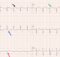
Lown Ganong Levine syndrome
Lown Ganong Levine syndrome
Lown Ganong Levine syndrome is one of the pre-excitation syndromes like the better known Wolff Parkinson White (WPW) syndrome. The electrocardiographic finding is a short PR interval with normal QRS duration, unlike the wide QRS in WPW syndrome. The description by Lown B, Ganong WF and Levine SA was in 1952 [1]. Lown B et al in their paper report that 11 such cases had been reported earlier. The earliest among the cited papers was in 1921 [2].
In the seminal paper Lown B et al observed that out of the 200 patients with short PR interval, 23 had paroxysmal tachycardia (11%), compared with 0.5 to 1% in a control group of 200 patients with normal PR interval. Among their group of 200 patients with short PR interval 184 had normal QRS complexes and 16 had WPW pattern. The incidence of tachycardia was 25% in those with WPW pattern and 10.4% in those without a wide QRS. Of the 23 patients in their group with paroxysmal tachycardia and short PR interval, 82% had a normal QRS complex and 18% had features of WPW syndrome. They noted that those with short PR interval, normal QRS and paroxysmal tachycardia (LGL syndrome) were predominantly females. The tachycardia in half of them started in the fourth decade of life.
References
- Lown B, Ganong WF, Levine SA. The syndrome of short P-R interval, normal QRS complex and paroxysmal rapid heart action. Circulation. 1952 May;5(5):693-706.
- Wedd AM. Paroxysmal tachycardia. Arch. Int. Med. 27: 571, 1921.