Role of cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) in heart failure
Role of cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) in heart failure
Reduced exercise tolerance is an important symptom of heart failure regardless of the left ventricular ejection fraction, meaning that is present in all forms of heart failure. Hence the role of objective assessment of functional capacity by cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET). Peak oxygen consumption measured by CPET is predictive of prognosis in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), heart failure with midrange ejection fraction (HFmrEF) and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). CPET is routinely used in prognostic evaluation in patients with HFrEF. Peak oxygen consumption (VO2) and the minute ventilation/carbon dioxide production (VE/VCO2) slope are powerful prognostic predictors in HFrEF. CPET is probably an underutilized test for risk stratification in HFpEF [1].
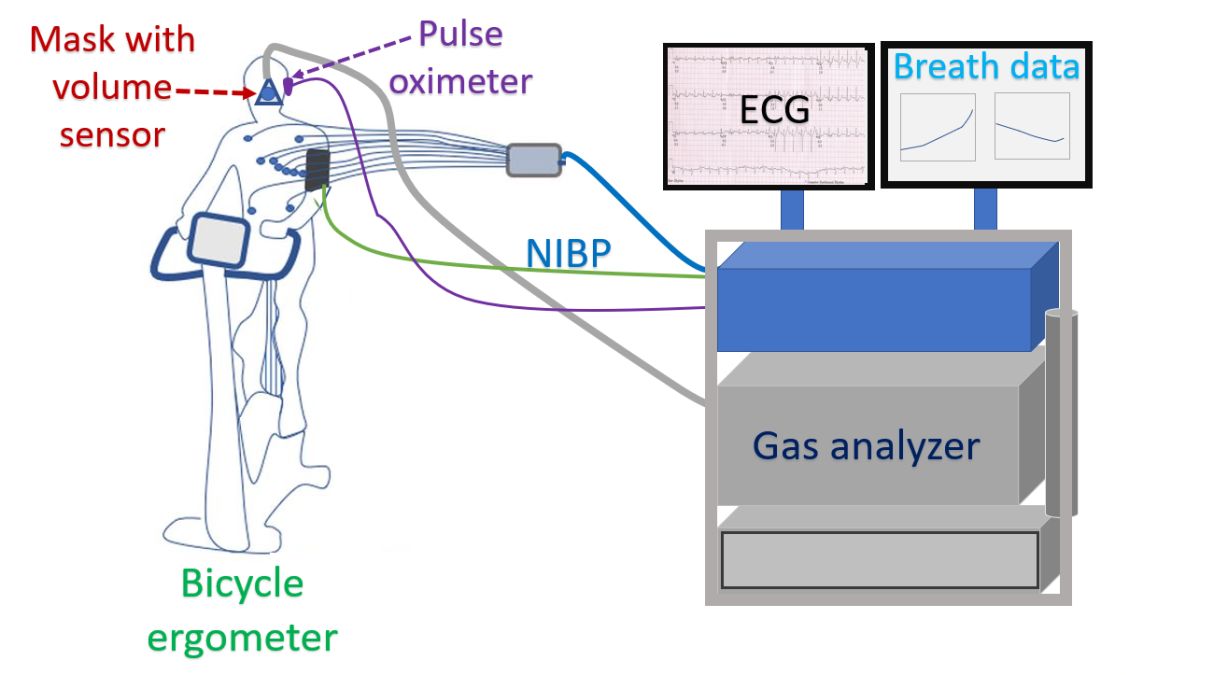
CPET is usually done using an upright cycle ergometer with the subject breathing room air, though it may be rarely done using a treadmill [2]. Ventilatory expired gas analysis system is used to measure minute ventilation (VE), oxygen consumption (VO2), and carbon dioxide production (VCO2). Fast responding oxygen and carbon dioxide sensors in the system acquire these information on a breath-to-breath basis, analyzes and displays it continuously. Highest 10-second averaged VO2 during the last stage of the symptom-limited exercise test is taken as the peak VO2. VE/VCO2 slope is taken from rest values to the gas exchange at peak exercise.
References
-
Nadruz W Jr, West E, Sengeløv M, Santos M, Groarke JD, Forman DE, Claggett B, Skali H, Shah AM. Prognostic Value of Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing in Heart Failure With Reduced, Midrange, and Preserved Ejection Fraction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Oct 31;6(11):e006000. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006000. PMID: 29089342; PMCID: PMC5721737.
- Nadruz W Jr, West E, Santos M, Skali H, Groarke JD, Forman DE, Shah AM. Heart Failure and Midrange Ejection Fraction: Implications of Recovered Ejection Fraction for Exercise Tolerance and Outcomes. Circ Heart Fail. 2016 Apr;9(4):e002826. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.115.002826. PMID: 27009553; PMCID: PMC4807736.