndrome preceded the diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis by five to nine years.
Abdominal fat biopsy can be used for diagnosis of amyloidosis, but has poor sensitivity. Endomyocardial biopsy has its own limitations in getting it done and the limited availability of good interpretation. Bone scintigraphy is now the cornerstone for diagnosis of ATTR cardiac amyloidosis. But it may be positive in AL amyloidosis also. Hence a concomitant for testing for light chains is needed. Serum free light chain concentration and urine immunofixation electrophoresis are needed to rule out AL cardiac amyloidosis [3].
Tafamidis can be used to treat TTR amyloidosis. Tafamidis binds the thyroxine binding sites of TTR with high affinity and selectivity. This slows the dissociation of TTR tetramers into monomers, inhibiting aggregation. Tafamidis has been shown to slow the progression of peripheral neurologic impairment in TTR polyneuropathy [4]. Tafamidis was approved by US FDA in 2019 for treatment of TTR cardiomyopathy [5].
Kidney, liver and nerve involvement may be associated features in amyloidosis. AL amyloidosis has a more severe course than transthyretin amyloidosis with median untreated survival of about six months from the onset of cardiac failure. The cardiotoxicity of circulating light chains in addition to the myocardial infiltration is thought to have a role in this more severe manifestation of AL amyloidosis. Capillary fragility due to amyloid infiltration can cause purpuric lesions with minimal trauma [6].
References
- Donnelly JP, Hanna M, Sperry BW, Seitz WH Jr. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Potential Early, Red-Flag Sign of Amyloidosis. J Hand Surg Am. 2019 Oct;44(10):868-876. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2019.06.016. Epub 2019 Aug 7. PMID: 31400950.
- Milandri A, Farioli A, Gagliardi C, Longhi S, Salvi F, Curti S, Foffi S, Caponetti AG, Lorenzini M, Ferlini A, Rimessi P, Mattioli S, Violante FS, Rapezzi C. Carpal tunnel syndrome in cardiac amyloidosis: implications for early diagnosis and prognostic role across the spectrum of aetiologies. Eur J Heart Fail. 2020 Mar;22(3):507-515. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1742. Epub 2020 Jan 23. PMID: 31975495.
- Kittleson MM, Maurer MS, Ambardekar AV, Bullock-Palmer RP, Chang PP, Eisen HJ, Nair AP, Nativi-Nicolau J, Ruberg FL; American Heart Association Heart Failure and Transplantation Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology. Cardiac Amyloidosis: Evolving Diagnosis and Management: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020 Jul 7;142(1):e7-e22. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000792. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Erratum in: Circulation. 2021 Jul 6;144(1):e10. Erratum in: Circulation. 2021 Jul 6;144(1):e11. PMID: 32476490.
- Coelho T, Maia LF, Martins da Silva A, Waddington Cruz M, Planté-Bordeneuve V, Lozeron P, Suhr OB, Campistol JM, Conceição IM, Schmidt HH, Trigo P, Kelly JW, Labaudinière R, Chan J, Packman J, Wilson A, Grogan DR. Tafamidis for transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy: a randomized, controlled trial. Neurology. 2012 Aug 21;79(8):785-92. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182661eb1. Epub 2012 Jul 25. PMID: 22843282; PMCID: PMC4098875.
- FDA approves new treatments for heart disease caused by a serious rare disease, transthyretin mediated amyloidosis. Available online from FDA website at URL: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-treatments-heart-disease-caused-serious-rare-disease-transthyretin-mediated. Accessed on 13 Feb 2022.
- Falk RH. Cardiac amyloidosis: a treatable disease, often overlooked. Circulation. 2011 Aug 30;124(9):1079-85. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.010447. PMID: 21875922.

