Pulse oximetry tracing of ventricular premature complex (VPC)
Pulse oximetry tracing of ventricular premature complex (VPC)
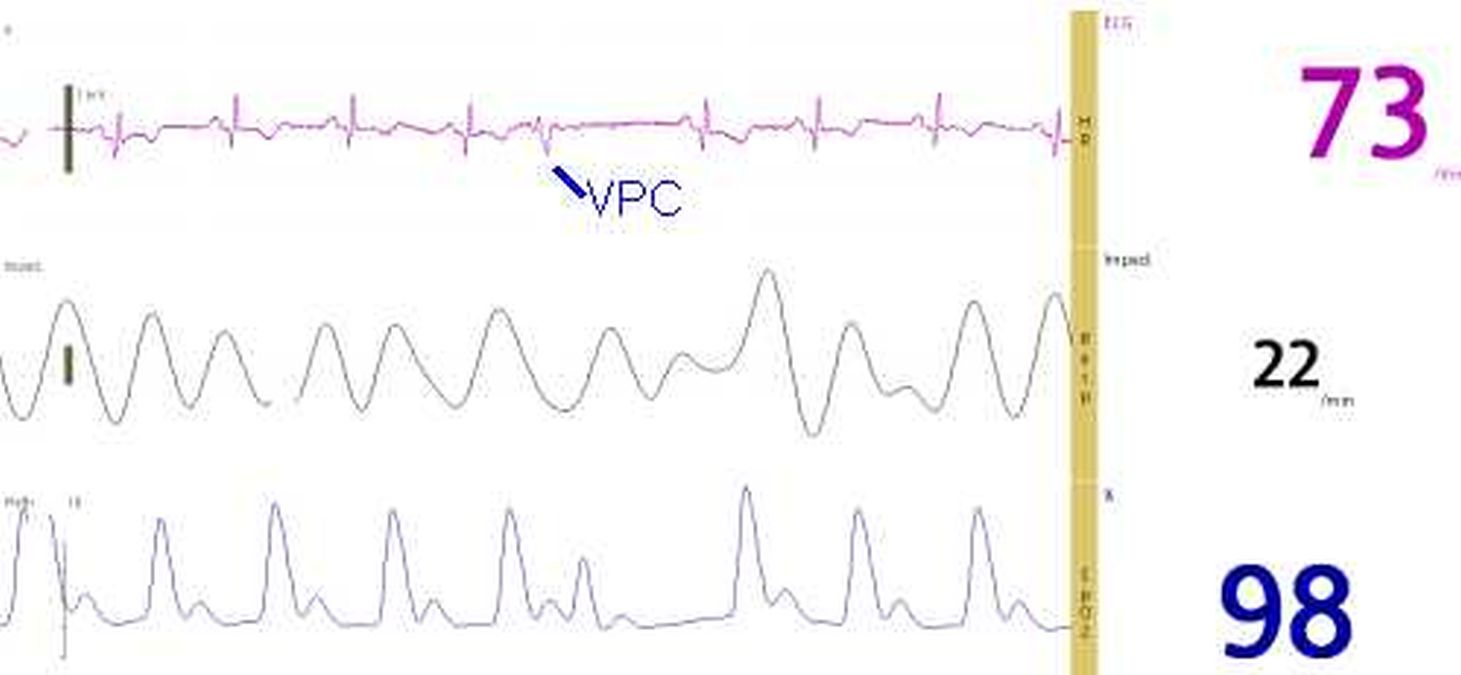
Monitor screen shot showing ECG (electrocardiogram), respiration by thoracic impedance and pulse oximetry wave form. The upper tracing shows an ECG at rate of 73 per minute. A ventricular premature complex (VPC) followed by a compensatory pause has been marked below the tracing. The VPC has a wide QRS and does not have a preceding P wave. All the other QRS complexes are narrow and have preceding P waves, indicating that they are sinus beats, in regular sinus rhythm. The middle tracing shows the variation in thoracic impedance with a respiratory rate of 22 per minute. Lower tracing is the pulse oximetry tracing and the oxygen saturation (SPO2) is displayed as 98 percent (in dark blue).
The pulse oximetry tracing of ventricular premature complex shows a lower amplitude corresponding to a lower pulse wave amplitude for a premature beat. Since ventricular premature beats (VPC or PVC or VPB) occur earlier than the expected sinus beat, there is less diastolic time for the filling of the ventricle after the previous sinus beat. This in addition to the absence of atrial help to ventricular filling (atrial booster) due to the absence of preceding P waves makes the ventricles underfilled at the onset of systole. Hence the stroke volume (fraction of end diastolic ventricular volume which is ejected out in systole) is lower for the VPC. This causes a low pulse pressure and volume. This is correspondingly reflected in the pulse oximetry tracing of ventricular premature complex. The next beat following the compensatory pause has a longer diastolic filling period as well as atrial booster with the preceding P wave. Hence the pulse volume is higher for the post ectopic beat. This is also reflected in the pulse oximetry tracing.
Sometimes when the VPC is very premature, the ensuing contraction may not be forceful enough to open the aortic valve and produce a pulse. In such cases, a person measuring the pulse rate will record a low pulse rate and suspect bradycardia if the ectopics are very frequent as in bigeminal rhythm. Second sounds may be inaudible after such extra systoles and those cardiac cycles may have only one heart sound.