Trifascicular Block
Trifascicular Block
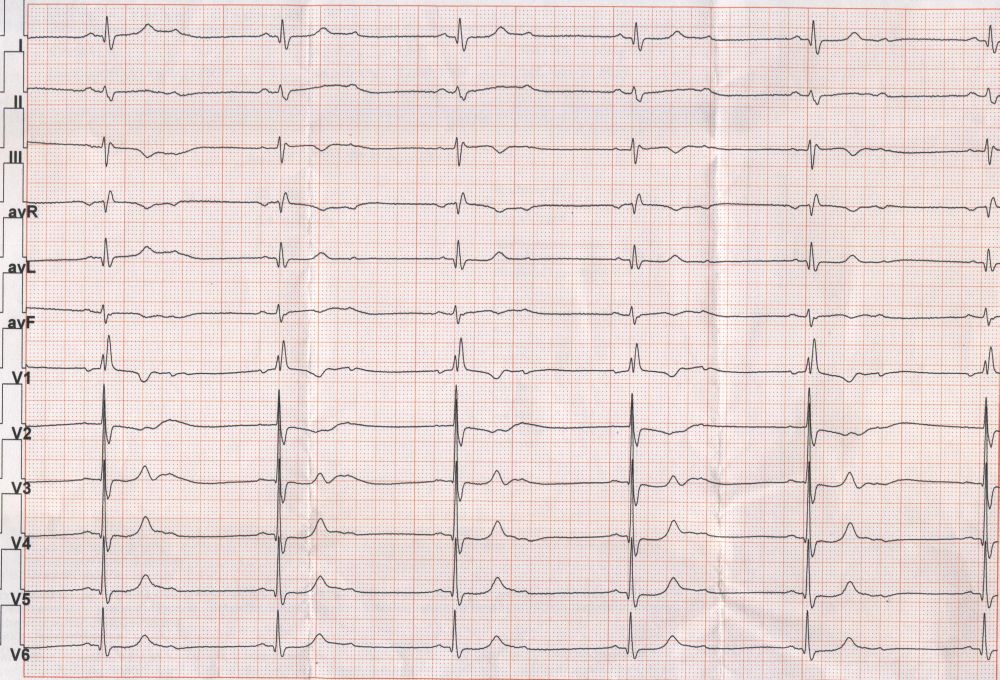
RR interval is 1800 ms and PP interval is 900 ms suggesting 2:1 AV conduction. There are small q waves in lateral leads. Slurred S waves are seen in lead I and aVl and rR pattern is seen in V1, suggesting right bundle branch block. 2:1 AV conduction in the presence of RBBB suggests that conduction in the left fascicles is delayed and blocked. Overall this constitutes one type of trifascicular block. This can also be considered as Mobitz type II second degree AV block. This type of block has a higher probability of progressing to complete heart block and producing Stokes Adams attacks. Mobitz type II second degree AV block is due to disease of the conduction below the level of the bundle of His and hence it is called infra Hisian block. When infra Hisian block progresses to complete heart block, the subsidiary pacemaker which takes over is usually the idioventricular rhythm which is intrinsically slower and unstable, leading to episodes of ventricular asystole causing Stokes Adams attacks. Sometimes ventricular tachyarrhythmias in the form of torsades de pointes can also occur in the situation of complete block causing Stokes Adams attacks due to poor ventricular output at very fast rate.

