Complete heart block
Complete heart block
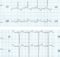
Complete heart block or complete AV block is a situation in which the sinus impulses are not conducted to the ventricles through the AV node. Hence the P waves and QRS complexes are dissociated (AV dissociation).
The four cardinal features of complete heart block on the ECG are:
- Regular PP interval
- Regular RR interval
- Varying PR interval
- PP interval shorter than RR interval (atrial rate more than the ventricular rate).
The QRS complexes can be either normal or wide, depending on the location of the block whether it is below the bundle of His (infra Hisian) or above it (supra Hisian). In supra Hisian block, the ventricles are controlled by a junctional focus and hence the QRS is narrow, while in infra Hisian block, the subsidiary pacemaker is ventricular, producing a wide QRS. Infra Hisian block has a poorer prognosis because the subsidiary ventricular focus is usually unstable and prone for Stokes-Adams attacks. A reversible cause of complete heart block is an indication for temporary pacing while a permanent one needs permanent pacing.
Initial response to atropine may be checked under cardiac monitoring. Infra Hisian blocks do not respond to atropine and needs isoprenaline infusion to accelerate the ventricular focus. Temporary transcutaneous (non-invasive) pacing is an option to tide over a crisis till transvenous pacing can be arranged.