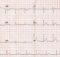
Wide QRS tachycardia at a rate of 300 per min
Wide QRS tachycardia at a rate of 300 per min
What are the possible types of Wide QRS tachycardia at a rate of 300 per min?
- Atrial fibrillation with Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome – rate is fast due to conduction through accessory pathway with low refractory period as well as through AV nodal pathway. It can quickly degenerate into ventricular fibrillation and needs early electrical cardioversion.
- Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in the setting of QT interval prolongation is called torsades des pointes.
- Atrial flutter with 1:1 atrioventricular conduction and aberrant ventricular conduction. The 1:1 response may be either spontaneous or drug induced and can occur with or without organic heart disease. The 1:1 response is often caused by sympathetic discharge associated with undue exertion or excitement [1].
- Ventricular tachycardia or supraventricular tachycardia with aberrancy in the very young.
Common form of wide QRS tachycardia is monomorphic ventricular tachycardia, which has a much lower rate, usually between 150 – 200/min.
A case of recurrent ventricular tachycardia in a person with Type A Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern has also been described [2]. So all wide QRS tachycardias in WPW syndrome need not be supraventricular or AF with preexcitation and rapid ventricular rate and wide QRS! But the rate may not be as high as 300/min. That case was diagnosed only 12 years after initial presentation, at electrophysiological study.
References
- Papa LA, Klinman SW, Chung EK. Atrial flutter with 1:1 AV conduction and aberrant ventricular conduction. Postgrad Med. 1975 Jun;57(7):161-2, 164-6.
- Reddy CP, Sartini JC, Kuo CS. Paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: case report and review of the literature. J Electrocardiol. 1982 Oct;15(4):403-10.