Cardiac CT – Pulmonary artery bifurcation
Cardiac CT – Pulmonary artery bifurcation
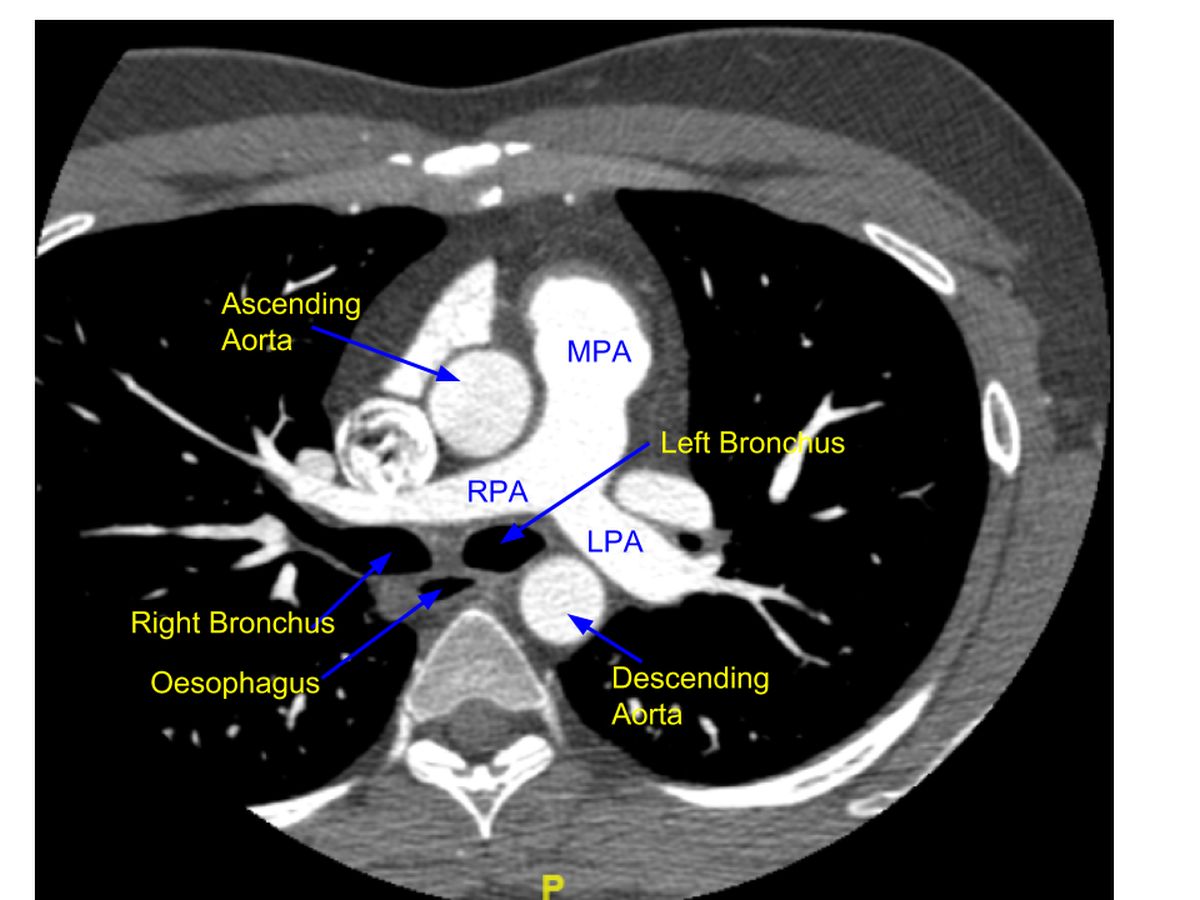
PA on contrast enhanced computed tomography (CECT): CECT scan of thorax showing the bifurcation of main pulmonary artery (MPA) into RPA (right pulmonary artery) and LPA (left pulmonary artery). The section is just below that of the aortic arch. Hence aorta is seen as two structures in cross section (ascending aorta anteriorly and descending aorta posteriorly). Diameter of ascending aorta is seen to be more than that of descending aorta. Trachea has divided into right and left bronchi at this level of the section. Left bronchus is seen in oval shape and right bronchus is almost as a longitudinal section. Air filled cross section of the esophagus is seen between the bronchi and the spine.
Major thrombi in the pulmonary arteries if any in these proximal segments, will be seen as negative shadows within the contrast filled region. If the branch is totally occluded, there will be a cut off seen. Total occlusion of a pulmonary artery by pulmonary embolism is potentially life threatening unless prompt thrombolytic therapy is initiated. Chronic thrombi can also be seen in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CETP), for which a surgical option of pulmonary thromboendarterectomy is available in specialised centers catering to patients with pulmonary hypertension.