ECG Quiz 34
ECG Quiz 34
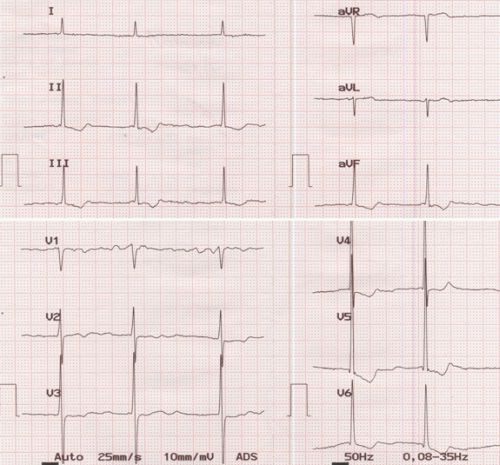
Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular rate and left ventricular hypertrophy. Slow ventricular rate is due to suppression of the atrioventricular conduction either due to drugs or due to disease of the atrioventricular node. Left ventricular hypertrophy is manifest as tall R waves with ST segment depression in lateral leads. Digoxin effect could also contribute to both slow rate and ST segment changes. The coarse fibrillary waves in V1 suggest possibility of a large atrium as in mitral stenosis. Fibrillary waves of more than 1 mm amplitude indicate atrial enlargement. Left ventricular hypertrophy indicates associated lesions like mitral regurgitation or aortic valve disease as left ventricular hypertrophy does not occur in isolated mitral stenosis.
ECG shows a paper speed of 25 mm/s and standardisation of 10 mm/mV. The filter settings are shown towards the right lower border. Notch filter of 50 Hz filters out alternating current interference from line voltage. 0.08 – 35 Hz gives the high pass and low pass filter settings. High pass filter passes all frequencies above it and low pass filter passes all frequencies below it. Hence the ECG amplifier with this setting picks up signals within this frequency range. Filtering lower frequencies avoids the baseline shift due to respiratory variation of thoracic impedance. Too much filtering of higher frequencies can remove important signals like pacemaker artifacts or pacing stimuli.
