Cardiology MCQs
Cardiology MCQs
Ischemic preconditioning is mediated by:
- ATP-sensitive potassium channel (KATP)
- Sodium channel
- Ikr, the rapid component of delayed rectifier potassium current
- L-type calcium channel
Correct answer: 1. ATP-sensitive potassium channel (KATP)
Blockers of ATP-sensitive potassium channel (KATP) like glibenclamide can prevent ischemic reconditioning. KATP channel opener nicorandil can mimic ischemic preconditioning and it is known as pharmacological preconditioning. Stimulation of adenosine receptors is known to simulate ischemic preconditioning. [Tomai F, Crea F, Gaspardone A, Versaci F, De Paulis R, Penta de Peppo A, Chiariello L, Gioffrè PA. Ischemic preconditioning during coronary angioplasty is prevented by glibenclamide, a selective ATP-sensitive K+ channel blocker. Circulation. 1994 Aug;90(2):700-5.]
First percutaneous intervention for a regurgitant lesion in humans was for:
- Aortic regurgitation
- Mitral regurgitation
- Pulmonary regurgitation
- Tricuspid regurgitation
Correct answer: 4. Pulmonary regurgitation
Bonhoeffer P et al described the development of a system for percutaneous stent implantation combined with valve replacement for right ventricle to pulmonary artery prosthetic conduit with valve dysfunction in 2000. [Bonhoeffer P, Boudjemline Y, Saliba Z, Merckx J, Aggoun Y, Bonnet D, Acar P, Le Bidois J, Sidi D, Kachaner J. Percutaneous replacement of pulmonary valve in a right-ventricle to pulmonary-artery prosthetic conduit with valve dysfunction. Lancet. 2000 Oct 21;356(9239):1403-5.]
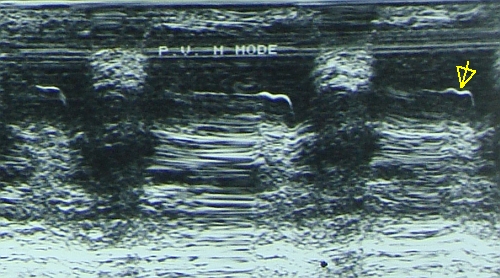
Which of the following is NOT a feature of pulmonary hypertension on pulmonary valve M-Mode echocardiogram:
- Flat EF slope
- Shallow a wave
- Deep a wave
- Mid systolic notch
Correct answer: 3. Deep a wave
Deep a wave is seen in pulmonary stenosis. All others are features of pulmonary hypertension on M-Mode echocardiogram.
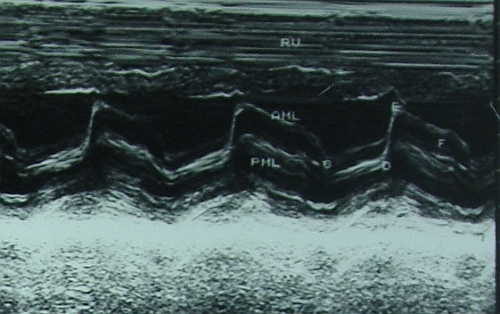
Feature of mitral stenosis on M-Mode echocardiogram:
- Flat EF slope
- Absent A wave
- Paradoxical anterior movement of posterior mitral leaflet
- All of the above
Correct answer: 4. All of the above
Which coronary vein is important in the genesis of atrial fibrillation?
- Great cardiac vein
- Oblique vein of Marshall
- Middle cardiac vein
- Small cardiac vein
Correct answer: 2. Oblique vein of Marshall
Oblique vein of Marshall, also known as oblique vein of left atrium, can give rise to atrial fibrillation. Three reasons described are the myocardial extensions into the structure, node like remnants within the vein and the rich autonomic innervation surrounding it [Habib A, Lachman N, Christensen KN, Asirvatham SJ. The anatomy of the coronary sinus venous system for the cardiac electrophysiologist. Europace. 2009 Nov;11 Suppl 5:v15-21].
Valve at the ostium of coronary sinus is known as:
- Thebesian valve
- Vieussen’s valve
- Eustachian valve
- None of the above.
Correct answer: 1. Thebesian valve
Valve at the ostium of the posterolateral vein at the junction of the great cardiac vein and coronary sinus is called Vieussen’s valve. Eustachian valve is at the ostium of the inferior vena cava, which directs blood to the foramen ovale in fetal life.
Greatest sensitivity for ST elevation in right ventricular infarction is for ST elevation in:
- V1
- V2
- V3R
- V4R
Correct answer: 4. V4R
ST elevation of 1 mm or more in V4R had the greatest sensitivity of 93% and predictive accuracy (93%) for right ventricular myocardial infarction [Braat SH, Brugada P, de Zwaan C, Coenegracht JM, Wellens HJ. Value of electrocardiogram in diagnosing right ventricular involvement in patients with an acute inferior wall myocardial infarction. Br Heart J. 1983 Apr;49(4):368-72].
Which of the following is NOT a usual clinical finding in right ventricular infarction?
- Elevated jugular venous pressure
- Positive Kussmaul’s sign
- Hypotension
- Basal crepitation
Correct answer: 4. Basal crepitation
Lung fields are usually clear in right ventricular infarction despite elevated jugular venous pressure. This is because the pulmonary capillary pressure is usually low due to reduced right ventricular output and left ventricular preload [Berger PB, Ryan TJ. Inferior myocardial infarction. High-risk subgroups. Circulation. 1990 Feb;81(2):401-11].


