Electrical axis of the heart
Electrical axis of the heart
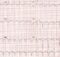
Electrical axis of the heart: Atrial activation is depicted by the P wave vector and ventricular activation by the QRS vector. The ventricular activation has an initial, middle and terminal component. The mean ventricular electrical activity is represented by the mean electrical axis of the QRS. QRS vector can be assessed in multiple planes: horizontal, sagittal and frontal. T wave vector can also be assessed. The relation between the T wave vector and the QRS vector is termed the ventricular gradient. Normal QRS axis in the frontal plane is roughly between 0 – 90 degrees.
Similar to QRS axis, P wave axis and T wave axis can also be calculated, but is not routinely done. In modern day computerized electrocardiographs printing ECG on a full sheet automatic graphical display of P, QRS and T wave axes is common. The measured values will indicate the exact values computed by the program. Deviations in QRS axis is routinely used for diagnostic purposes, though P and T wave axes are seldom used. Left axis deviation without any other cause is a feature of left anterior hemiblock. Right axis deviation without any other causes is taken as a feature of left posterior hemiblock which is much rarer than left anterior hemiblock. QRS axis deviations can occur ventricular hypertrophy. Right axis deviation is one of the features of right ventricular hypertrophy.