Cardiac chambers and pericardium on CXR
Cardiac chambers and pericardium on CXR
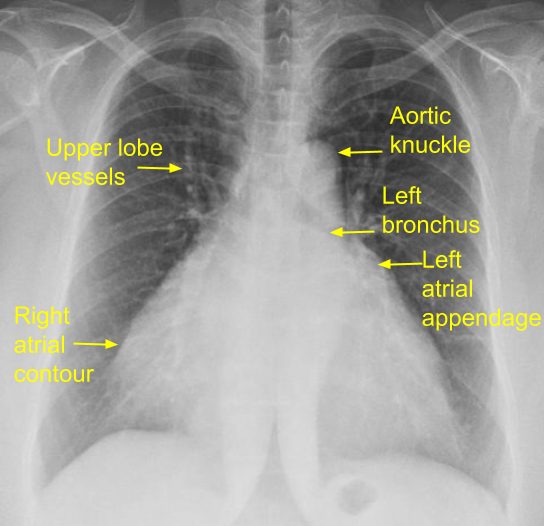
Right atrium: Right atrium forms the right heart border, usually seen just outside the right side of spine. Right atrial enlargement is noted as rightward shift of the right heart border on CXR).
Left atrium: Left atrial appendage comes in the left heart border just below the pulmonary bay. If it is enlarged, it bulges out forming the third mogul sign. Aortic knuckle and main pulmonary artery are the first and second moguls. When the left atrium is enlarged, it forms a double atrial contour or shadow within shadow or double atrial shadow near the right heart border. An aneurysmal left atrium can occasionally extend even beyond the right atrial border. Elevation of left bronchus and widening of subcarinal angle are other radiological signs indicating left atrial enlargement on CXR.
Right ventricle: Right ventricle does not contribute to the cardiac borders and right ventricular enlargement is difficult to appreciate on CXR PA view. In lateral view enlarged right ventricle occupies the retrosternal space. In tetralogy of Fallot, a right ventricular type of upturned apex with concave pulmonary segment is known as coeur en sabot or peasant’s boot appearance may be seen. Sabot was a wooden shoe used by poor peasants. A dilated right ventricular outflow tract as in Ebstein’s anomaly and endomyocardial fibrosis, may form a bulge along the left upper border, below the main pulmonary artery segment.
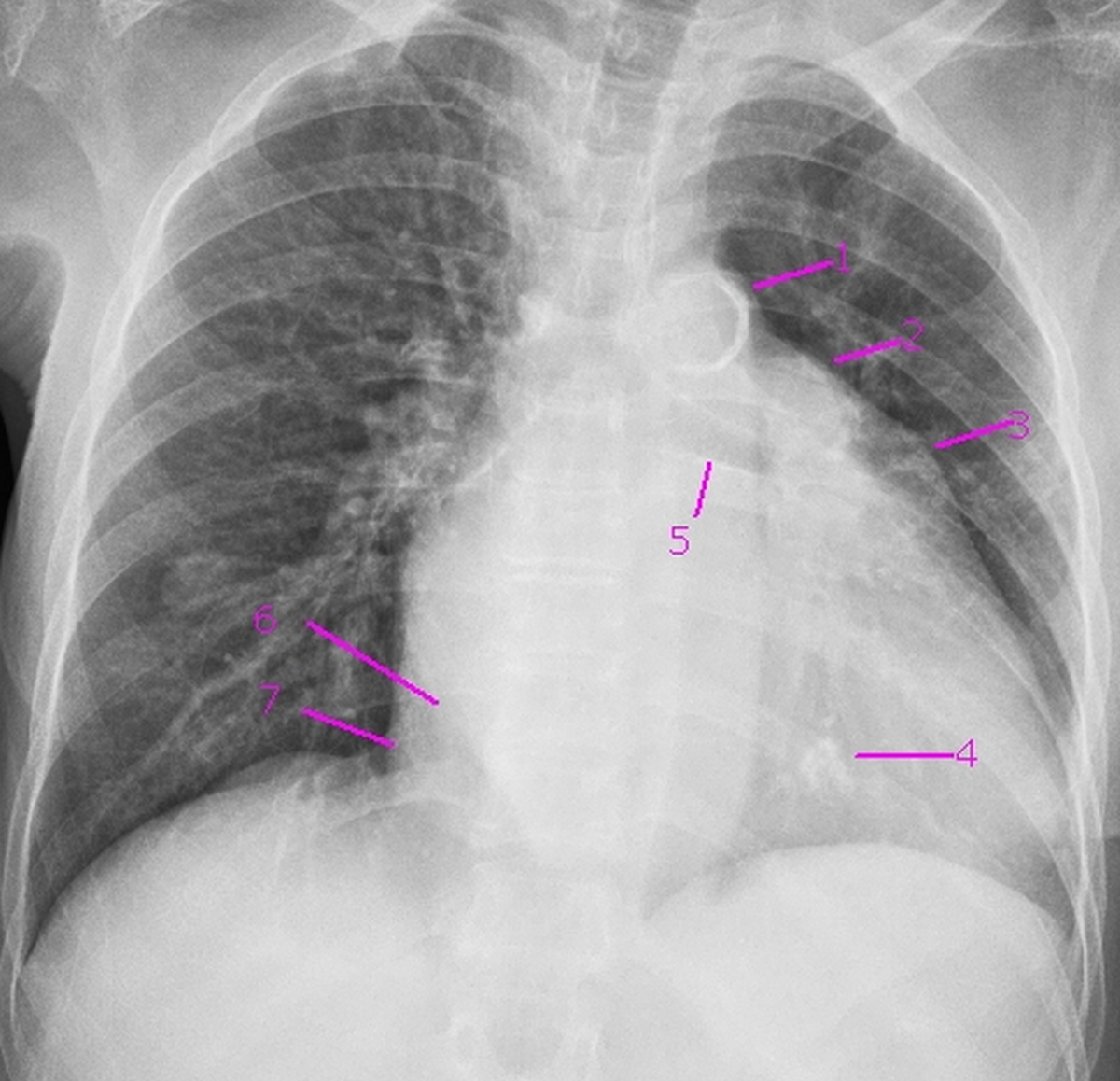
X-ray chest PA view showing mitral valve calcification in severe calcific mitral stenosis. 1. Aortic knuckle with intimal calcification (first mogul). 2. Prominent main pulmonary artery segment (second mogul). 3. Prominent left atrial appendage (third mogul). 4. Calcification in mitral valve. 5. Elevated left bronchus – feature of left atrial enlargement. 6. Double atrial contour – border of enlarged left atrium (shadow within shadow). 7. Right atrial border shifted to right, suggestive of right atrial enlargement.
Left ventricle: Though the major bulk of the left ventricle is posterior, a small strip forms the lower left heart border. In left ventricular enlargement, the apex is shifted down and out, sometimes appearing to dip below the diaphragm on CXR. Left ventricular aneurysm manifests as a bulge on the lower left border above the apex. A submitral left ventricular aneurysm is situated higher up, below the pulmonary bay.
Pericardium: Cardiac silhouette is enlarged in pericardial effusion. A “stenciled out” appearance is described due to reduced cardiac motion. It is called water bottle sign and flask shaped heart. In hydropneumopericardium, an air-fluid level is visible. Pericardial calcification is a feature of chronic constrictive pericarditis. It is often better seen on fluoroscopy rather than plain CXR. Calcification may be more prominent in the atrioventricular groove.