Basic electrocardiography
Basic electrocardiography
Electrocardiogram is the recording of the electrical signals of the heart. Electrocardiogram (ECG) recorded from the body surface is known as surface ECG while that recorded with intracardiac electrodes are called electrograms. Standard surface ECG uses four electrodes on the limbs of which one is an indifferent electrode and 6 electrodes on the chest. Various combinations of limb electrodes record 6 ECG leads while chest electrodes record 6 chest leads to make a total of 12 leads in the standard 12 lead ECG. The leads can be recorded in sequence, groups of 3 each or simultaneous 12 leads. Multiple simultaneous leads are useful in the analysis of rhythm disturbances. A long rhythm strip is needed for analysis of arrhythmia.
Recording paper speed and standardization
Standard recording speed of the ECG paper is 25 mm/s. If needed, a 50 mm/s is also there in most ECG machines. Intracardiac electrograms are recorded at much higher speeds. One millimeter on the X-axis of the recording paper will correspond to 40 milliseconds (0.04 second) at the standard speed of 25 mm/s.
Standardization is checked by giving a 1 mV rectangular pulse. Normal standardization is to have 10 mm vertical deflection for a 1 mV pulse. If needed, higher standardizations like 20 mm to 1 mV can also be used. In the normal standardization, 1 mm on the Y-axis will correspond to 0.1 mV.
Waves and intervals on the ECG
The normal ECG has P, QRS and T waves. P wave is due to atrial depolarization, QRS complex is due to ventricular depolarization and the T wave due to ventricular depolarization. Ta wave caused by atrial repolarization is seldom seen. Sometimes a U wave may be seen after the T wave. Abnormal waves which can be seen in certain disease conditions are the delta wave at the beginning of the QRS complex and epsilon wave at the end of the QRS.
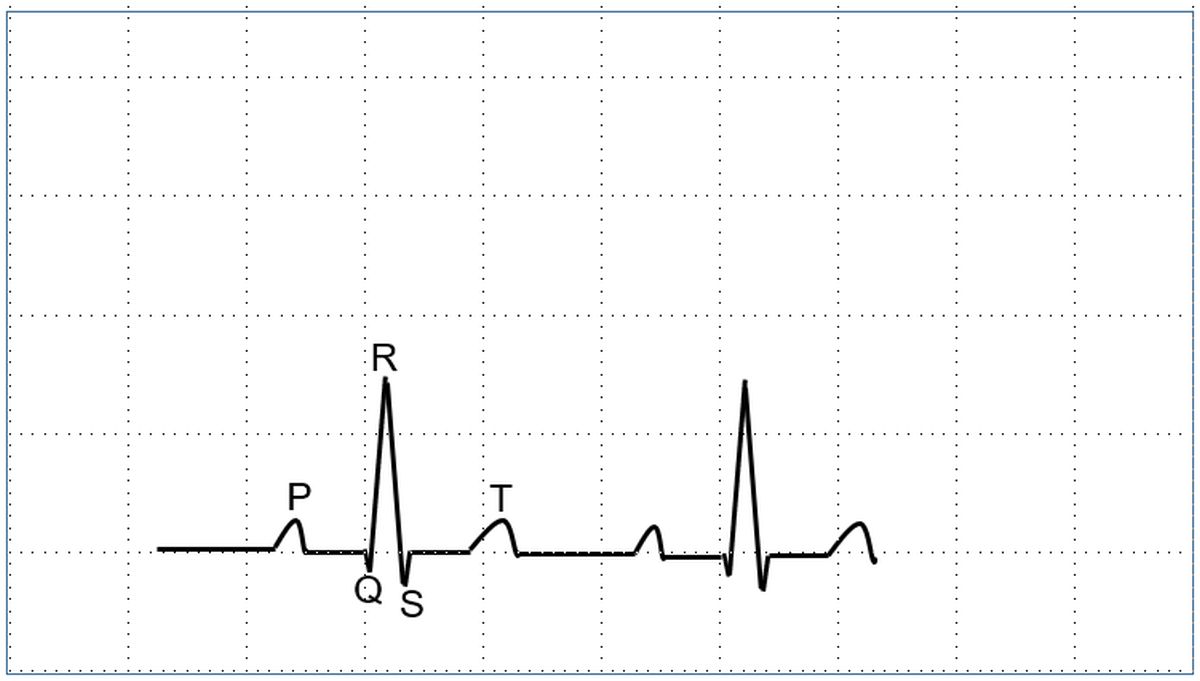
The region between two waves are known as segments. PR segment is between the P wave and the QRS complex. ST segment separates the QRS complex from the T wave. TP segment is the isoelectric interval between the T wave and the P wave of the next cardiac cycle.
