Pulmonary Edema on CXR
What is the diagnosis?
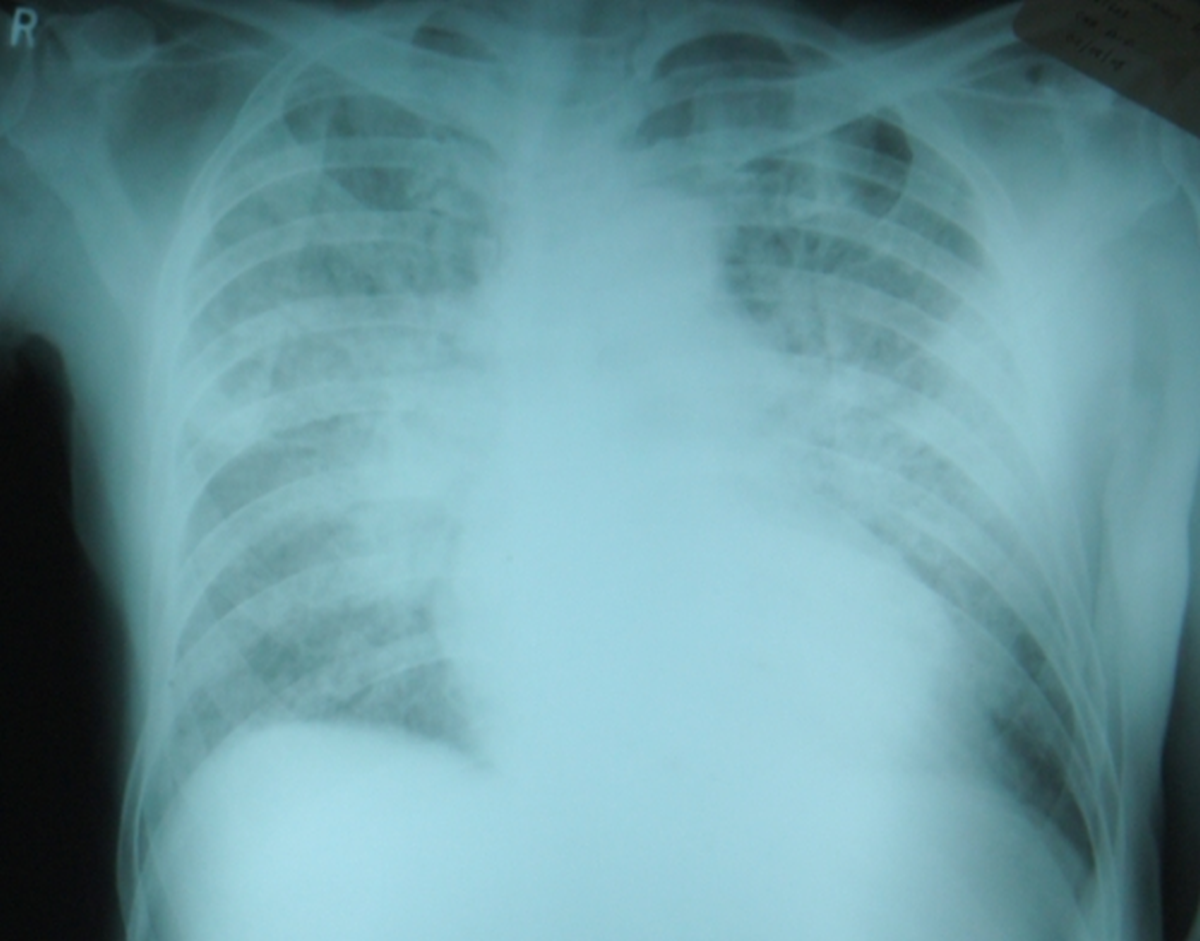
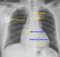
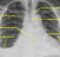
Classical bat wing appearance is visible as bilateral hilar haze. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema occurs when the pulmonary capillary pressure exceeds 25 mm Hg. Above this level, the plasma oncotic pressure is unable to prevent transudation of fluid into the interstitium. Initially interstitial pulmonary edema occurs which manifests clinically as shortness of breath and tachypnoea. As it progresses, alveolar edema occurs which manifests as dyspnoea with frothy blood stained sputum and bilateral basal crepitations. In more advanced stage, the crepitations extends throughout the lung fields. Myocardial infarction with acute left ventricular failure is one of the commonest causes of pulmonary edema. It can also occur in critical mitral stenosis, severe mitral regurgitation and aortic regurgitation. Acute fulminant myocarditis is relatively rare cause of pulmonary edema.