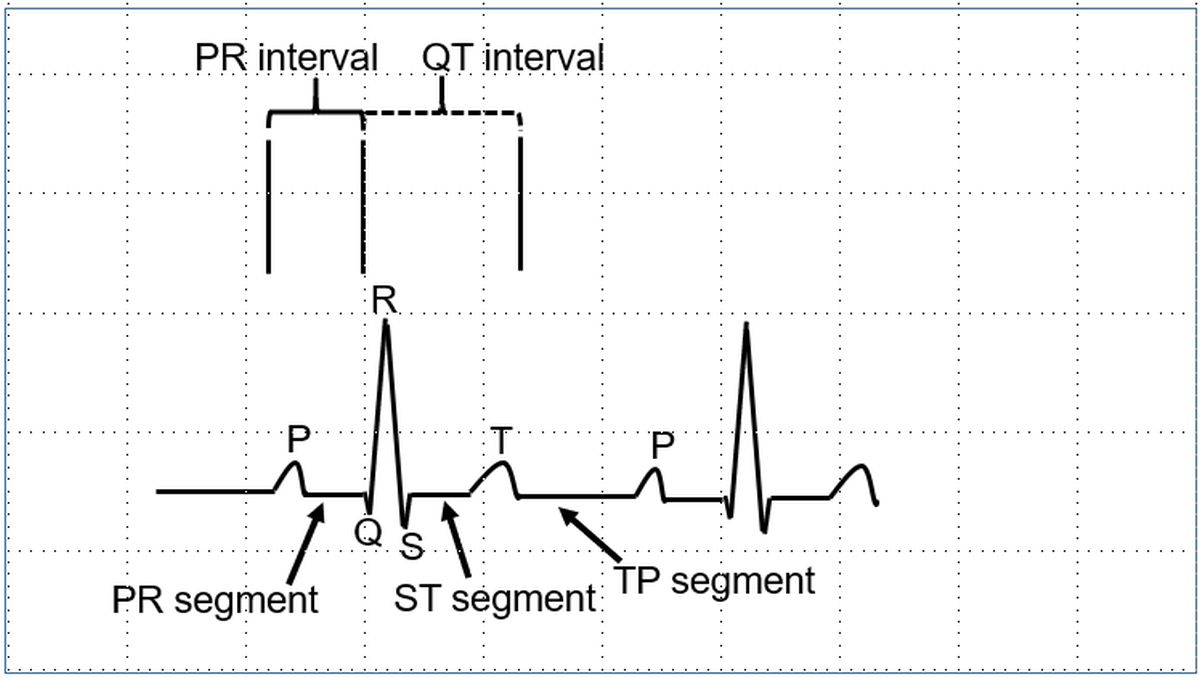
An interval contains a segment and one or more waves. PR interval contains the P wave and the PR segment. QT interval contains the QRS complex, ST segment and the T wave.
While naming the components of the QRS complex, initial negative wave is called Q wave. Initial positive wave is called R wave. A negative wave after a positive wave regardless of whether there was a Q wave or not is named S wave. Additional R waves are named R’ and additional S waves are named S’. If only single negative wave is present, it is called QS complex.